Abstract
The ciliary body contains an epithelial bilayer consisting of an outer pigmented cell layer (PE) and an inner nonpigmented cell layer (NPE) responsible for aqueous humor secretion. Secretion may be mediated in part by cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i), but whether or how the two layers could coordinate their Ca2+ signals to regulate secretion is unclear. To investigate interactions between PE and NPE, we examined [Ca2+]i signaling in isolated intact ciliary epithelial bilayers using confocal microscopy. Phenylephrine selectively increased [Ca2+]i in PE and acetylcholine increased [Ca2+]i in NPE, but epinephrine increased [Ca2+]i in both layers. This increase spread from PE to NPE, and [Ca2+]i signaling across the bilayer remained coordinated during [Ca2+]i oscillations. All epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signaling was blocked by the α1-adrenergic antagonist prazosin, whereas signaling in the NPE but not PE was blocked by the β-adrenergic antagonist propranolol, the gap junction blockers octanol and 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid, or the A kinase inhibitor Rp diastereomer of adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphothioate. The β-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol failed to increase Ca2+ by itself, but isoproterenol plus phenylephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signals across the bilayer similar to those induced by epinephrine. Finally, isoproterenol increased cell-to-cell spread of lucifer yellow via gap junctions, whereas cell-to-cell spread of [Ca2+]i signals could be induced by photorelease of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Thus, calcium signals are coordinated in the epithelial bilayer so that adrenergic stimulation can increase [Ca2+]i in NPE, but only if NPE are primed by activation of endogenous adenylyl cyclase, whereupon they receive stimulation from adjacent PE via gap junctions. This novel interplay between endocrine and paracrine pathways may coordinate [Ca2+]i signaling across the ciliary epithelial bilayer.
The epithelial bilayer of the ciliary body produces aqueous humor, a fluid essential for maintenance of intraocular pressure and nourishment of the avascular transparent tissues that comprise the anterior segment of the eye. Understanding the process of aqueous humor formation has been complicated by the unique anatomy of the epithelium. The two constituent layers, the inner aqueous-facing nonpigmented epithelium (NPE) and the outer serosal-facing pigmented epithelium (PE), originate from the neural crest during embryogenesis, then become apposed at their apices when the invagination of the optic vesicle occurs (1). The layers thereafter remain apposed to each other along their apical membranes, across which gap junctions are densely expressed to establish a heterocellular junctional path and a virtual syncytium (2–4).
Signal transduction to regulate aqueous humor secretion probably involves multiple pathways (1, 5), possibly including spontaneous (6) and induced elevations in cytosolic calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) (7–10). Furthermore, different [Ca2+]i signaling patterns occur in the ciliary body in response to agents that also affect aqueous humor formation, like adrenergic and muscarinic agonists (11–16). Although the spatial organization of [Ca2+]i waves in ciliary epithelium is not known, [Ca2+]i waves regulate secretion in other epithelial cells (17–21), and cell-to-cell spread of these waves via gap junctions may play a role in this regulation (20, 22). To understand whether there is similar coordination of [Ca2+]i signaling in the epithelial bilayer of the ciliary body, we observed patterns of induced [Ca2+]i signaling in intact segments of the bilayer (23) using time-lapse confocal microscopy (24).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and Materials.
Male albino New Zealand rabbits weighing 2–3 kg obtained from Millbrook Farms (Amherst, MA) were used for all experiments. Acetylcholine, phenylephrine, epinephrine, isoproterenol, prazosin, propranolol, yohimbine, octanol, 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid (αGA), lucifer yellow (LY), and Hanks’ balanced salt solution were obtained from Sigma. Fluo-3 in acetoxy-methoxylated form and pluronic F-127 were obtained from Molecular Probes. Caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and the Rp diastereomer of adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphothioate (Rp-cAMP[S]), a protein kinase A inhibitor, were obtained from Calbiochem, and suramin was obtained from Biomol (Plymouth Meeting, PA). All other chemicals were of the highest quality commercially available.
Preparation of Isolated Ciliary Epithelium.
Isolated ciliary bilayer epithelium were prepared as described previously (23, 25) with slight modification. Briefly, rabbits were anesthetized with an i.m. injection of ketamine hydrochloride and xylazine and then euthanized by i.v. injection of pentobarbital sodium and phenytoin sodium. The eyes were enucleated promptly and then the anterior segments were isolated after careful removal of the lens. From the isolated anterior segment of the eye, ciliary processes were separated from the iris and cut into 10–20 strips, each 2–3 mm in length. All procedures conformed with National Institutes of Health recommendations as developed by the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Resolution on the Use of Animals in Research.
Confocal Microscopic Measurements of [Ca2+]i.
Isolated ciliary epithelia were loaded with fluo-3/acetoxy-methoxylated (50 μM) and pluronic F-127 for 1 hr at room temperature in Hanks’ balanced salt solution containing 10% fetal calf serum. Specimens were then placed between two glass coverslips in a gravity-driven perifusion chamber on the stage of a Zeiss Axiovert microscope and perifused at a rate of 1–2 ml/min. The tissue was observed through a ×63 objective using a Bio-Rad MRC-600 laser scanning confocal imaging system. An argon laser was used to excite the dye at 488 nm and emission signals above 515 nm were collected. Optical sections 1–2 μm in thickness were obtained. Neither autofluorescence nor other background signals were detectable at the machine settings used, and there was no change in size, shape, or location of cells during the experiments. In most experiments, two-dimensional images consisting of 768 × 512 pixels (0.26 μm/pixel) were recorded at a rate of 1 frame/s on an optical disc recorder and analyzed subsequently using the mean pixel values of preselected areas to monitor intensity changes. Increases in [Ca2+]i were normalized by the initial fluorescence (F0), then expressed as (F/F0) × 100% (24). In selected experiments, tissues instead were examined using the line scanning mode of the confocal microscope to increase temporal resolution (to 10 ms or 100 ms). In this mode, fluorescence is determined at each point along a single line across the image rather than at each point across the entire image. Line scans were displayed as images consisting of 768 × 512 pixels, with a spatial resolution of 0.26 μm/pixel (in the x direction) and a temporal resolution of 10 ms/pixel or 100 ms/pixel (in the y direction). Velocities of [Ca2+]i waves in individual cells were determined from the rate at which initial fluorescence increases moved along the scan line (21).
Microinjection Studies.
In selected studies, LY or caged IP3 were delivered into cells by microinjection and then the tissue was examined by confocal video microscopy as described above. Micropipettes with an internal diameter of <0.5 μm were made from glass capillary tubes using a Narishige PD-5 micropipette puller. A series 5171 Eppendorf micromanipulator was used for positioning and an Eppendorf series 5242 microinjector was used for pressure microinjections (24). Micropipettes were loaded with LY or caged IP3 dissolved in an intracellular-like buffer (150 mM KCl plus 1 mM Hepes), and Texas red was coinjected with caged IP3 as a marker of successful microinjection. We found that the mechanical stimulus of microinjections induced transient [Ca2+]i signals in the bilayer, as has been described in other epithelia (24), so caged IP3 was released in cells by UV flash photolysis after injection-induced [Ca2+]i transients had subsided. For photolysis, a custom-built system was used that couples a 75-W mercury lamp to a 1-mm quartz fiberoptic cable through a Uniblitz shutter and an AZI filterwheel.
Experimental Design.
Preparations of ciliary bilayer epithelia were stimulated with either the muscarinic agonist acetylcholine (10 μM), the α1-adrenergic agonist phenylephrine (100 μM), the combined α- and β-agonist epinephrine (100 μM), or the β-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol (100 μM). Selected tissues were treated sequentially with the gap junction conductance inhibitors octanol or αGA, then epinephrine, in which case tissues were exposed to octanol (1 mM) for a total of 30 s immediately before stimulation with epinephrine or to αGA (100 μM) for 2 min before and then during stimulation with epinephrine. Brief exposure to either octanol (26) or αGA (27) induces a complete but transient and reversible block of gap junction conductance. Tissues treated with both an adrenergic or purinergic antagonist [either 50 μM prazosin (α1), 100 μM propranolol (β), 100 μM yohimbine (α2), or 100 μM suramin (P2)] and epinephrine were exposed to the antagonist 30 s prior to stimulation with epinephrine and then during epinephrine stimulation as well. Tissues treated with both Rp-cAMP[S] and epinephrine were exposed to Rp-cAMP[S] (100 μM) for 30 min before stimulation with epinephrine. Rp-cAMP[S] blocks cAMP-mediated signal transduction by inhibiting protein kinase A (28). This combination of stimuli was chosen to evaluate the role of the adenylyl cyclase system in [Ca2+]i signaling in the bilayer. For LY microinjections, cells were either untreated or pretreated with octanol or isoproterenol. All results are expressed as means ± SEM (n).
RESULTS
Agonist-Induced [Ca2+]i Rises.
Stimulation of isolated ciliary bilayer epithelium with agonists caused a rise in [Ca2+]i as described previously (14, 15). Epinephrine increased [Ca2+]i in both epithelial layers (Fig. 1 A–G); the [Ca2+]i increase in the PE preceded the NPE [Ca2+]i signal in 12 of 18 experiments, with no measurable time lag in the remaining 6 experiments. In contrast, the α1-adrenergic agonist phenylephrine increased [Ca2+]i only in the PE layer (n = 15 experiments; Fig. 1H), whereas acetylcholine increased [Ca2+]i only in the NPE layer in 25 of 35 experiments, with increases in [Ca2+]i observed in both layers in the remaining 10 experiments (Fig. 1I). Furthermore, acetylcholine but not epinephrine increased [Ca2+]i in isolated NPE monolayers (n = 5 each, data not shown). These findings show that PE and NPE each independently has the capacity to increase [Ca2+]i in response to an appropriate stimulus.
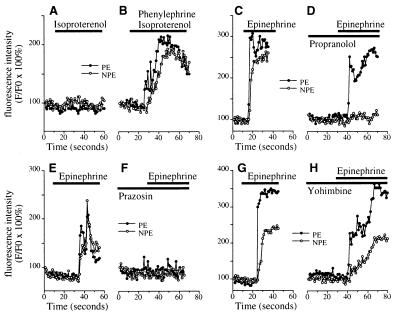
Figure 1.
Spatial pattern of [Ca2+]i signaling in the ciliary bilayer. (A) Confocal microscopic image of an isolated ciliary bilayer loaded with the Ca2+-sensitive dye fluo-3. Individual cells are outlined in white. The PE (cuboidal) and NPE (columnar) cells whose responses are graphed in G are indicated by the white arrow and arrowhead, respectively. (Bar, 5 μm.) (B–F) Sequential pseudocolored images of the same preparation at 10, 13, 15, 17, and 19 s after stimulation with 100 μM epinephrine. Fluorescence intensity in this and subsequent confocal images and line scans is represented by the pseudocolor scale shown on the bottom. Note that the [Ca2+]i increase begins in the PE, then spread to the NPE. (G) Fluorescence increase in the two cells indicated in A. Open and closed circles represent normalized fluorescence intensity (F/F0) in the NPE and PE, respectively; each measured over a 1.7-μm2 region. Tracing is typical of that seen in 12 separate experiments. The black bar indicates the period of the stimulation. (H) [Ca2+]i signaling in the PE and NPE during stimulation with 100 μM phenylephrine. Tracing is typical of that seen in 15 separate experiments. (I) [Ca2+]i signaling in the PE and NPE during stimulation with 10 μM acetylcholine. Tracing is typical of that seen in 25 of 35 experiments.
Pharmacology of the Adrenergic Response.
Additional studies were performed to determine why the PE and NPE respond jointly to epinephrine. In five consecutive experiments, the β-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol alone had no significant effect on [Ca2+]i in the epithelial bilayer (Fmax/F0 = 108.0 ± 2.9% in the PE and 111.5 ± 1.7% in the NPE; n = 5 each), but isoproterenol plus phenylephrine induced serial [Ca2+]i signals in the PE (Fmax/F0= 199.1 ± 15.6%; P < 0.01 relative to isoproterenol alone by paired t test) and then NPE (Fmax/F0 = 182.6 ± 5.3%; P < 0.0005 relative to isoproterenol alone), similar to the pattern induced by epinephrine (Fig. 2 A and B). Similarly, the β-adrenergic antagonist propranolol (Fig. 2 C and D) blocked the epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i increase in the NPE (Fmax/F0 = 122.1 ± 3.0% in the presence of propranolol and 236.3 ± 14.9% with epinephrine alone; n = 5, P < 0.005) but not the PE (221.5 ± 18.9% and 245.3 ± 15.6%, respectively). The α1-adrenergic antagonist prazosin (Fig. 2 E and F) blocked the epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i increase in both layers (Fmax/F0 = 217.7 ± 17.9% vs. 113.4 ± 3.6% in the PE without and with prazosin, respectively, and Fmax/F0 = 211.7 ± 21.5% vs. 108.8 ± 3.0% in the NPE without and with prazosin, respectively; n = 5, P < 0.01), whereas the α2-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine (Fig. 2 G and H) did not affect the epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i increase in either layer (Fmax/F0 = 255.8 ± 24.4% vs. 234.2 ± 32.1% in the PE without and with yohimbine, respectively, and Fmax/F0 = 193.7 ± 23.4% vs. 182.4 ± 14.0% in the NPE without and with yohimbine, respectively; n = 5, P > 0.1). These findings show that the sequential signaling induced in the PE, then NPE, by epinephrine requires both α1- and β- adrenergic stimulation.
Figure 2.
Pharmacology of adrenergic signaling in the ciliary bilayer. (A and B) The β-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol (100 μM) alone (A) does not increase [Ca2+]i in either the NPE or PE, but together with 100 μM phenylephrine (B) increases [Ca2+]i in both cell layers. Results are representative of the pattern seen in five consecutive experiments. (C and D) Epinephrine (100 μM)-induced [Ca2+]i signaling in the NPE but not the PE is blocked by the β-adrenergic antagonist propranolol (100 μM). Results shown are typical of those seen in five consecutive experiments. (E and F) Epinephrine (100 μM)-induced [Ca2+]i signaling in both layers is blocked by the α1-adrenergic antagonist prazosin (50 μM). Results shown are typical of those seen in five consecutive experiments. (G and H) The α2-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine (100 μM) does not block [Ca2+]i signaling in cells in the ciliary bilayer stimulated with 100 μM epinephrine. Results shown are typical of those seen in five consecutive experiments.
Organization of the [Ca2+]i Waves Within Each Layer.
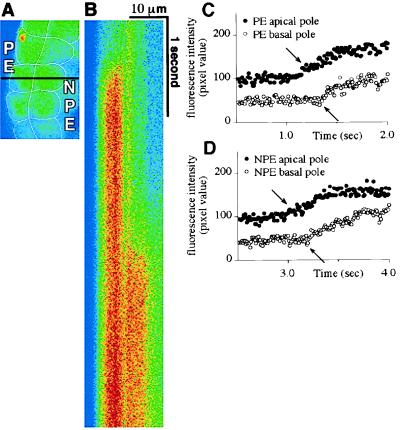
The temporal pattern of [Ca2+]i signaling in the bilayer was examined in greater detail with confocal line scanning microscopy. In each layer, epinephrine triggered an abrupt increase in [Ca2+]i in the apical region, and this [Ca2+]i rise then spread rapidly to the basal region (Fig. 3). The speed of epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i waves was 26.6 ± 2.2 μm/s (n = 15) in the PE and 25.9 ± 1.9 μm/s (n = 10) in the NPE. The time lag between the onset of [Ca2+]i rises in the PE and NPE cells was easier to quantify by line scanning, given the increased temporal resolution. The initial rise in epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signals began 1.93 ± 0.49 s (n = 10) sooner in the PE (P < 0.0001 by paired t test).
Figure 3.
[Ca2+]i signals begin apically in both the PE and NPE. (A) Confocal microscopic image of a segment of the isolated ciliary bilayer loaded with fluo-3. The confocal line scan in B was performed along the black horizontal line across this image. Note that this line is perpendicular to the bilayer, so it runs from the basal to the apical pole of an NPE and a PE cell. (B) Confocal line scan collected along the line indicated in A during stimulation with 100 μM epinephrine. Fluorescence intensity along the x axis reflects distance (across the scan line) and along the y axis reflects time (between serial scans). Horizontal lines comprising this scan were obtained every 10 ms for a total of 5.12 s (from top to bottom). Note that the [Ca2+]i signal in the PE precedes the signal in the NPE, but the increase in fluorescence in both cells begins apically, then spreads to the opposite (basal) pole. Results are representative of those seen in 10 preparations. (C and D) Graphical representation of the fluorescence intensity over time at an apical and a basal point (represented by closed and open circles, respectively) in the PE (C) and NPE (D) cells that were scanned. The increases in [Ca2+]i (arrows) within the PE cell occur 260 ms apart and the two points are separated by a distance of 6.03 μm, which corresponds to a wave speed of 23.2 μm/s. The increases in [Ca2+]i (arrows) within the NPE cell occur 290 ms apart and the two points are separated by a distance of 6.55 μm, which corresponds to a wave speed of 22.6 μm/s.
Signaling During [Ca2+]i Oscillations.
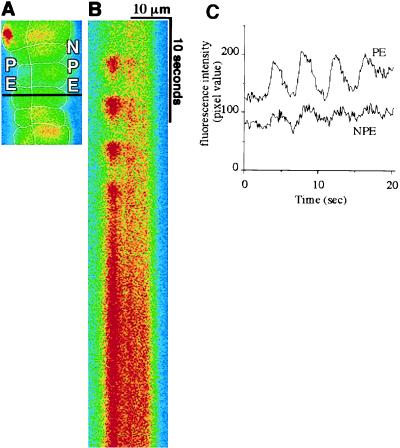
To further evaluate intercellular [Ca2+]i signaling in this tissue, adjacent pairs of PE and NPE cells within the epithelial bilayer were examined during [Ca2+]i oscillations. Oscillations were detected in 65% (13 of 20) of ciliary specimens stimulated with epinephrine. In each case, oscillations were synchronized across the bilayer (Fig. 4). The duration of each individual [Ca2+]i spike and the oscillation period were 2.50 ± 0.27 s and 4.49 ± 0.43 s, respectively (n = 13). These results further demonstrate that epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signals are coordinated in the bilayer.
Figure 4.
[Ca2+]i oscillations induced by epinephrine are coordinated across the ciliary bilayer. (A) Confocal microscopic image of an isolated ciliary bilayer loaded with fluo-3. The confocal line scan in B was performed along the black horizontal line across this image. (B) Confocal line scan collected during stimulation with 100 μM epinephrine. In contrast to the line scan in Fig. 3, lines here were collected every 100 ms for a total of 51.2 s (from top to bottom). Repetitive increases in fluorescence indicate [Ca2+]i oscillations. Note that the oscillations are synchronized across the bilayer. Results shown are representative of those seen in 13 preparations. (C) Graphical representation of [Ca2+]i in the PE and NPE cells shown in the line scan. Note that repetitive [Ca2+]i spikes (i.e., oscillations) occur in both cells and in a synchronized fashion. Tracings are offset for clarity. The [Ca2+]i spikes have higher amplitudes in the PE cell in this particular example, but this was not a general feature.
Role of Gap Junctions and cAMP.
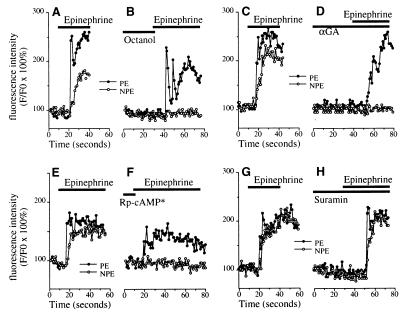
To understand the mechanism by which [Ca2+]i signaling is coordinated across the bilayer, specimens were pretreated with octanol, αGA, or Rp-cAMP[S]. In specimens pretreated with octanol (Fig. 5 A and B), epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signaling was unchanged in the PE (Fmax/F0 = 207.9 ± 6.1% vs. 196.9 ± 7.0% without and with octanol, respectively; n = 8, P > 0.15) but was nearly abolished in the NPE (Fmax/F0 = 183.8 ± 11.5% vs. 110.7 ± 3.8% without and with octanol, respectively; P < 0.001). Similarly, in specimens pretreated with αGA (Fig. 5 C and D), epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signaling was unchanged in the PE (Fmax/F0 = 212.5 ± 14.2% vs. 201.4 ± 17.9% without and with αGA, respectively; n = 5, P > 0.3) but was nearly abolished in the NPE (Fmax/F0 = 174.7 ± 13.8% vs. 105.2 ± 2.0% without and with αGA, respectively; P < 0.0005). In specimens pretreated with Rp-cAMP[S] (Fig. 5 E and F), the epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i increase was abolished in the NPE (Fmax/F0 = 187.8 ± 18.1% vs. 105.4 ± 2.3% without and with Rp-cAMP[S], respectively; P < 0.01), but was reduced only slightly (by 8%) in the PE (Fmax/F0 = 217.5 ± 20.1% vs. 200.9 ± 17.6% without and with Rp-cAMP[S], respectively; n = 5, P = 0.02). [Ca2+]i signals in epithelia also may spread from cell to cell via ATP secretion coupled to activation of extracellular P2 ATP receptors (24), but the P2 receptor antagonist suramin (100 μM; Fig. 5 G and H) did not inhibit epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signals in either the PE (Fmax/F0 = 237.2 ± 19.4% vs. 225.8 ± 19.2% without and with suramin, respectively; n = 5, P > 0.2) or NPE (Fmax/F0 = 192.2 ± 12.4% vs. 197.8 ± 14.5% without and with suramin, respectively; P > 0.7). These findings demonstrate that epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signals in the PE depend only on activation of α1-adrenergic receptors, but that spread of the signal to the NPE further depends on gap junction conductance and A kinase activation.
Figure 5.
Mechanism of epinephrine (100 μM)-induced [Ca2+]i signaling in the NPE. (A and B) Epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signals in the NPE depend on gap junction conductance. Ciliary bilayer stimulated with epinephrine alone (A) or with the gap junction blocker octanol (1 mM, B). Results are typical of those seen in eight consecutive experiments. (C and D) Additional evidence that epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signals in the NPE depend on gap junction conductance. Ciliary bilayer stimulated with epinephrine alone (C) or with the gap junction blocker αGA (100 μM, D). Results are typical of those seen in five consecutive experiments. (E and F) Epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signals in the NPE depend on A kinase activation. [Ca2+]i signaling in cells in the ciliary bilayer stimulated with epinephrine alone (E) or following preincubation (∗ for 30 min) with the protein kinase A inhibitor Rp-cAMP[S] (100 μM, F). Results are representative of those seen in five consecutive experiments. (G and H) Epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signals in the ciliary bilayer do not involve P2 ATP receptors. [Ca2+]i signaling in cells in the bilayer stimulated with epinephrine alone (G) or following preincubation with the P2 receptor antagonist suramin (100 μM, H). Results are representative of those seen in five consecutive experiments.
Regulation of Gap Junction Conductance.
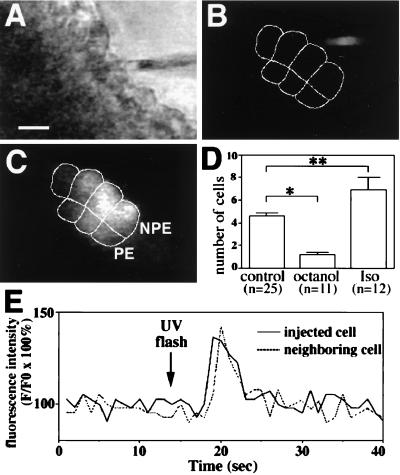
Microinjection studies were performed to directly investigate cell-to-cell transfer via gap junctions within the ciliary bilayer, and to determine the effects of octanol and isoproterenol on gap junction conductance in this cell system. LY was microinjected into a single cell within the bilayer and then spread of the dye to neighboring cells was monitored by confocal video microscopy (Fig. 6). LY spread quickly to neighboring cells, achieving steady-state distribution of fluorescence within 15–30 s after injection (Fig. 6 A–C). LY spread to 4.6 ± 0.3 cells under control conditions (n = 25; Fig. 6D), confirming that epithelial cells within the ciliary bilayer are functionally coupled (29). In contrast, the dye spread to only 1.2 ± 0.2 cells in the presence of octanol (n = 11; P < 0.005), confirming that octanol can be used to block gap junction conductance in this particular cell system. In addition, the dye spread to 6.9 ± 1.1 cells in the presence of isoproterenol (n = 12; P < 0.05), suggesting that β-adrenergic stimulation increases gap junction conductance in the bilayer. Finally, direct transmission of second messengers via gap junctions was investigated by UV flash photolysis of microinjected caged IP3. Photolysis of the caged IP3 resulted in an increase in [Ca2+]i in the injected cell plus its neighbors in three separate experiments (Fig. 6E). This finding demonstrates that either [Ca2+]i or IP3 itself can spread from cell to cell via gap junctions in this cell system.
Figure 6.
Intercellular communication in the ciliary bilayer. (A–C) Intercellular spread of lucifer yellow (LY). (A) Transmission image shows the bilayer and the microinjection pipette loaded with LY. (Bar, 10 μm.) (B and C) Serial confocal images show fluorescence in the same field immediately before and 30 s after injection of one of the cells with LY. The micropipette tip can be seen immediately before injection (B), whereas the dye labels four NPE cells and three PE cells (outlined) 30 s afterward (C). (D) Octanol (1 mM) blocks and isoproterenol (100 μM) facilitates cell-to-cell spread of LY. Values are means ± SEM (∗, P < 0.005; ∗∗, P < 0.05). (E) IP3-mediated increases in [Ca2+]i spread from cell to cell in the ciliary bilayer. Caged IP3 was injected into a cell in the bilayer and then uncaged by flash photolysis. A transient increase in [Ca2+]i occurs first in the injected cell, then in a neighboring cell 1 s later. Results are typical of those seen in three separate experiments.
DISCUSSION
The spatial pattern of [Ca2+]i signals, both within individual cells (19, 30, 31) and from cell to cell (22, 32, 33), plays a role in the regulation of cell and tissue function. We examined the spatial organization of [Ca2+]i signals in the secretory ciliary epithelial bilayer of the eye. The NPE and PE layers each exhibited the capacity to generate [Ca2+]i signals through stimulation of muscarinic receptors on the NPE and α1-adrenergic receptors on the PE. Stimulation with the endogenous agonist epinephrine increased [Ca2+]i in both cell layers, though. This increase reflects sequential [Ca2+]i signaling, first in the PE, then in the adjacent NPE. Epinephrine-induced signaling in the PE resulted from α1-adrenergic stimulation of those cells, whereas signaling in the NPE required not only α1 stimulation of the PE but β-adrenergic stimulation, presumably of the NPE. The spread of [Ca2+]i signals to the NPE further depended on gap junctional communication between the two layers, plus A kinase activation through β-adrenergic stimulation. Thus, epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signaling in the NPE appears to require a “priming” signal imparted through direct neuroendocrine stimulation of the NPE, followed by paracrine stimulation of these cells by the PE, via gap junctions. The priming signal is activation of A kinase, and this effect may act by increasing the sensitivity of NPE IP3 receptors (34), or, more likely, by increasing the conductance of gap junctions (35, 36) that couple the NPE to the PE (37). Direct evidence in support of the latter mechanism was provided by the observation that isoproterenol increases dye transfer in the bilayer (Fig. 6D). Previous work in T84 colonic epithelia has also shown that cAMP can increase the conductance of gap junctions (38). In the ciliary bilayer this increased conductance likely results from phosphorylation of connexin 43 (37), the principal connexin isoform of the gap junctions linking PE to NPE (39).
Cell-to-cell spread of [Ca2+]i signals has been examined in several epithelia, including hepatocytes (20, 27), pancreatic acinar cells (22), and respiratory epithelia (40, 41). Both [Ca2+]i and IP3 can cross gap junctions in these cell types; therefore, increases in [Ca2+]i or IP3 in a single cell leads to an increase in [Ca2+]i in neighboring cells (22, 40–42). Here, we showed that IP3-mediated [Ca2+]i signals can spread from cell to cell within the ciliary epithelial bilayer as well. In other tissues, simultaneous stimulation of cells linked via gap junctions results in highly synchronized [Ca2+]i signals (20, 27). This coordinated response depends not only on gap junctions but on agonist-induced increases in basal levels of IP3 in each of the cells (22, 27). Communication via gap junctions potentiates cAMP signaling as well (43). The current work extends these observations in two ways. First, this work shows that signaling via [Ca2+]i and cAMP can work synergistically to induce the spread of [Ca2+]i waves. Second, this study shows that [Ca2+]i waves can spread, via gap junctions, from one type of epithelium to another.
We used two different agents, octanol and αGA, to block gap junction conductance. Long-chain alcohols block gap junctions as demonstrated by both cell-to-cell transfer of dyes (44) and direct electrophysiologic measurements (26, 45). Although nonspecific inhibitory effects of octanol have been described (46), we have not observed such effects in epithelia transiently exposed to octanol (20, 47), as done here. αGA is an alternative agent to block gap junctions, perhaps more specific than octanol (27), and αGA also blocked epinephrine-induced [Ca2+]i signaling in the NPE but not the PE.
What is the functional significance of coordinated PE-to-NPE [Ca2+]i signaling in the eye? In single epithelial cells, polarized movement of [Ca2+]i waves is thought to direct fluid and electrolyte secretion by sequential activation of apical, then basolateral chloride channels (17, 19). Intercellular [Ca2+]i signaling may also organize mechanical actions to facilitate secretion, such as ciliary beating in the lung (40) or canalicular peristalsis in the liver (32). In the exocrine pancreas, intercellular [Ca2+]i signals may serve to coordinate and thus decrease the threshold for secretion (22). Secretion by the ciliary body may be more complex because it results from the action of two separate but communicating epithelia. The PE is responsible for extracting selected substances from the blood, whereas the NPE must then secrete these substances into the posterior chamber to form the aqueous humor (48). Ca2+-sensitive transport mechanisms have been identified in both the PE (49) and NPE (50). For example, Ca2+-activated potassium channels (51–53) may provide the electrical driving force known to be required for vectorial chloride secretion across the bilayer (51, 52). The sequential PE-to-NPE [Ca2+]i signaling demonstrated here also depends on β-adrenergic activation of A kinase, consistent with previous observations in both rabbit and humans that β-adrenergic stimulation modulates aqueous humor formation (1, 54). Thus, this paracrine regulation of [Ca2+]i signaling may provide a mechanism whereby the PE can direct the NPE to complete the transport of aqueous humor constituents initiated by the PE.
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Angela D. Burgstahler for help with microinjections and Philippe Male for expert technical assistance. This work was supported by U.S. Public Health Service Grants National Institutes of Health MERIT Award EY-08879, EY-00785, and DK-45710, the E. Matilda Ziegler Foundation, an Established Investigator Grant from the American Heart Association, and the Morphology Core Facility of the Yale Liver Center (National Institutes of Health DK-34989).
Footnotes
This paper was submitted directly (Track II) to the Proceedings Office.
Abbreviations: αGA, 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid; [Ca2+]i, cytosolic Ca2+ concentration; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; LY, lucifer yellow; NPE, nonpigmented epithelium; PE, pigmented epithelium; Rp-cAMP[S], Rp diastereomer of adenosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphothioate; Fluo-3, (1-[2-amino-5-(2,7-dichloro-6-hydroxy-3-oxy-9xanthenyl)-phenoxy]-2-[2-amino-5-methylphenoxy]ethane-N,N,N′,N′tetraacetic acid).
References
- 1.Sears M L. In: Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Sears M L, editor. Berlin: Springer; 1984. pp. 193–248. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ohkuma M, Nishiura M. Acta Soc Ophthalmol Jpn. 1974;78:1419–1430. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Reale E, Spitznas M. Albrecht Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1975;195:1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02390025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Raviola G, Raviola E. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1978;17:958–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wax M. In: Pharmacology of Glaucoma. Drance S M, Van Buskirk E M, Neufeld A H, editors. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1992. pp. 184–210. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Giovannelli A, Fucile S, Mead A, Mattei E, Eusebi F, Sears M. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;220:472–477. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lee C H, Reisine T D, Wax M B. Exp Eye Res. 1989;48:733–743. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(89)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ohuchi T, Yoshimura N, Tanihara H, Kuriyama S, Ito S, Honda Y. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992;33:1696–1705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Crook R B, Polansky J R. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992;33:1706–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yoshimura N, Tanabe-Ohuchi T, Takagi H, Honda Y. Curr Eye Res. 1995;14:629–635. doi: 10.3109/02713689508998489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Farahbakhsh N A, Cilluffo M C. J Physiol. 1994;477:215–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Farahbakhsh N A, Cilluffo M C. Exp Eye Res. 1997;64:173–179. doi: 10.1006/exer.1996.0194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schutte M, Diadori A, Wang C, Wolosin J M. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996;37:212–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schutte M, Wolosin J M. J Physiol. 1996;496:25–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Suzuki Y, Nakano T, Sears M. Curr Eye Res. 1997;16:166–175. doi: 10.1076/ceyr.16.2.166.5095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shi X P, Zamudio A C, Candia O A, Wolosin J M. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996;37:1037–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kasai H, Augustine G J. Nature (London) 1990;348:735–738. doi: 10.1038/348735a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kasai H, Li Y X, Miyashita Y. Cell. 1993;74:669–677. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90514-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ito K, Miyashita Y, Kasai H. EMBO J. 1997;16:242–251. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nathanson M H, Burgstahler A D. Mol Biol Cell. 1992;3:113–121. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nathanson M H, Padfield P J, O’Sullivan A J, Burgstahler A D, Jamieson J D. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:18118–18121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yule D I, Stuenkel E, Williams J A. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:C1285–C1294. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.271.4.C1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sears M L, Yamada E, Cummins D, Mori N, Mead A, Murakami M. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1991;89:131–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schlosser S F, Burgstahler A D, Nathanson M H. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:9948–9953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.18.9948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Matsui H, Murakami M, Wynns G C, Conroy C W, Mead A, Maren T H, Sears M L. Exp Eye Res. 1996;62:409–417. doi: 10.1006/exer.1996.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Spray D C, Ginzberg R D, Morales E A, Gatmaitan Z, Arias I M. J Cell Biol. 1986;103:135–144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tordjmann T, Berthon B, Claret M, Combettes L. EMBO J. 1997;16:5398–5407. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.17.5398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rothermel J D, Parker Botelho L H. Biochem J. 1988;251:757–762. doi: 10.1042/bj2510757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Oh J, Krupin T, Tang L, Sveen J, Lahlum R A. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35:2509–2514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Timmerman L A, Clipstone N A, Ho S N, Northrop J P, Crabtree G R. Nature (London) 1996;383:837–840. doi: 10.1038/383837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hardingham G E, Chawla S, Johnson C M, Bading H. Nature (London) 1997;385:260–265. doi: 10.1038/385260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nathanson M H, Burgstahler A D, Mennone A, Fallon M B, Gonzalez C B, Saez J C. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:G167–G171. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.269.1.G167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dora K A, Doyle M P, Duling B R. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:6529–6534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Joseph S K, Ryan S V. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:23059–23065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Giaume C, Marin P, Cordier J, Glowinski J, Premont J. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:5577–5581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Saez J C, Spray D C, Nairn A C, Hertzberg E L, Greengard P, Bennett M V. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:2473–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sears J, Nakano T, Sears M. Curr Eye Res. 1998;17:104–107. doi: 10.1076/ceyr.17.1.104.5260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chanson M, White M M, Garber S S. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:C533–C539. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.271.2.C533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Coca-Prados M, Ghosh S, Gilula N B, Kumar N M. Curr Eye Res. 1992;11:113–122. doi: 10.3109/02713689209000061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sanderson M J, Charles A C, Dirksen E R. Cell Regul. 1990;1:585–596. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.8.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Boitano S, Dirksen E R, Sanderson M J. Science. 1992;258:292–295. doi: 10.1126/science.1411526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Saez J C, Connor J A, Spray D C, Bennett M V L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vander Molen M A, Rubin C T, McLeod K J, McCauley L K, Donahue H J. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:12165–12171. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.21.12165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chanson M, Orci L, Meda P. Am J Physiol. 1991;261:G28–G36. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.1.G28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wolosin J M, Candia O A, Peterson-Yantorno K, Civan M M, Shi X P. Exp Eye Res. 1997;64:945–952. doi: 10.1006/exer.1997.0291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Deutsch D E, Williams J A, Yule D I. Am J physiol. 1995;269:G779–G788. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.269.5.G779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fallon M B, Nathanson M H, Mennone A, Saez J C, Burgstahler A D, Anderson J M. Am J Physiol. 1995;268:C1186–C1194. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.5.C1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mead A, Sears J, Sears M. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 1996;12:253–258. doi: 10.1089/jop.1996.12.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stelling J W, Jacob T J. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:C203–C209. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.271.1.C203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mito T, Delamere N A, Coca-Prados M. Am J Physiol. 1993;264:C519–C526. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.3.C519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jacob T J C. Am J Physiol. 1991;261:C808–C813. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.5.C808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Jacob T J C. Am J Physiol. 1991;261:C1055–C1062. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.6.C1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Barros F, Lopez-Briones L G, Coca-Prados M, Belmonte C. Curr Eye Res. 1991;10:731–738. doi: 10.3109/02713689109013867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sears M L. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985;100:194–198. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]