Abstract
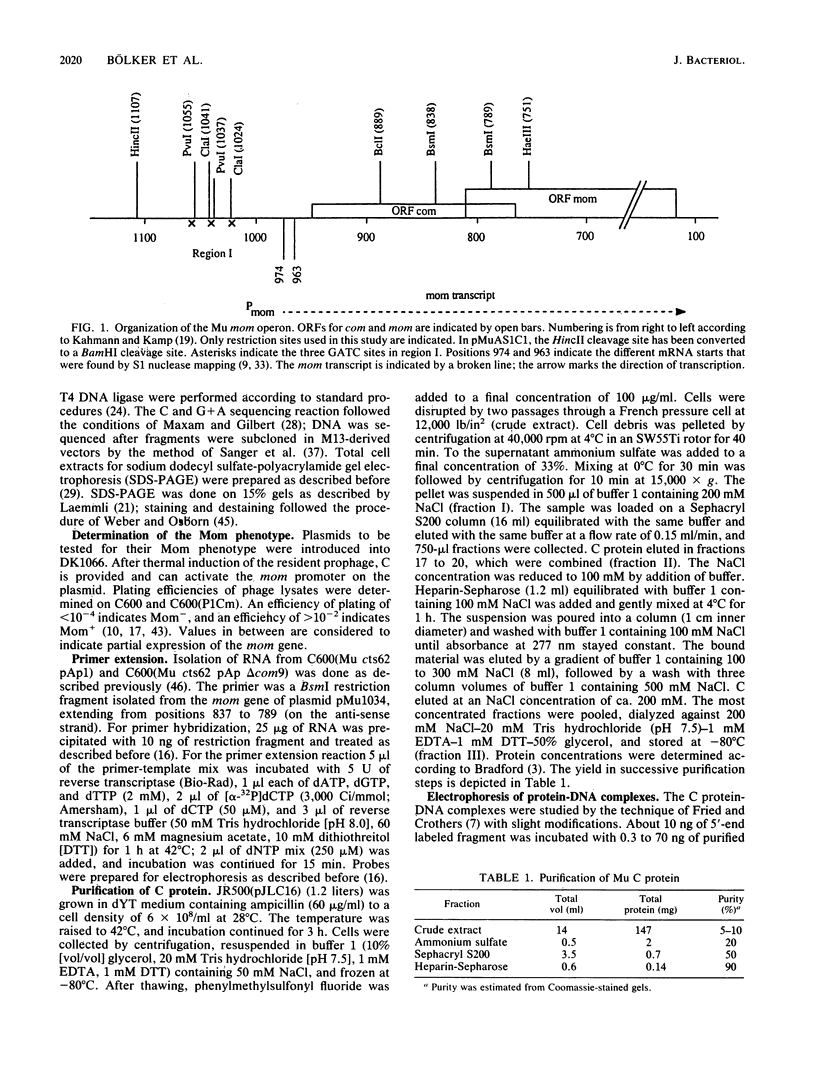
The phage Mu C gene product is a specific activator of Mu late gene transcription, including activation of the mom operon. Fusion of the C gene to the efficient translation initiation region of the Escherichia coli atpE gene allowed significant overproduction of C protein, which was subsequently purified and assayed for DNA binding by gel retardation and nuclease footprinting techniques. C protein binds to a site immediately upstream of the -35 region both of the mom promoter and the related phage D108 mod promoter. The location of the mom promoter has been determined by primer extension. Upstream deletions extending more than 3 base pairs into the C-binding site abolished activation of the mom promoter in vivo. In vitro binding of C was not significantly affected by DNA methylation. A second, C-dependent promoter was identified just downstream of the C coding region; comparison with the mom promoter revealed common structural elements.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of Lambda Lysogenicity during Bacterial Recombination in Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):429–439. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Kahmann R., Kamp D. Electron microscopic characterization of DNAs of non-defective deletion mutants of bacteriophage Mu. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 15;113(4):591–609. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Systematic method for the detection of potential lambda Cro-like DNA-binding regions in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Nye J. S., Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Mutant lambda phage repressor with a specific defect in its positive control function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2236–2239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S., Goradia M., Monaghan C., Bukhari A. I. Regulation of the DNA-modification function of bacteriophage Mu. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):647–653. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S., Ives J. S1 nuclease mapping of the phage Mu mom gene promoter: a model for the regulation of mom expression. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):185–198. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisig P., Kahmann R. The sequence and mom-transactivation function of the C gene of bacteriophage Mu. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Cleavage of DNA with methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II): reaction conditions and product analyses. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3934–3945. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Wulff D. L., Rosenberg M. Bacteriophage lambda protein cII binds promoters on the opposite face of the DNA helix from RNA polymerase. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):703–708. doi: 10.1038/304703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Irwin N., Ptashne M. Repressor structure and the mechanism of positive control. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90451-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Translational and transcriptional control elements in the untranslated leader of the heat-shock gene hsp22. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R. Methylation regulates the expression of a DNA-modification function encoded by bacteriophage Mu. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):639–646. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Seiler A., Wulczyn F. G., Pfaff E. The mom gene of bacteriophage mu: a unique regulatory scheme to control a lethal function. Gene. 1985;39(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach D., Symonds N. The isolation and characterisation of a plaque-forming derivative of bacteriophage Mu carrying a fragment of Tn3 conferring ampicillin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 4;172(2):179–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00268280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N. L., Gielow W. O., Wallace R. G. Mechanism of araC autoregulation and the domains of two overlapping promoters, Pc and PBAD, in the L-arabinose regulatory region of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin W., Howe M. M. Localization and DNA sequence analysis of the C gene of bacteriophage Mu, the positive regulator of Mu late transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4881–4897. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin W., Rao G., Howe M. M. Bacteriophage Mu late promoters: four late transcripts initiate near a conserved sequence. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2003–2018. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2003-2018.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G., Morris N. R. Pleiotropic effects of a DNA adenine methylation mutation (dam-3) in Escherichia coli K12. Mutat Res. 1975 Apr;28(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens G., Hoffmann A., Blöcker H., Frank R., Kahmann R. Gin-mediated site-specific recombination in bacteriophage Mu DNA: overproduction of the protein and inversion in vitro. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2415–2421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraja V., Hecht G., Hattman S. The phage Mu 'late' gene transcription activator, C, is a site-specific DNA binding protein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 May 1;37(9):1809–1810. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90457-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Vollering M., Brinkman A., Van de Putte P. Analysis of the methylation-regulated Mu mom transcript. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauder B., Blöcker H., Frank R., McCarthy J. E. Inducible expression vectors incorporating the Escherichia coli atpE translational initiation region. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler A., Blöcker H., Frank R., Kahmann R. The mom gene of bacteriophage Mu: the mechanism of methylation-dependent expression. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2719–2728. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinton D., Hattman S., Crain P. F., Cheng C. S., Smith D. L., McCloskey J. A. Purification and characterization of the unusual deoxynucleoside, alpha-N-(9-beta-D-2'-deoxyribofuranosylpurin-6-yl)glycinamide, specified by the phage Mu modification function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7400–7404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szatmari G. B., Lapointe M., DuBow M. S. The right end of transposable bacteriophage D108 contains a 520 base pair protein-encoding sequence not present in bacteriophage Mu. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6691–6704. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint A. The DNA modification function of temperate phage Mu-1. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulczyn F. G., Kahmann R. Post-transcriptional regulation of the bacteriophage Mu mom gene by the com gene product. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E., Sampson L., Hayden M., Parr R., Huang W. M., Casjens S. Plasmid vectors useful in the study of translation initiation signals. Gene. 1986;43(3):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]