Abstract
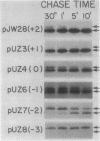
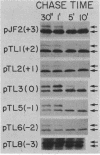
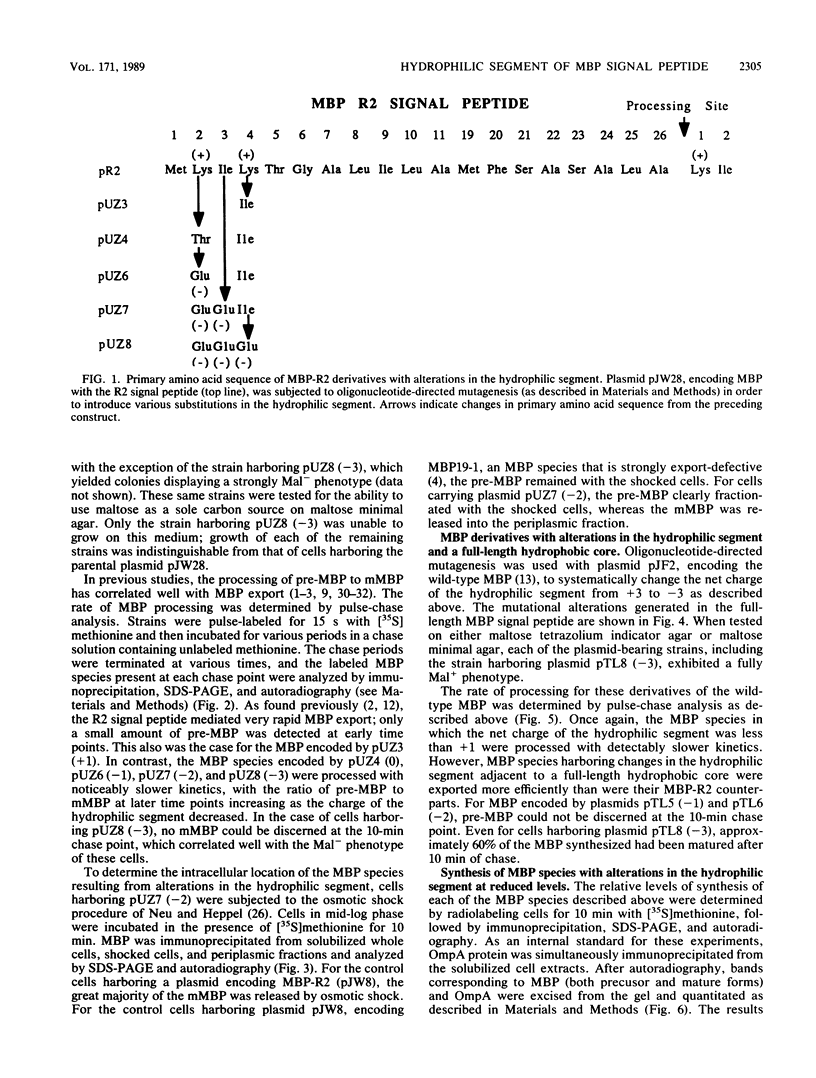
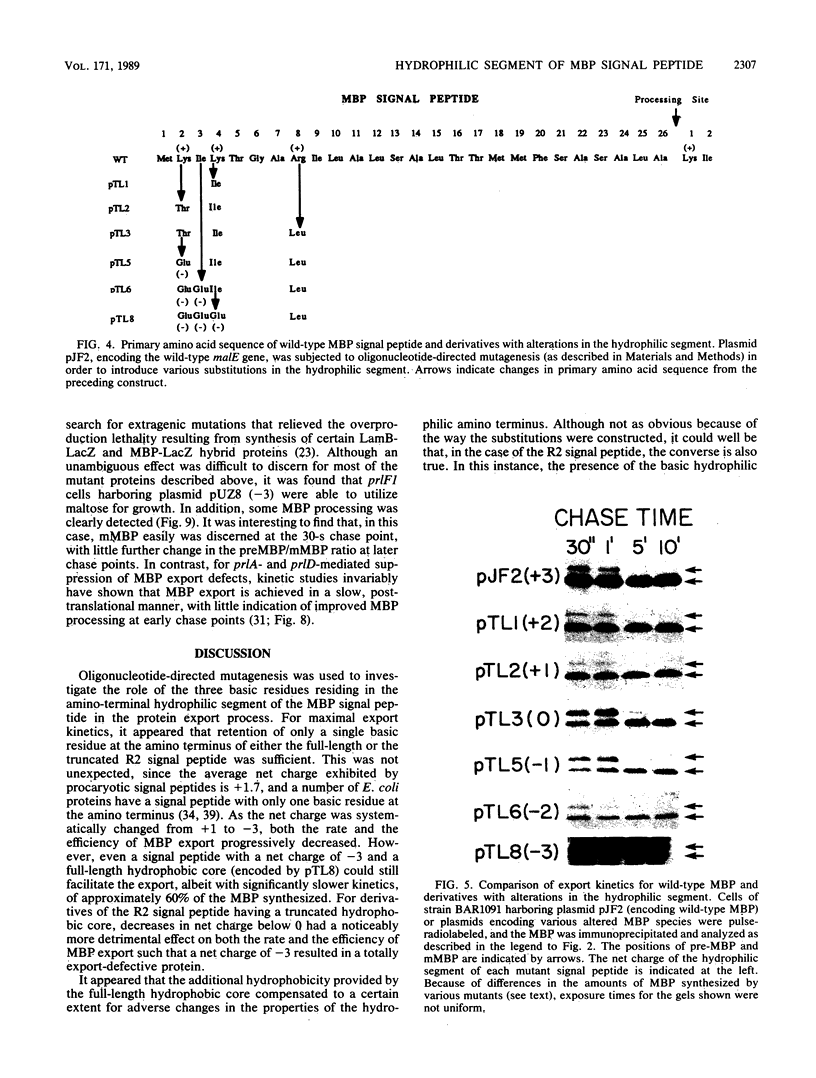
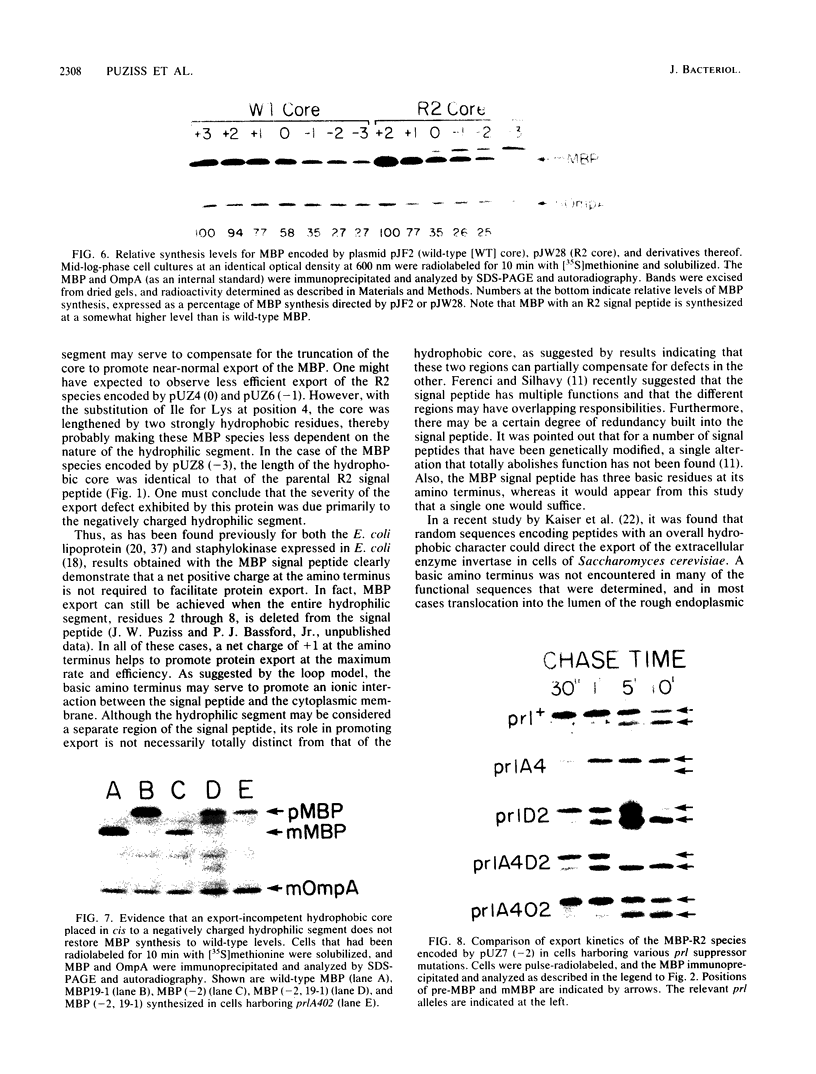
Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis was employed to investigate the role of the hydrophilic segment of the Escherichia coli maltose-binding protein (MBP) signal peptide in the protein export process. The three basic residues residing at the amino terminus of the signal peptide were systematically substituted with neutral or acidic residues, decreasing the net charge in a stepwise fashion from +3 to -3. It was found that a net positive charge was not absolutely required for MBP export to the periplasm. However, export was most rapid and efficient when the signal peptide retained at least a single basic residue and a net charge of +1. The nature of the adjacent hydrophobic core helped to determine the effect of charge changes in the hydrophilic segment on MBP export, which suggested that these two regions of the signal peptide do not have totally distinct functions. Although the stepwise decrease in net charge of the signal peptide also resulted in a progressive decrease in the level of MBP synthesis, the data do not readily support a model in which MBP synthesis and export are obligately coupled events. The export defect resulting from alterations in the hydrophilic segment was partially suppressed in strains harboring certain prl alleles but not in strains harboring prlA alleles that are highly efficient suppressors of signal sequence mutations that alter the hydrophobic core.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Proper interaction between at least two components is required for efficient export of proteins to the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):169–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.169-178.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr The synthesis of export-defective proteins can interfere with normal protein export in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12193–12200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Rasmussen B. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Intragenic suppressor mutations that restore export of maltose binding protein with a truncated signal peptide. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankier A. T., Weston K. M., Barrell B. G. Random cloning and sequencing by the M13/dideoxynucleotide chain termination method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:51–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S. A., Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli K12. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:101–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Bassford P. J., Jr Localization and processing of outer membrane and periplasmic proteins in Escherichia coli strains harboring export-specific suppressor mutations. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5852–5860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hanley-Way S., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations that restore export of a protein with a defective signal sequence. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Silhavy T. J. Sequence information required for protein translocation from the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5339–5342. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5339-5342.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes J. D., Bankaitis V. A., Ryan J. P., Bassford P. J., Jr Mutational alterations affecting the export competence of a truncated but fully functional maltose-binding protein signal peptide. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2345–2351. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2345-2351.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes J. D., Bassford P. J., Jr Export of unprocessed precursor maltose-binding protein to the periplasm of Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2352–2359. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2352-2359.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes J. D., Bassford P. J., Jr Novel secA alleles improve export of maltose-binding protein synthesized with a defective signal peptide. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):402–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.402-409.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Gabay J., Débarbouillé M., Schwartz M. A role for mRNA secondary structure in the control of translation initiation. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):616–618. doi: 10.1038/295616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Gabay J., Schwartz M. Evidence for a coupling of synthesis and export of an outer membrane protein in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):15–19. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T., Sako T. Inhibition and resumption of processing of the staphylokinase in some Escherichia coli prlA suppressor mutants. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19077–19082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T., Takahashi M., Sako T. Role of amino-terminal positive charge on signal peptide in staphylokinase export across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7412–7417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Halegoua S. Secretion and membrane localization of proteins in Escherichia coli. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;7(4):339–371. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K. Identification of the secY (prlA) gene product involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):204–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00330964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Preuss D., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Many random sequences functionally replace the secretion signal sequence of yeast invertase. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):312–317. doi: 10.1126/science.3541205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiino D. R., Silhavy T. J. Mutation prlF1 relieves the lethality associated with export of beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):878–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.878-883.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J., Thom J. R. Export of protein: a biochemical view. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:507–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen B. A., MacGregor C. H., Ray P. H., Bassford P. J., Jr In vivo and in vitro synthesis of Escherichia coli maltose-binding protein under regulatory control of the lacUV5 promoter-operator. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):665–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.665-673.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Bassford P. J., Jr Post-translational export of maltose-binding protein in Escherichia coli strains harboring malE signal sequence mutations and either prl+ or prl suppressor alleles. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14832–14837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Duncan M. C., Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Intragenic reversion mutations that improve export of maltose-binding protein in Escherichia coli malE signal sequence mutants. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. G., Rollo E. E., Grodberg J., Oliver D. B. Nucleotide sequence of the secA gene and secA(Ts) mutations preventing protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3404–3414. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3404-3414.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. N., Pardue R. L., Tutt M. C., Briggs R. C., Brinkley B. R., Hnilica L. S. Identification of cytokeratin antigens in Novikoff ascites hepatoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3138–3142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström M., Wold S., Wieslander A., Rilfors L. Signal peptide amino acid sequences in Escherichia coli contain information related to final protein localization. A multivariate data analysis. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):823–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Inouye S., Ito H., Itakura K., Inouye M. Effects of the complete removal of basic amino acid residues from the signal peptide on secretion of lipoprotein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7141–7148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., MacGregor C. H., Collier D. N., Fikes J. D., Ray P. H., Bassford P. J., Jr Factors influencing the in vitro translocation of the Escherichia coli maltose-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3021–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]