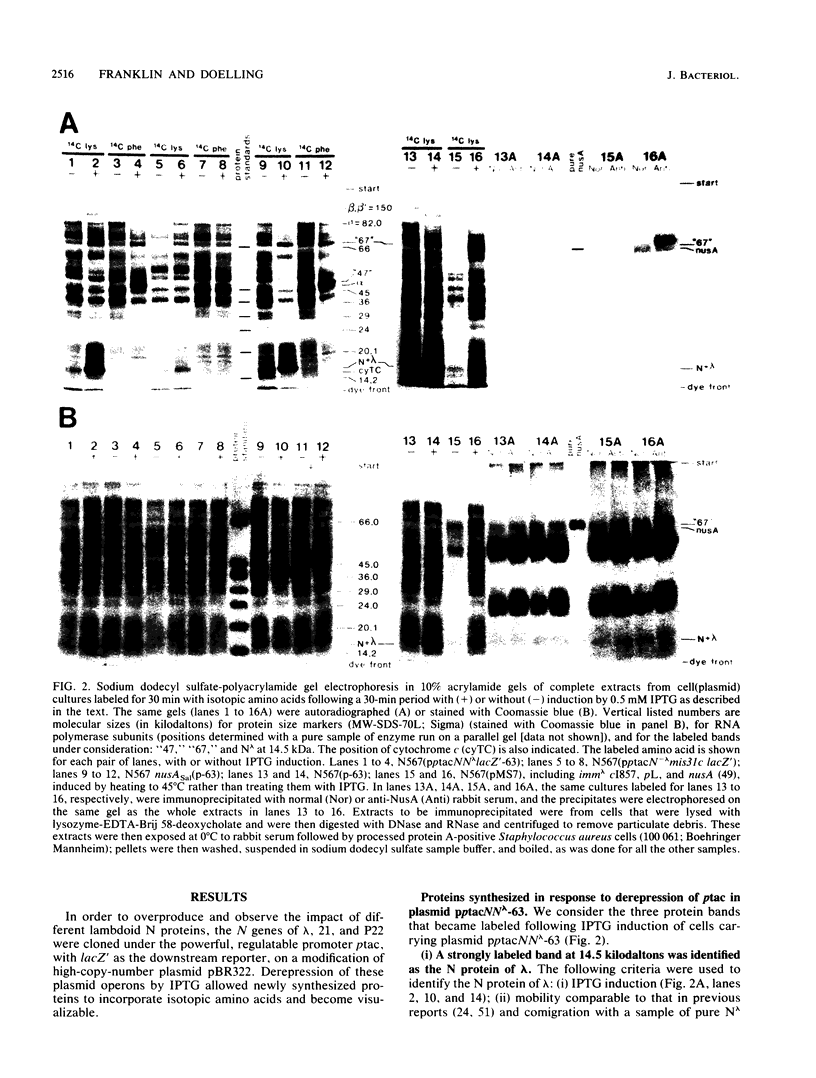
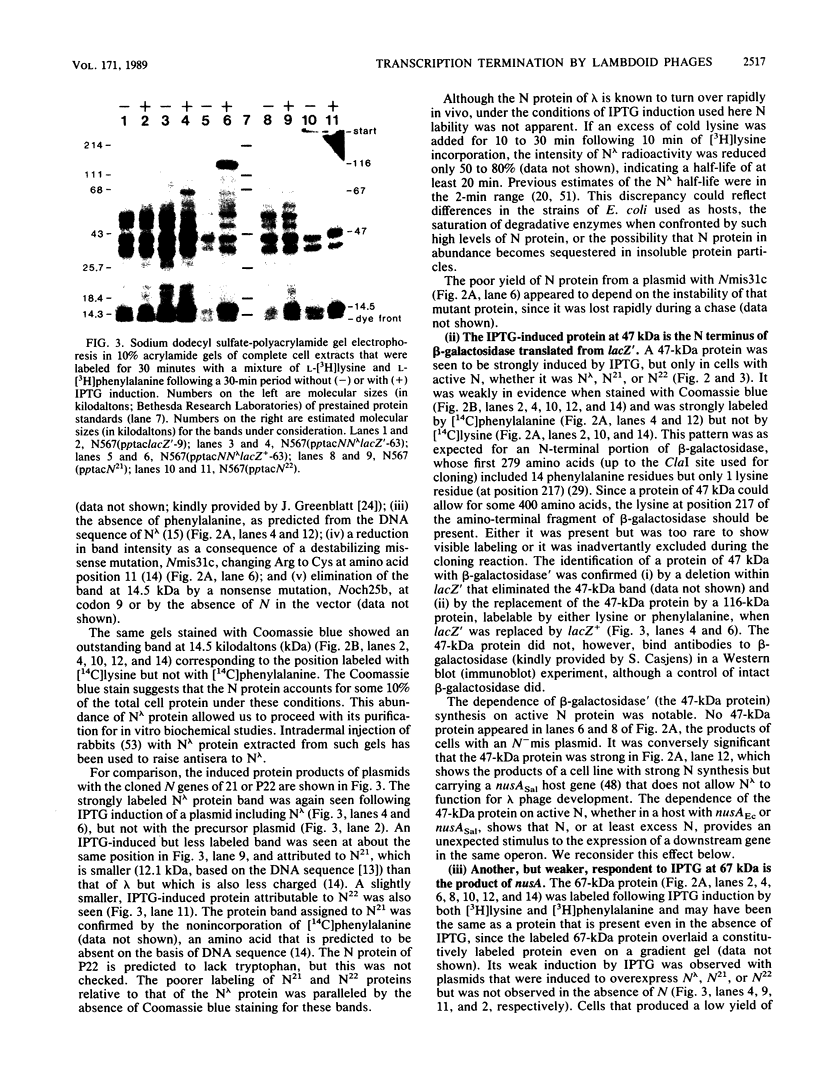
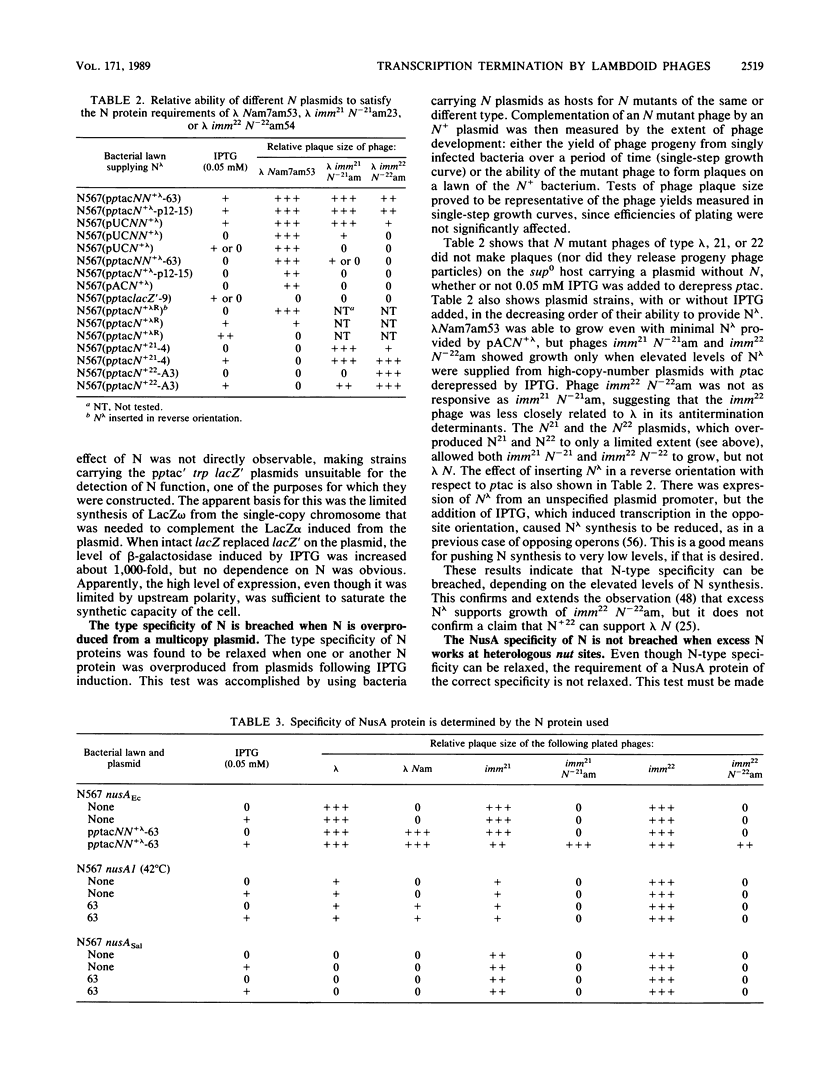
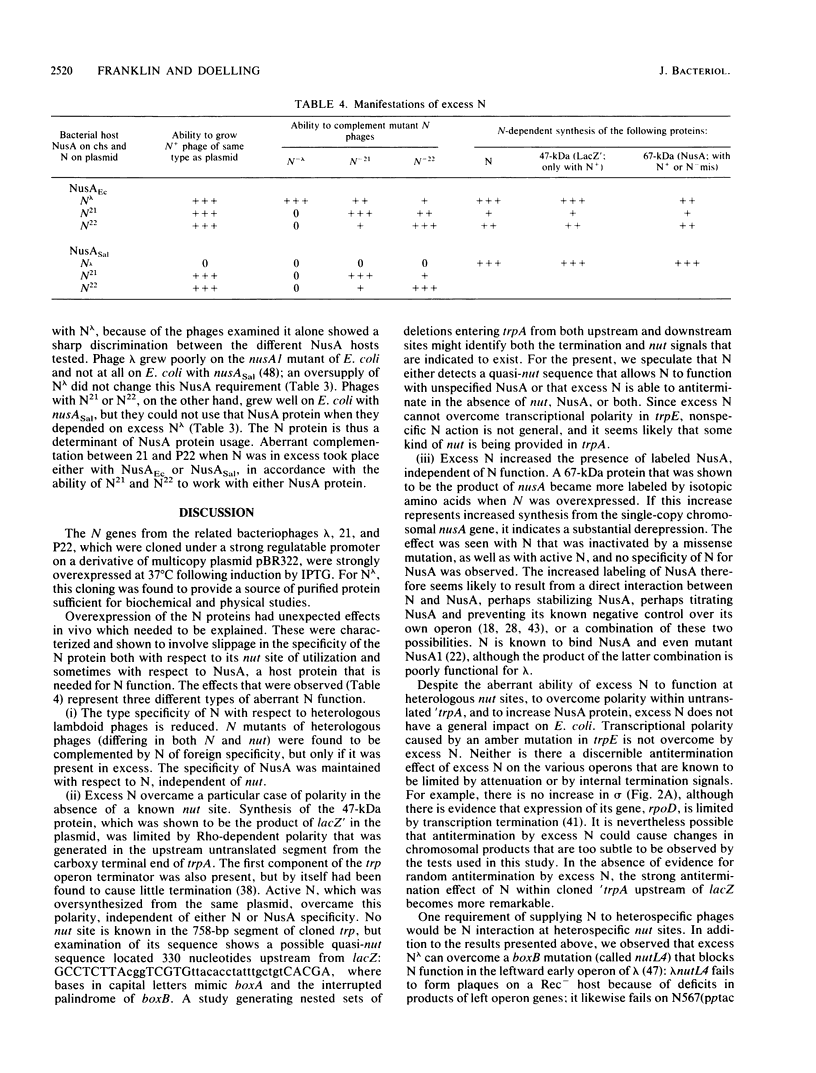
Abstract
The N protein of bacteriophage lambda (N lambda) modifies Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in such a way that it transcribes through termination signals, a process called antitermination. N antitermination normally occurs only if the template contains a specific utilization or nut site upstream of the terminators and only in the presence of host-encoded Nus proteins. The lambda-related phages 21 and P22 produce N analogs, N21 and N22, but these require different nut sites and show a different pattern of functional interaction with one of the Nus factors, NusA, according to whether this protein is of E. coli or Salmonella origin (NusAEc or NusASal). We report the overproduction of N lambda, N21, or N22, each of which was induced by isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside at 37 degrees C from its cloned position downstream from ptac on a high-expression plasmid, each in a host that provided NusAEc or NusASal. Overproduction of each of these N proteins resulted in relaxed specificity for nut, which was shown by the ability to complement N mutants of heterologous phages; NusA specificity was determined by the N type that was present in these complementation tests. We also observed that excess N was able to suppress transcriptional polarity in the particular case of cloned 'trpA, the last gene of the tryptophan operon, although there was no effect on polarity within chromosomal trpE. Such polarity is attributed to the presence of cryptic intragenic terminators that become exposed in the absence of translation. Because there is no known nut site cis to 'trpA, we suggest that the 'trpA segment itself fortuitously contains a nut sequence that is able to function with excess N of any of the types tested and with either NusAEc or NusASal. We also found that excess N of any specificity, or even inactive N with missense mutation, could cause an increase in the level of NusAEc or NusASal, possibly because interaction between N and NusA, but independent of nut, whether functional or not, interferes with the autoregulation of NusA synthesis. These observations highlight the importance of protein concentration for the specificity of interactions both with other proteins and with nucleic acids. They also indicate that the interaction between N and NusA requires nut participation both for specificity and functionality.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M., De Crombrugghe B. Release of polarity in Escherichia coli by gene N of phage lambda: termination and antitermination of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2534–2538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backman K., Boyer H. W. Tetracycline resistance determined by pBR322 is mediated by one polypeptide. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barik S., Ghosh B., Whalen W., Lazinski D., Das A. An antitermination protein engages the elongating transcription apparatus at a promoter-proximal recognition site. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):885–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Jackson D. A., Mertz J. E. Isolation of a lambda dv plasmid carrying the bacterial gal operon. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1063–1069. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1063-1069.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Clark A. J. Deletions generated by the transposon Tn10 in the srl recA region of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Genetics. 1979 Oct;93(2):321–343. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C. "N" transcription antitermination proteins of bacteriophages lambda, phi 21 and P22. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C. A plasmid to visualize and assay termination and antitermination of transcription in Escherichia coli. Plasmid. 1989 Jan;21(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C. Altered reading of genetic signals fused to the N operon of bacteriophage lambda: genetic evidence for modification of polymerase by the protein product of the N gene. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C., Bennett G. N. The N protein of bacteriophage lambda, defined by its DNA sequence, is highly basic. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C. Conservation of genome form but not sequence in the transcription antitermination determinants of bacteriophages lambda, phi 21 and P22. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90325-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. R., Georgopoulos C., Tilly K., Herskowitz I., Banuett F. Interactions of bacteriophage and host macromolecules in the growth of bacteriophage lambda. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):299–325. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.299-325.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goda Y., Greenblatt J. Efficient modification of E. coli RNA polymerase in vitro by the N gene transcription antitermination protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2569–2582. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Gottesman M., Shaw J. E., Pearson M. L. Protein degradation in E. coli: the lon mutation and bacteriophage lambda N and cII protein stability. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90518-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayhack E. J., Yang X. J., Lau L. F., Roberts J. W. Phage lambda gene Q antiterminator recognizes RNA polymerase near the promoter and accelerates it through a pause site. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):259–269. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Li J. Interaction of the sigma factor and the nusA gene protein of E. coli with RNA polymerase in the initiation-termination cycle of transcription. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90332-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Li J. The nusA gene protein of Escherichia coli. Its identification and a demonstration that it interacts with the gene N transcription anti-termination protein of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Malnoe P., Li J. Purification of the gene N transcription anti-termination protein of bacteriophage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1465–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker S., Botstein D. Specificity of genetic elements controlling regulation of early functions in temperate bacteriophages. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):537–566. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz R. J., Li J., Greenblatt J. An elongation control particle containing the N gene transcriptional antitermination protein of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman H. C., Honigman A. Transcription termination and processing sites in the bacteriophage lambda pL operon. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Ihara M., Maekawa T., Nakamura Y., Uchida H., Imamoto F. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned nusA gene and its flanking region of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3333–3342. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalnins A., Otto K., Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):593–597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Yanofsky C. Polarity suppressors increase expression of the wild-type tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 15;103(2):395–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley K. E., Villarejo M. R., Fowler A. V., Zamenhof P. J., Zabin I. Molecular basis of beta-galactosidase alpha-complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1254–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk K. C., Szybalski W. Characterization of the cloned terminators tR1, tL3 and tI and the nut R antitermination site of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. H., Reznikoff W. S., Beckwith J. R. Genetic fusions defining trp and lac operon regulatory elements. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 15;93(3):331–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott J. E., Galloway J. L., Platt T. Maturation of Escherichia coli tryptophan operon mRNA: evidence for 3' exonucleolytic processing after rho-dependent termination. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1887–1891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Masukata H., Tomizawa J. Transcriptional regulation of early functions of bacteriophage phi 80. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock S., Lupski J. R., Godson G. N., Weissbach H. In vitro stimulation of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase sigma subunit synthesis by NusA protein. Gene. 1985;33(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W. Revised sequence of the tetracycline-resistance gene of pBR322. Gene. 1983 May-Jun;22(2-3):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumbridge J. A., Dondon J., Nakamura Y., Grunberg-Manago M. Effect of NusA protein on expression of the nusA,infB operon in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3371–3388. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose R. E. The nucleotide sequence of pACYC184. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):355–355. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salstrom J. S., Szybalski W. Coliphage lambdanutL-: a unique class of mutants defective in the site of gene N product utilization for antitermination of leftward transcription. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):195–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson L. L., Hendrix R. W., Huang W. M., Casjens S. R. Translation initiation controls the relative rates of expression of the bacteriophage lambda late genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5439–5443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer A. T., Carver D. L., Bigelow B., Baron L. S., Friedman D. I. lambda N antitermination system: functional analysis of phage interactions with the host NusA protein. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):679–690. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Chamberlin M. J. Amplification and isolation of Escherichia coli nusA protein and studies of its effects on in vitro RNA chain elongation. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):197–203. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa T., Imamoto F. Diversity of regulation of genetic transcription. II. Specific relaxation of polarity in read-through transcription of the translocated trp operon in bacteriophage lambda trp. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):741–754. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Jones B. B., Pearson M. L. Identification of the N gene protein of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2225–2229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L. Production of antisera with small doses of immunogen: multiple intradermal injections. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. F., DeLong A., Gottesman M. E. Escherichia coli nusB mutations that suppress nusA1 exhibit lambda N specificity. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):73–85. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. F., Murray N. E. Convergent transcription in bacteriophage lambda: interference with gene expression. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 15;133(2):249–266. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90533-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Platt T., Crawford I. P., Nichols B. P., Christie G. E., Horowitz H., VanCleemput M., Wu A. M. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6647–6668. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X. M., Munson L. M., Reznikoff W. S. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of trp-lac fusion deletions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 25;172(3):355–362. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Comstock L. J., Vasser M. The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Mudryj M., DiLauro R., Gottesman M. Specificity of the bacteriophage lambda N gene product (pN): nut sequences are necessary and sufficient for antitermination by pN. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]