Abstract
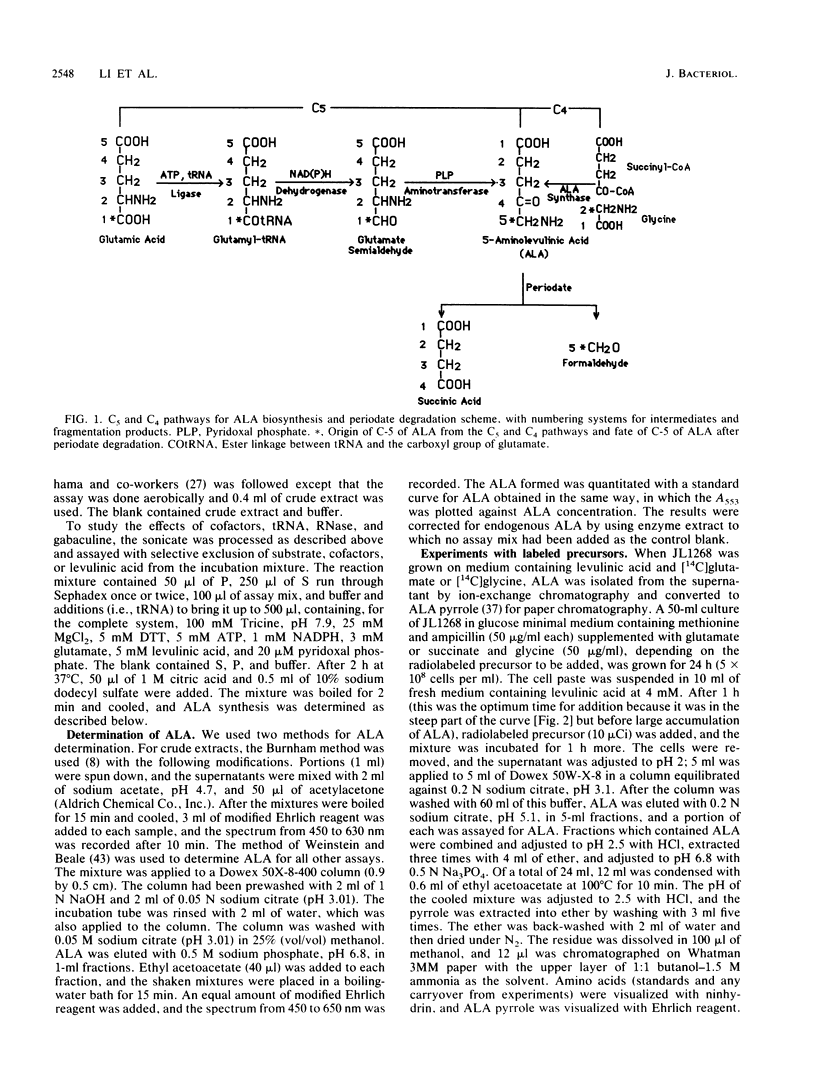
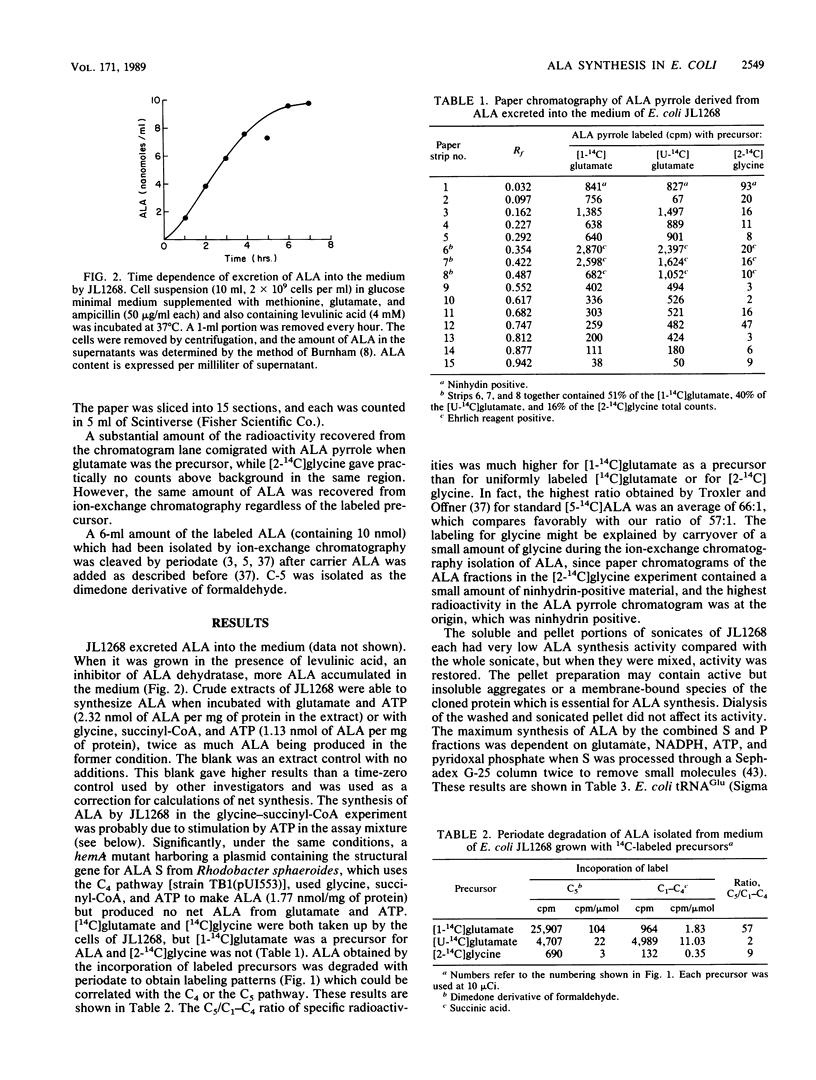
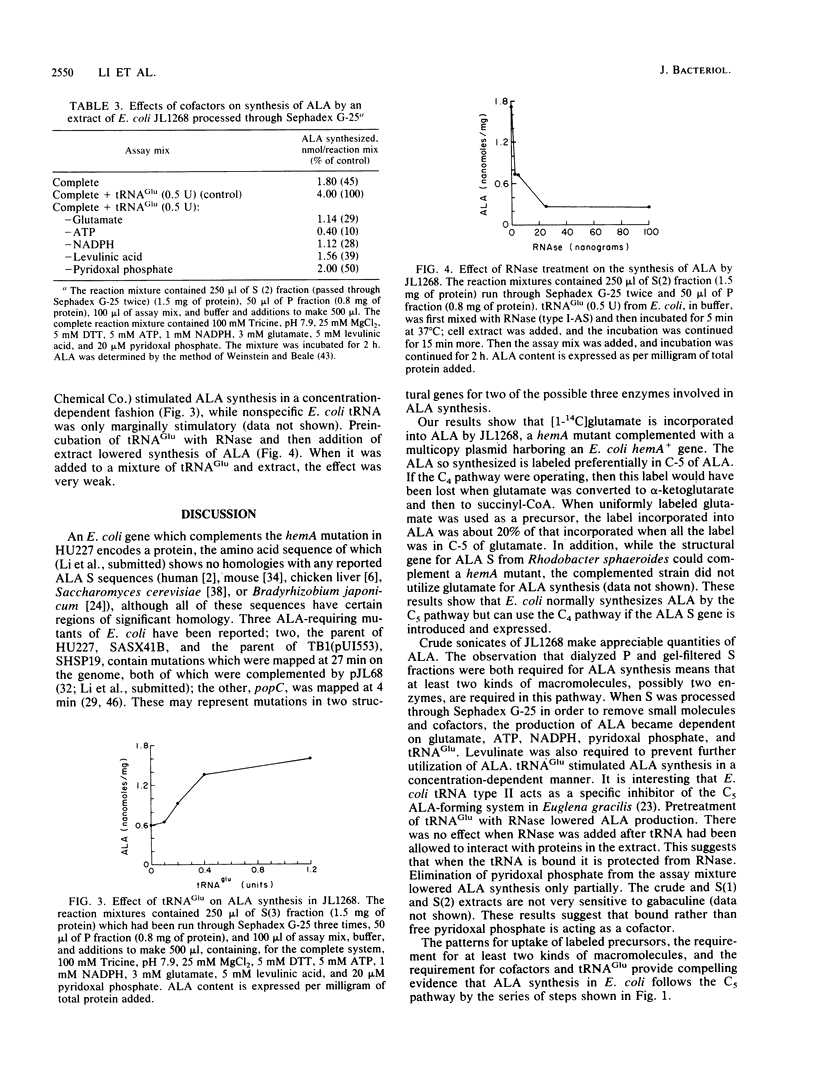
A hemA mutant of Escherichia coli containing a multicopy plasmid which complemented the mutation excreted 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) into the medium. [1-14C]glutamate was substantially incorporated into ALA by this strain, whereas [2-14C]glycine was not. Periodate degradation of labeled ALA showed that C-5 of ALA was derived from C-1 of glutamate. The synthesis of ALA by two sonicate fractions which had been processed by gel filtration and dialysis, respectively, was dependent on glutamate, ATP, NADPH, tRNA(Glu), and pyridoxal phosphate. tRNA(Glu) stimulated ALA synthesis in a concentration-dependent manner. Pretreatment with RNase reduced this stimulation. The amino acid sequence of the cloned insert, derived from the nucleotide sequence (J.-M. Li, C. S. Russell, and S. D. Cosloy, J. Cell Biol. 107:617a, 1988), showed no homology with any ALA synthase sequenced to date. These results suggest that E. coli synthesizes ALA by the C5 pathway from the intact five-carbon chain of glutamate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avissar Y. J. Biosynthesis of 5-aminolevulinate from glutamate in Anabaena variabilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;613(1):220–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bawden M. J., Borthwick I. A., Healy H. M., Morris C. P., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Sequence of human 5-aminolevulinate synthase cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8563–8563. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale S. I., Castelfranco P. A. The Biosynthesis of delta-Aminolevulinic Acid in Higher Plants: I. Accumulation of delta-Aminolevulinic Acid in Greening Plant Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1974 Feb;53(2):291–296. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale S. I., Gough S. P., Granick S. Biosynthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid from the intact carbon skeleton of glutamic acid in greening barley. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2719–2723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick I. A., Srivastava G., Day A. R., Pirola B. A., Snoswell M. A., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of hepatic 5-aminolaevulinate synthase precursor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Aug 1;150(3):481–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley S. S., Smithee G. A. Characterization and measurement of delta-aminolaevulinate synthetase in bone marrow cell mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 24;159(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford S. H., Friedmann H. C. Formation of delta-aminolevulinic acid from glutamic acid by a partially purified enzymes system from wheat leaves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 15;569(2):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON K. D., NEUBERGER A., SCOTT J. J. The purification and properties of delta-aminolaevulic acid dehydrase. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):618–629. doi: 10.1042/bj0610618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel E., Ne'eman E. Alternative Routes for the Synthesis of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid in Maize Leaves : II. Formation from Glutamate. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):1062–1067. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. D., Wang W. Y. Chlorophyll biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas starts with the formation of glutamyl-tRNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13451–13455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIKUCHI G., KUMAR A., TALMAGE P., SHEMIN D. The enzymatic synthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1214–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein O., Senger H. Two Biosynthetic Pathways to delta-Aminolevulinic Acid in a Pigment Mutant of the Green Alga, Scenedesmus obliquus. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):10–13. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong S. A., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Heme biosynthesis in Rhizobium. Identification of a cloned gene coding for delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase from Rhizobium meliloti. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8724–8730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. The occurrence and determination of delta-amino-levulinic acid and porphobilinogen in urine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marver H. S., Collins A., Tschudy D. P., Rechcigl M., Jr Delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase. II. Induction in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4323–4329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mau Y. H., Wang W. Y., Tamura R. N., Chang T. E. Identification of an intermediate of delta-aminolevulinate biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas by high-performance liquid chromatography. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 May 15;255(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer S. M., Beale S. I., Weinstein J. D. Enzymatic conversion of glutamate to delta-aminolevulinic acid in soluble extracts of Euglena gracilis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12541–12549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClung C. R., Somerville J. E., Guerinot M. L., Chelm B. K. Structure of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum gene hemA encoding 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase. Gene. 1987;54(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh-hama T., Seto H., Miyachi S. 13C NMR evidence for bacteriochlorophyll c formation by the C5 pathway in green sulfur bacterium, Prosthecochloris. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;159(1):189–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh-hama T., Seto H., Miyachi S. 13C-NMR evidence of bacteriochlorophyll a formation by the C5 pathway in Chromatium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Apr;246(1):192–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90463-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh-hama T., Stolowich N. J., Scott A. I. 5-Aminolevulinic acid formation from glutamate via the C5 pathway in Clostridium thermoaceticum. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80591-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porra R. J., Irving E. A., Tennick A. M. The detection of delta-aminolaevulinic acid synthetase in anaerobically grown Torulopsis utilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Apr;149(2):563–565. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. A., Cox R., McConville M., Charles H. P. Mutations affecting porphyrin biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Enzyme. 1973;16(1):65–73. doi: 10.1159/000459363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieble S., Beale S. I. Transformation of glutamate to delta-aminolevulinic acid by soluble extracts of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and other oxygenic prokaryotes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8864–8871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneegurt M. A., Beale S. I. Characterization of the RNA Required for Biosynthesis of delta-Aminolevulinic Acid from Glutamate : Purification by Anticodon-Based Affinity Chromatography and Determination That the UUC Glutamate Anticodon Is a General Requirement for Function in ALA Biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1988 Feb;86(2):497–504. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenhaut D. S., Curtis P. J. Nucleotide sequence of mouse 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase cDNA and expression of its gene in hepatic and erythroid tissues. Gene. 1986;48(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Săsărman A., Surdeanu M., Horodniceanu T. Locus determining the synthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1882–1884. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1882-1884.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait G. H. 5-Aminolaevulinate synthetase of Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):32P–32P. doi: 10.1042/bj1280032pa. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait G. H. Aminolaevulinate synthetase of Micrococcus denitrificans. Purification and properties of the enzyme, and the effect of growth conditions on the enzyme activity in cells. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):389–403. doi: 10.1042/bj1310389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler R. F., Offner G. D. delta-Aminolevulinic acid synthesis in a Cyanidium caldarium mutant unable to make chlorophyll a and phycobiliproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jun;195(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban-Grimal D., Volland C., Garnier T., Dehoux P., Labbe-Bois R. The nucleotide sequence of the HEM1 gene and evidence for a precursor form of the mitochondrial 5-aminolevulinate synthase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 2;156(3):511–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. Y., Huang D. D., Stachon D., Gough S. P., Kannangara C. G. Purification, Characterization, and Fractionation of the delta-Aminolevulinic Acid Synthesizing Enzymes from Light-Grown Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Cells. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):569–575. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J. D., Beale S. I. Enzymatic conversion of glutamate to delta-aminolevulinate in soluble extracts of the unicellular green alga, Chlorella vulgaris. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Mar;237(2):454–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90299-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J. D., Beale S. I. Separate physiological roles and subcellular compartments for two tetrapyrrole biosynthetic pathways in Euglena gracilis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6799–6807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J. D., Mayer S. M., Beale S. I. Formation of delta-Aminolevulinic Acid from Glutamic Acid in Algal Extracts : Separation into an RNA and Three Required Enzyme Components by Serial Affinity Chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):244–250. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright M. S., Cardin R. D., Biel A. J. Isolation and characterization of an aminolevulinate-requiring Rhodobacter capsulatus mutant. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):961–966. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.961-966.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulff D. L. Delta-aminolevulinic acid-requiring mutant from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1473–1474. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1473-1474.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



