Abstract
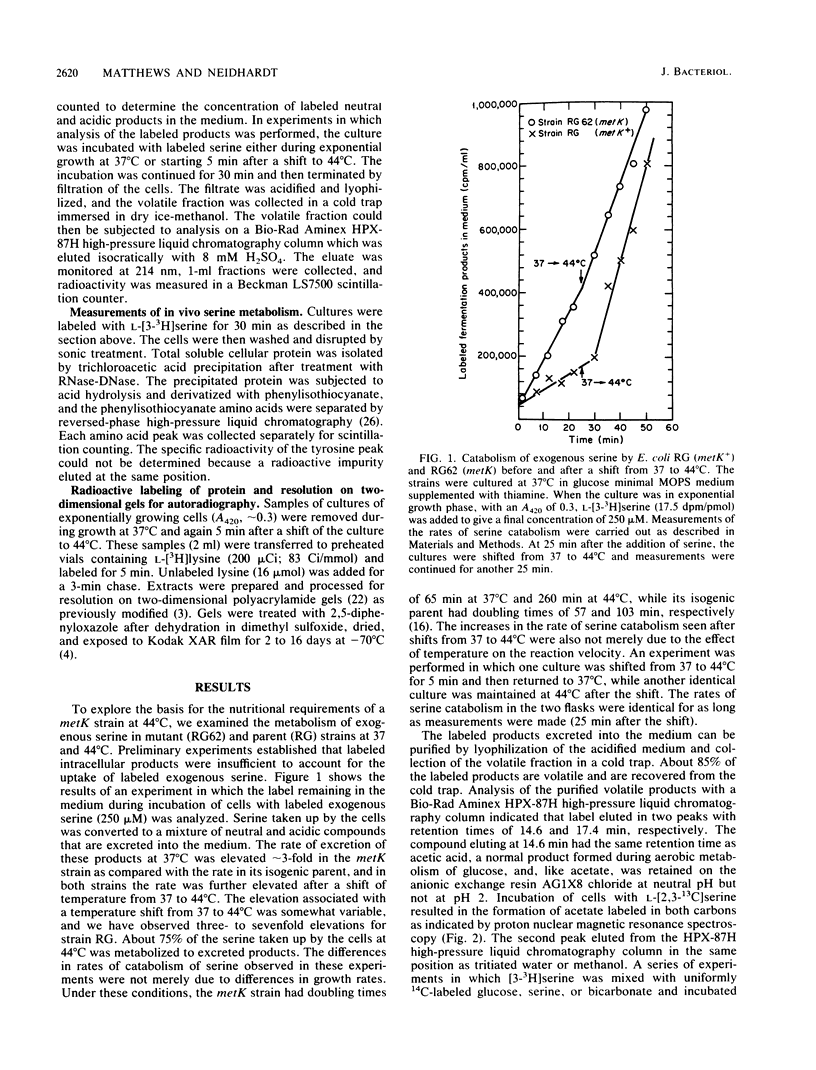
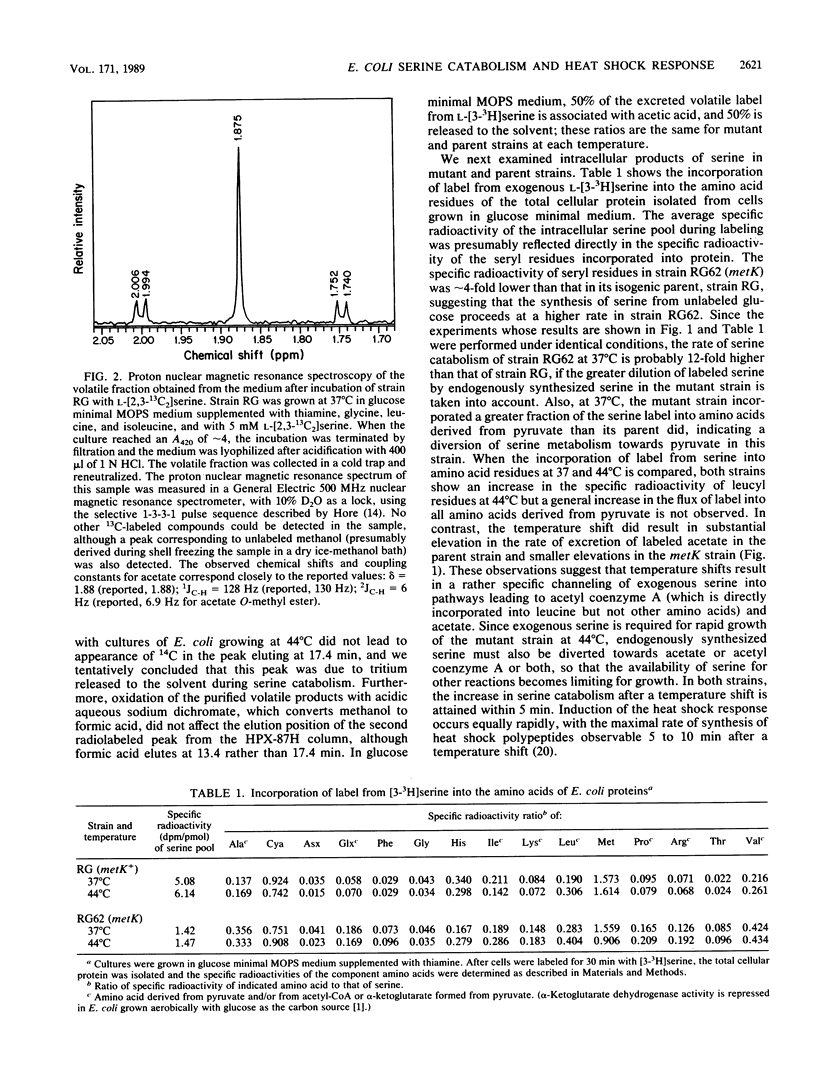
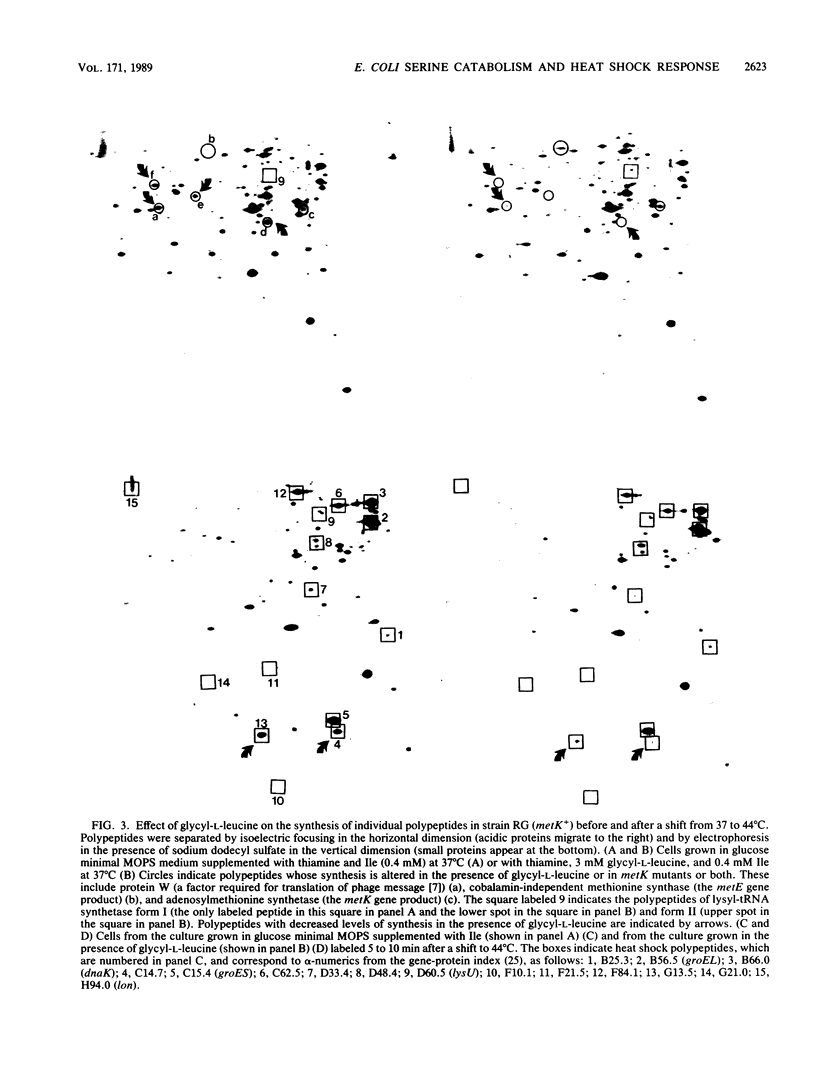
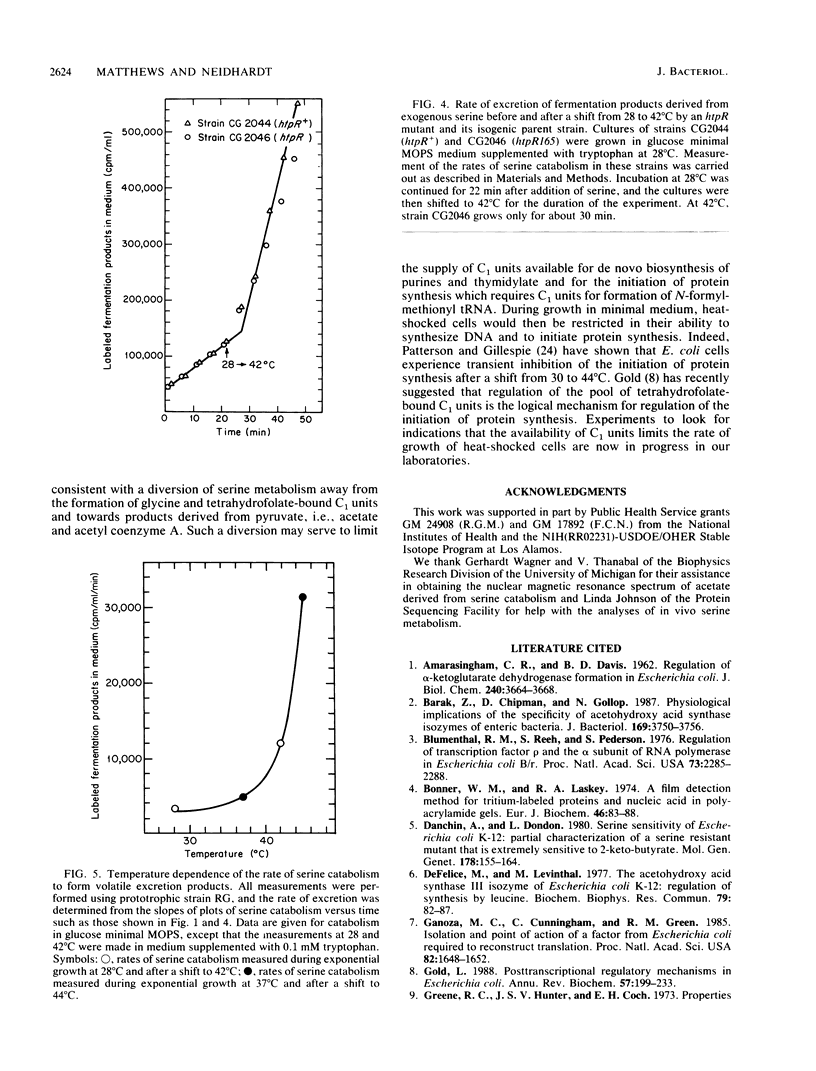
The biochemical events associated with the heat shock response are not well understood in any organism, nor have the signals that initiate the induction of heat shock protein synthesis been identified. In this work, we demonstrate that the rate of serine catabolism of Escherichia coli cells grown in glucose minimal medium supplemented with serine is elevated three- to sevenfold when the growth temperature is shifted from 37 to 44 degrees C. Elevations in growth temperature and mutations or treatments that lead to elevated basal rates of serine catabolism at 37 degrees C result in the excretion into the culture medium of acetate derived from exogenous serine. Increases in the basal level of serine catabolism at 37 degrees C do not per se induce a heat shock response but are associated with abnormalities in the pattern of induction of heat shock polypeptides following a temperature shift. We postulate that the events responsible for or resulting from the elevation in serine catabolism associated with a shift-up in temperature modulate the induction of 3 of the 17 heat shock polypeptides identified in E. coli. These observations suggest that heat shock diverts serine away from the production of glycine and C1 units, which are required for initiation of protein synthesis and for nucleotide biosynthesis, and towards acetyl coenzyme A and acetate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amarasingham C. R., Davis B. D. Regulation of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase formation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3664–3668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak Z., Chipman D. M., Gollop N. Physiological implications of the specificity of acetohydroxy acid synthase isozymes of enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3750–3756. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3750-3756.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal R. M., Reeh S., Pedersen S. Regulation of transcription factor rho and the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli B/r. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2285–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danchin A., Dondon L. Serine sensitivity of Escherichia coli K 12: partial characterization of a serine resistnat mutant that is extremely sensitive to 2-ketobutyrate. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):155–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00267224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Felice M., Levinthal M. The acetohydroxy acid synthase III isoenzyme of Escherichia coli K-12: regulation of synthesis by leucine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Nov 7;79(1):82–87. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Cunningham C., Green R. M. Isolation and point of action of a factor from Escherichia coli required to reconstruct translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Taylor W. E., Burton Z. F., Burgess R. R., Gross C. A. Stringent response in Escherichia coli induces expression of heat shock proteins. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90110-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshfield I. N., Bloch P. L., Van Bogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. Multiple forms of lysyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):345–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.345-351.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg S., Newman E. B. Studies on L-serine deaminase in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):53–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.53-58.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. G., Neidhardt F. C. Abnormal induction of heat shock proteins in an Escherichia coli mutant deficient in adenosylmethionine synthetase activity. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1582–1588. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1582-1588.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Lau E. T. Molecular cloning and expression of a gene that controls the high-temperature regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):597–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.597-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Ahmad D., Walker C. L-Serine deaminase activity is induced by exposure of Escherichia coli K-12 to DNA-damaging agents. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):702–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.702-705.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARDEE A. B., PRESTIDGE L. S. Induced formation of serine and threonine deaminases by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1955 Dec;70(6):667–674. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.6.667-674.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Gillespie D. Effect of elevated temperatures on protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1177–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1177-1183.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., Danchin A. A rapid test for the rel A mutation in E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 5;69(3):751–758. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90939-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Acton M. A., Neidhardt F. C. Induction of the heat shock regulon does not produce thermotolerance in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Aug;1(6):525–531. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.6.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Kodaira R., Neidhardt F. C. Physiological regulation of a decontrolled lac operon. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):212–222. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.212-222.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



