Abstract
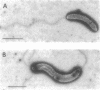
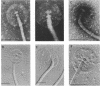
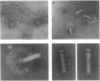
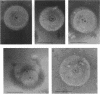
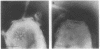
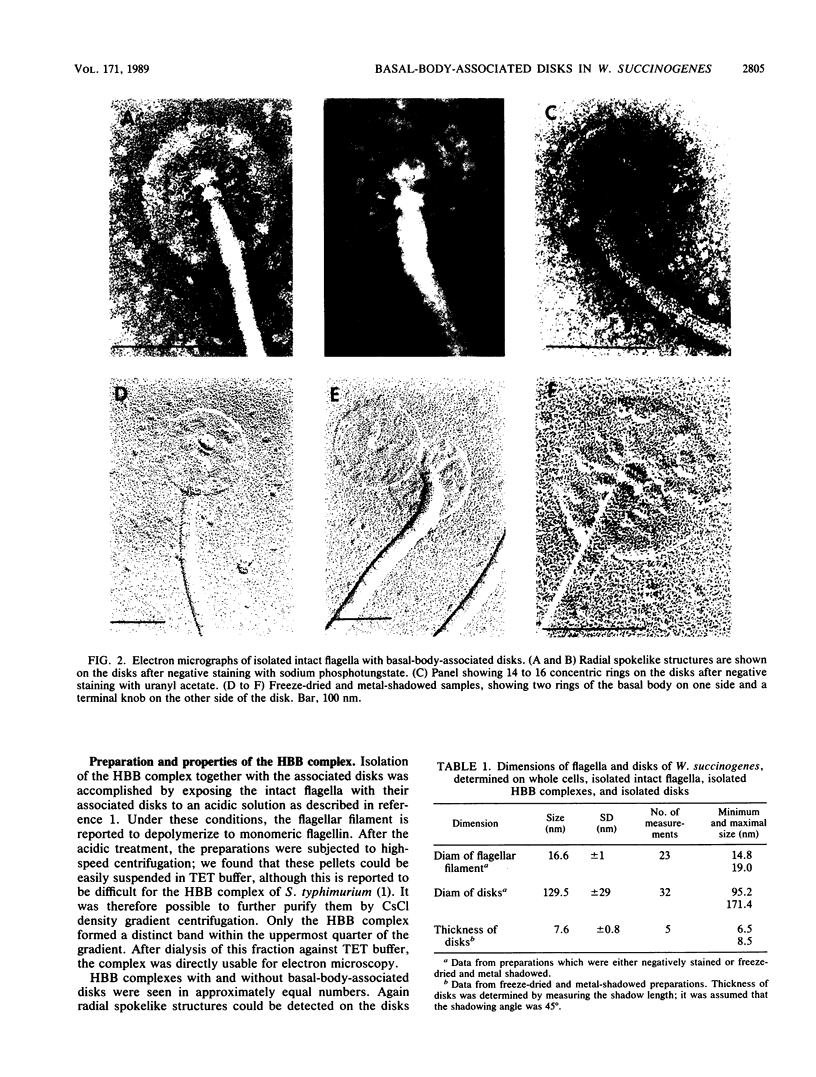
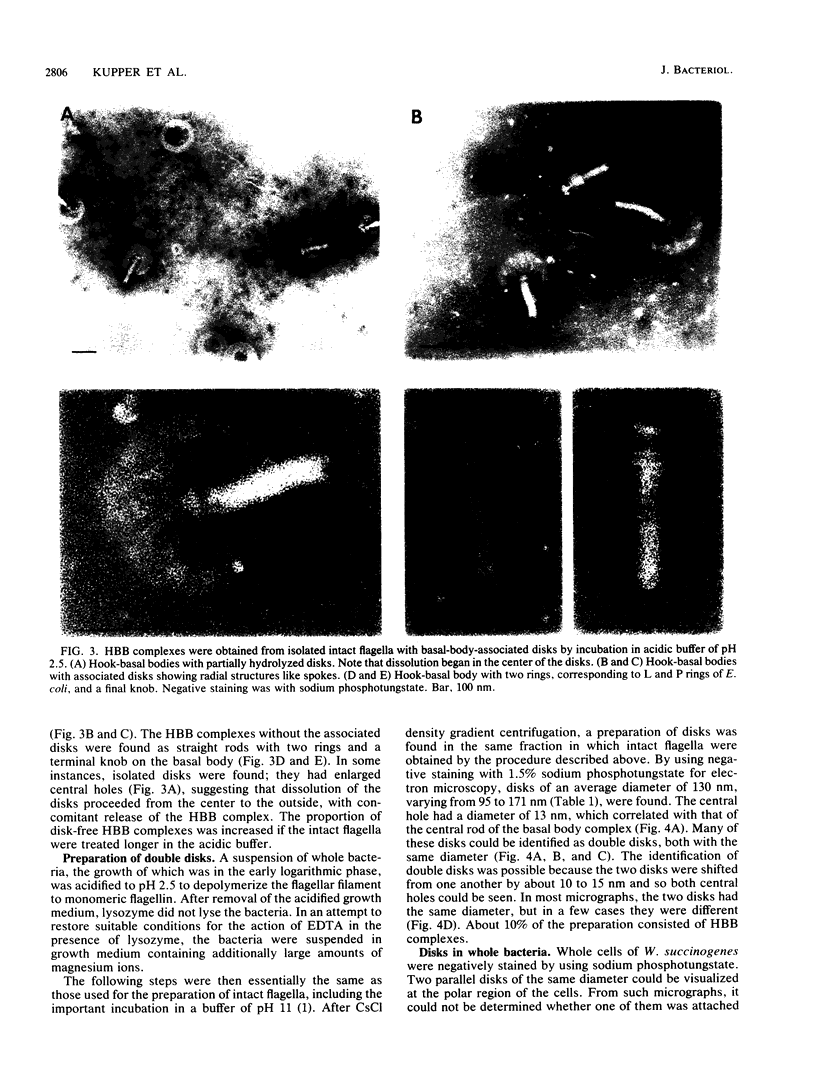
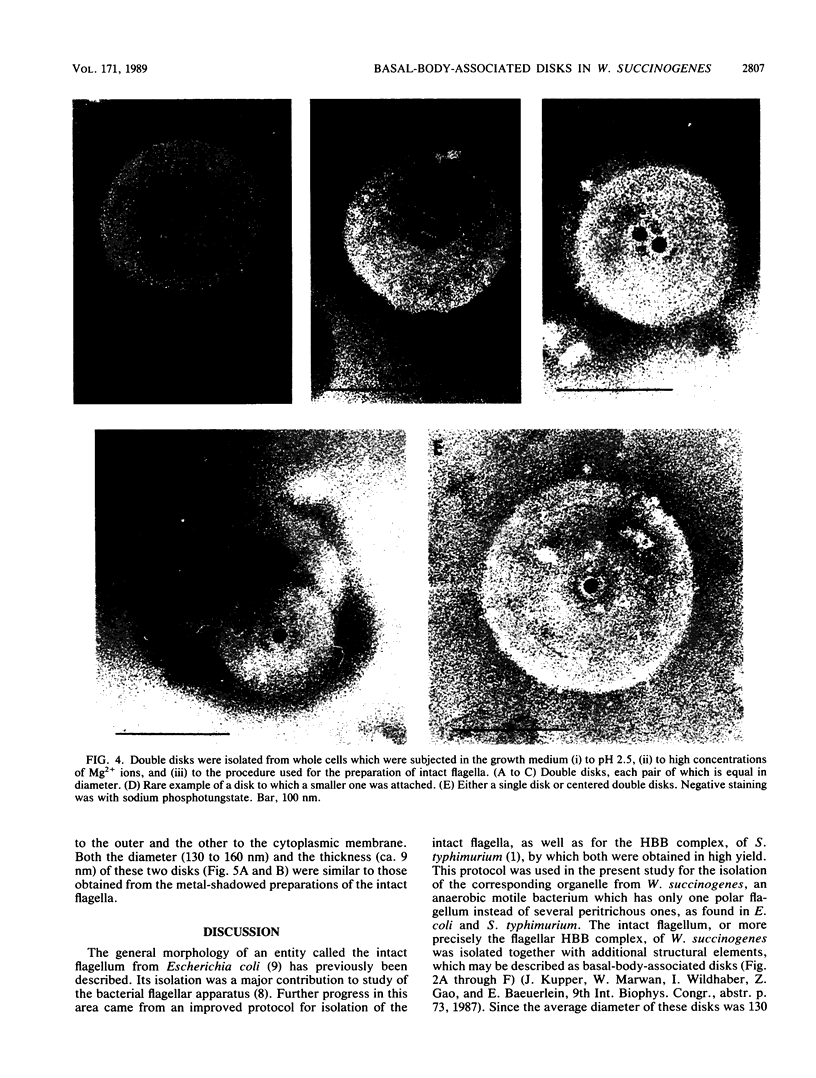
The intact flagella of Wolinella succinogenes, a gram-negative, anaerobic bacterium with a single polar flagellum, were obtained by an improved procedure, introduced recently by Aizawa et al. (S.-J. Aizawa, G. E. Dean, C. J. Jones, R. M. Macnab, and S. Yamaguchi, J. Bacteriol. 161:836-849, 1985) for the flagellum of Salmonella typhimurium. Disks with a diameter of 130 +/- 30 nm, which were attached to the basal body of the isolated intact flagella, could be identified by electron microscopy as additional structural elements of the bacterial flagellar apparatus. In freeze-dried and metal-shadowed samples, two rings of the basal body were detected on one side and a terminal knob was located on the other side of the disks. Suspension of the flagellar apparatus in acidic solution dissociated the flagellar filaments, yielding hook-basal body complexes with and without the associated disks. If whole cells were subjected to low pH, double disks of the same diameter and with a central hole of about 13 nm could be isolated. Similar parallel disks could be seen also in negatively stained whole cells. When uranyl acetate was used for negative staining of the intact flagella, concentric rings were detected on the disks, similar to the concentric membrane rings found by Coulton and Murray (J. W. Coulton and R. G. E. Murray, J. Bacteriol. 136:1037-1049, 1978) on platelike arrays of proteins in outer membrane preparations of Aquaspirillum serpens. Because the disks of W. succinogenes can be isolated together with the flagellar hook-basal body complex, they appear to be basal-body-rather than secondary membrane-associated structures. It is possible that these disks are the bearing or stator of this rotary device.
Full text
PDF

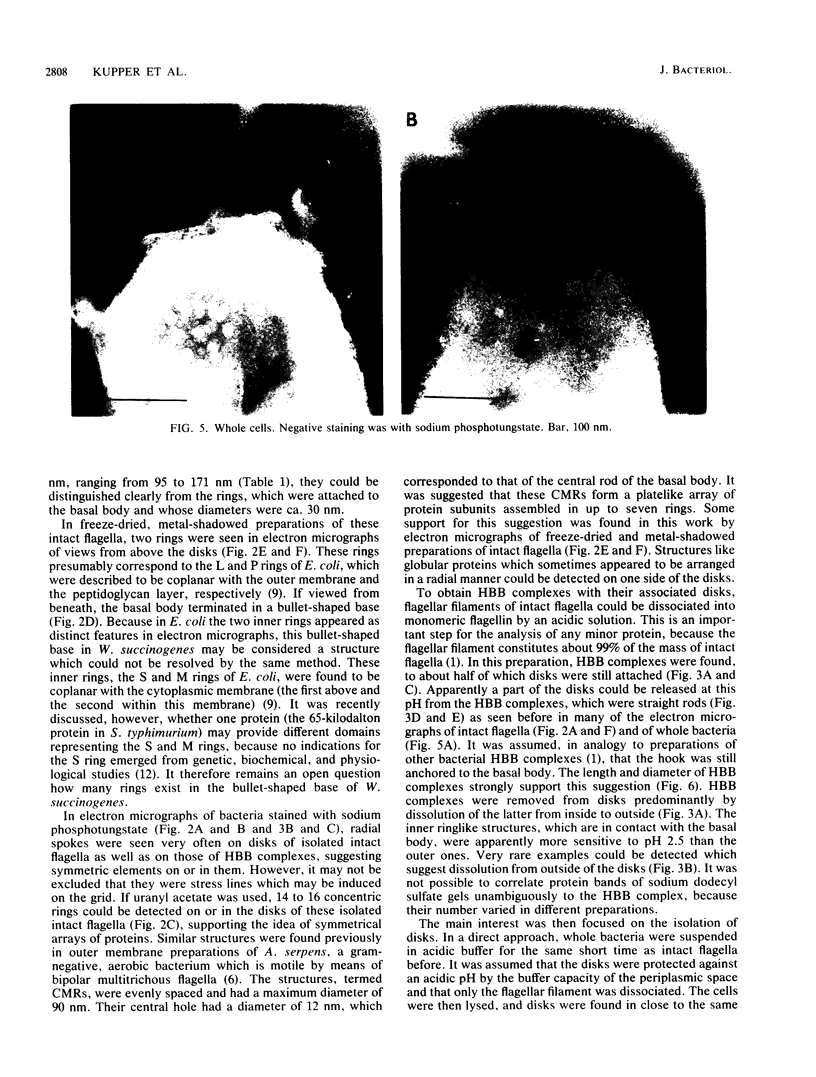
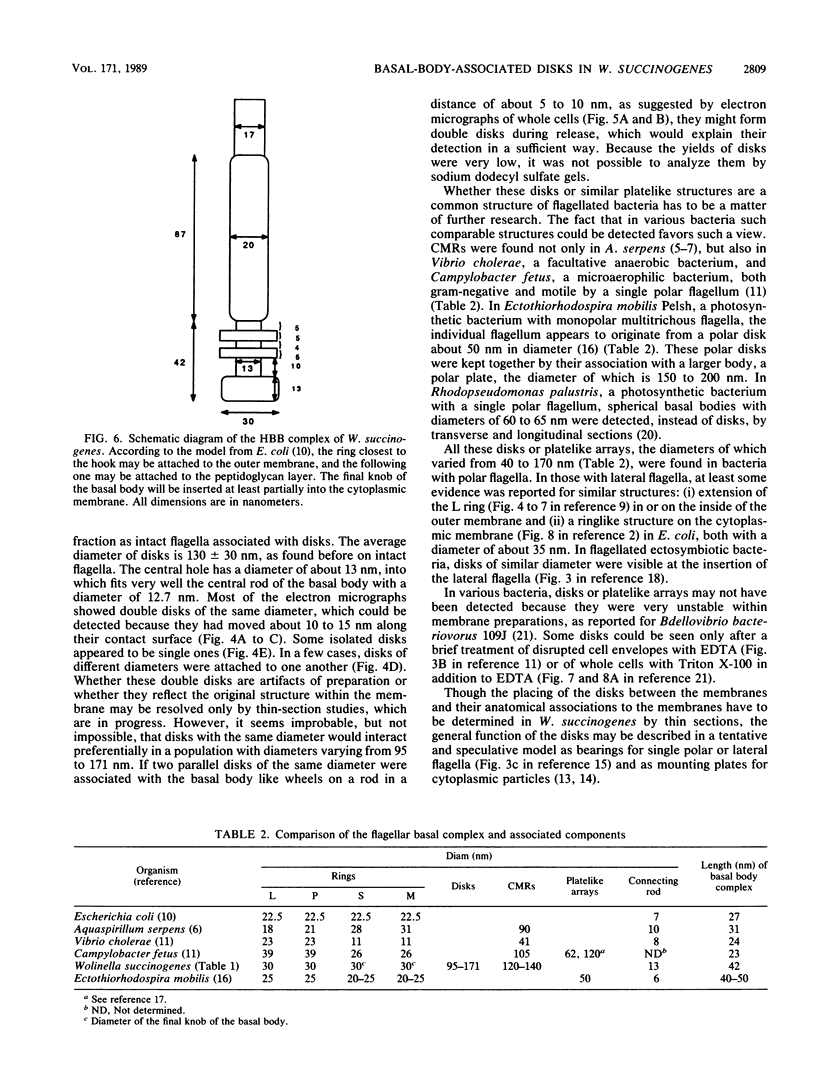

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa S. I., Dean G. E., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M., Yamaguchi S. Purification and characterization of the flagellar hook-basal body complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):836–849. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.836-849.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronder M., Mell H., Stupperich E., Kröger A. Biosynthetic Pathways of Vibrio succinogenes growing with fumarate as terminal electron acceptor and sole carbon source. Arch Microbiol. 1982 May;131(3):216–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00405882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulton J. W., Murray R. G. Cell envelope associations of Aquaspirillum serpens flagella. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1037–1049. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1037-1049.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulton J. W., Murray R. G. Membrane-associated components of the bacterial flagellar apparatus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):290–310. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Attachment of flagellar basal bodies to the cell envelope: specific attachment to the outer, lipopolysaccharide membrane and the cyoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):396–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.396-407.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Fine structure and isolation of the hook-basal body complex of flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):384–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.384-395.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Purification of intact flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.376-383.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris F. G., Beveridge T. J., Marceau-Day M. L., Larson A. D. Structure and cell envelope associations of flagellar basal complexes of Vibrio cholerae and Campylobacter fetus. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Mar;30(3):322–333. doi: 10.1139/m84-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Aizawa S., Dean G. E., Macnab R. M. Identification of the M-ring protein of the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7483–7487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Dapice M., Reese T. S. Effects of mot gene expression on the structure of the flagellar motor. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):575–584. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Meister M., Berg H. C. Constraints on flagellar rotation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):645–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Watson S. W., Waterbury J. B., Trüper H. G. Fine structure of Ectothiorhodospira mobilis Pelsh. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2374–2392. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2374-2392.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. E., Keeler R. F., Bryner J. H. Anatomical features of Vibrio fetus: Electron microscopic survey. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jun;43(3):427–438. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-3-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm S. L. Flagellated ectosymbiotic bacteria propel a eucaryotic cell. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):697–709. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Rittenberg S. C. Waveform analysis and structure of flagella and basal complexes from Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1038–1046. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1038-1046.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN M. J., WOLIN E. A., JACOBS N. J. Cytochrome-producing anaerobic Vibrio succinogenes, sp. n. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:911–917. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.911-917.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]