Abstract
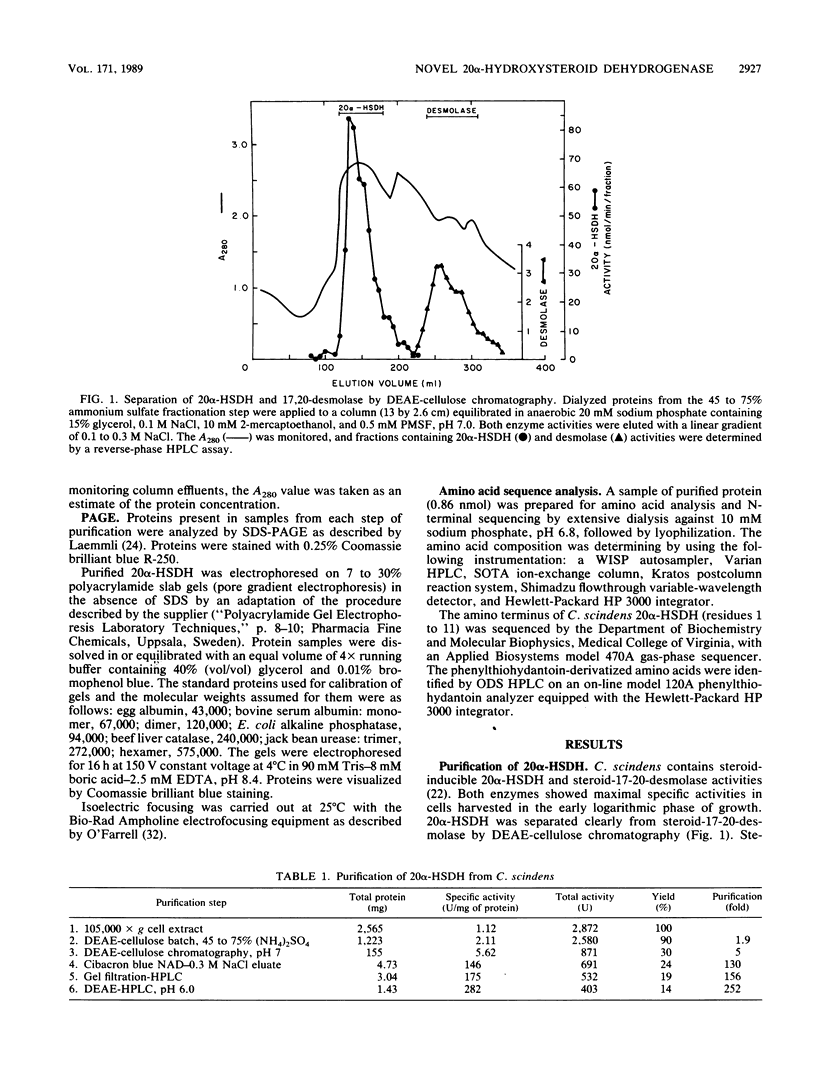
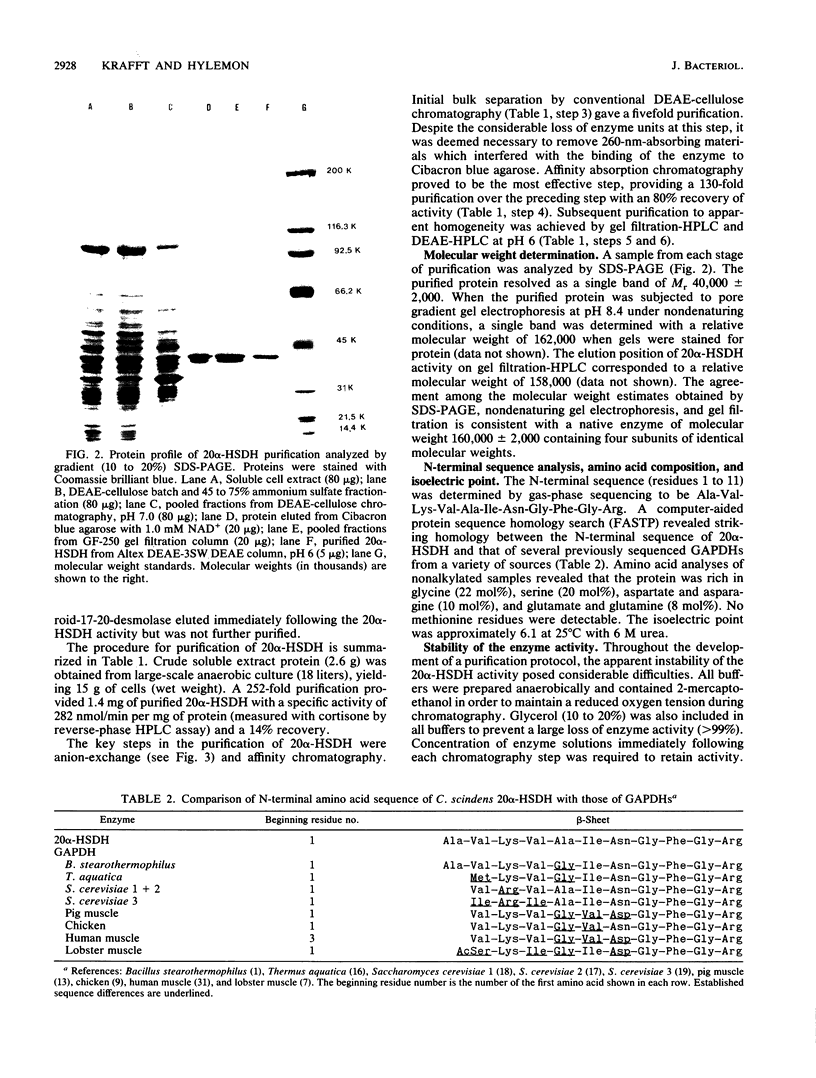
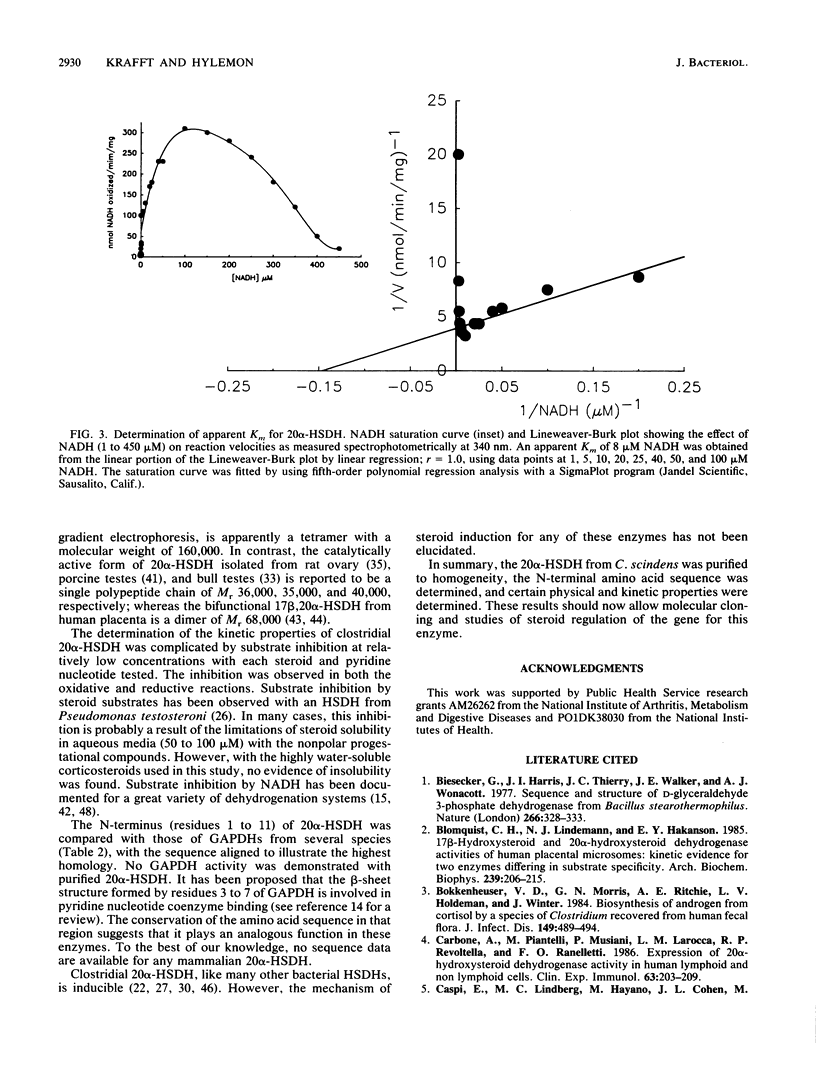
We have purified a steroid-inducible 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Clostridium scindens to apparent homogeneity. The final enzyme preparation was purified 252-fold, with a recovery of 14%. Denaturing and nondenaturing polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis showed that the native enzyme (Mr, 162,000) was a tetramer composed of subunits with a molecular weight of 40,000. The isoelectric point was approximately pH 6.1. The purified enzyme was highly specific for adrenocorticosteroid substrates possessing 17 alpha, 21-dihydroxy groups. The purified enzyme had high specific activity for the reduction of cortisone (Vmax, 280 nmol/min per mg of protein; Km, 22 microM) but was less reactive with cortisol (Vmax, 120 nmol/min per mg of protein; Km, 32 microM) at pH 6.3. The apparent Km for NADH was 8.1 microM with cortisone (50 microM) as the cosubstrate. Substrate inhibition was observed with concentrations of NADH greater than 0.1 mM. The purified enzyme also catalyzed the oxidation of 20 alpha-dihydrocortisol (Vmax, 200 nmol/min per mg of protein; Km, 41 microM) at pH 7.9. The apparent Km for NAD+ was 526 microM. The initial reaction velocities with NADPH were less than 50% of those with NADH. The amino-terminal sequence was determined to be Ala-Val-Lys-Val-Ala-Ile-Asn-Gly-Phe-Gly-Arg. These results indicate that this enzyme is a novel form of 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biesecker G., Harris J. I., Thierry J. C., Walker J. E., Wonacott A. J. Sequence and structure of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Nature. 1977 Mar 24;266(5600):328–333. doi: 10.1038/266328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist C. H., Lindemann N. J., Hakanson E. Y. 17 beta-hydroxysteroid and 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities of human placental microsomes: kinetic evidence for two enzymes differing in substrate specificity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 May 15;239(1):206–215. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90828-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokkenheuser V. D., Morris G. N., Ritchie A. E., Holdeman L. V., Winter J. Biosynthesis of androgen from cortisol by a species of Clostridium recovered from human fecal flora. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):489–494. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPI E., LINDBERG M. C., HAYANO M., COHEN J. L., MATSUBA M., ROSENKRANTZ H., DORFMAN R. I. The C-20alpha reduction of steroids by hog liver preparations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Apr;61(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone A., Piantelli M., Musiani P., Larocca L. M., Revoltella R. P., Ranelletti F. O. Expression of 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity in human lymphoid and non lymphoid cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jan;63(1):203–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrach M., Krehbiel R. E., Deeth L. A. Separation of soluble mouse liver 21-desoxy-20-alpha-hydroxysteroid: NADP 20-alpha-oxidoreductase from 21-hydroxy-20-alpha-hydroxysteroid: NADP 20-alpha-oxidoreductase. Can J Biochem. 1968 Aug;46(8):715–724. doi: 10.1139/o68-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. E., Sajgò M., Noller H. F., Harris J. I. Amino-acid sequence of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from lobster muscle. Nature. 1967 Dec 23;216(5121):1181–1185. doi: 10.1038/2161181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Haron J. A., Stone E. M., Dennison O. E., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Cloning and sequencing of a deoxyribonucleic acid copy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid isolated from chicken muscle. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1605–1613. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. F., Oshima H., Troen B. R., Troen P. Studies of the human testis. IV. Testicular 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 26;360(1):88–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda T., Hirato K., Yanaihara T., Nakayama T. Microsomal 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity for progesterone in human placenta. Endocrinol Jpn. 1986 Jun;33(3):361–368. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.33.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBENER H. J., FUKUSHIMA D. K., GALLAGHER T. F. Substrate specificity of enzymes reducing the 11- and 20-keto groups of steroids. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jun;220(2):499–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. I., Perham R. N. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from pig muscle. Nature. 1968 Sep 7;219(5158):1025–1028. doi: 10.1038/2191025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatefi Y., Stempel K. E. Isolation and enzymatic properties of the mitochondrial reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2350–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking J. D., Harris J. I. D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Amino-acid sequence of the enzyme from the extreme thermophile Thermus aquaticus. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):567–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. Structural comparison of two nontandemly repeated yeast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2596–2605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. The primary structure of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9839–9845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Labieniec L., Swimmer C., Holland M. J. Homologous nucleotide sequences at the 5' termini of messenger RNAs synthesized from the yeast enolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene families. The primary structure of a third yeast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5291–5299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krafft A. E., Winter J., Bokkenheuser V. D., Hylemon P. B. Cofactor requirements of steroid-17-20-desmolase and 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities in cell extracts of Clostridium scindens. J Steroid Biochem. 1987 Jul;28(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(87)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krehbiel R., Darrach M. Ftudies on mouse liver 21-desoxy- and 21-hydroxy-20-alpha-hydroxysteroid: NADP 20-alpha-oxidoreductase. Can J Biochem. 1968 Sep;46(9):1075–1080. doi: 10.1139/o68-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS P. I., TALALAY P. Induction and purification of alpha- and beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):661–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS P. I., TALALAY P. On the molecular specificity of steroid-enzyme combinations; the kinetics of beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1955 Aug 16;144(914):116–132. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1955.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHIJSSEN C., MANDEL J. E., SEIDEN P. T. SEPARATION OF A PURIFIED ADRENAL 20-ALPHA-HYDROXY-STEROID DEHYDROGENASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 26;89:363–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESEMANN G., HUEBENER J. H., JUNK R., SCHMIDT-THOME J. [20beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. 1. Culture of Streptomyces hydrogenans and induction of the enzyme]. Biochem Z. 1960;333:88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nancarrow C. D., Sharaf M. A., Sweet F. Purification of 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase from bovine fetal erythrocytes. Steroids. 1981 May;37(5):539–553. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak K., Wolny M., Banaś T. The complete amino acid sequence of human muscle glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 16;134(2):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80587-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURDY R. H., HALLA M., LITTLE B. 20-ALPHA-HYDROXYSTEROID DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITY A FUNCTION OF HUMAN PLACENTAL 17-BETA-HYDROXYSTEROID DEHYDROGENASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 18;89:557–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pineda J. A., Salinas M. E., Warren J. C. Purification and characterization of 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from bull testis. J Steroid Biochem. 1985 Dec;23(6A):1001–1006. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(85)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollow K., Lübbert H., Boquoi E., Pollow B. Progesterone metabolism in normal human endometrium during the menstrual cycle and in endometrial carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Oct;41(4):729–737. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-4-729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongsawasdi P., Anderson B. M. Kinetic studies of rat ovarian 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 25;799(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECKNAGEL R. O. Adrenocortical steroid C-20-keto reductase. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jul;227(1):273–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabe T., Kiesel L., Runnebaum B. Partial characterization of the cytoplasmic 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.149) of the human placenta at term. J Steroid Biochem. 1982 Jun;16(6):737–743. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(82)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricigliano J. W., Penning T. M. Active-site directed inactivation of rat ovarian 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):717–723. doi: 10.1042/bj2400717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWEAT M. L., GROSSER B. I., BERLINER D. L., SWIM H. E., NABORS C. J., Jr, DOUGHERTY T. F. The metabolism of cortisol and progesterone by cultured uterine fibroblasts, strain U12-705. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Jun;28(3):591–596. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90524-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato F., Takagi Y., Shikita M. 20 -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase of porcine testes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):815–823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shikita M., Tsuneoka K. Non-oligomeric nature of porcine testicular 20alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 1;66(1):4–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80571-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. M., Velick S. F. The glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenases of liver and muscle. Cooperative interactions and conditions for functional reversibility. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):273–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickler R. C., Tobias B., Covey D. F. Human placental 17 beta-estradiol dehydrogenase and 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Two activities at a single enzyme active site. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):316–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickler R. C., Tobias B. Estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase and 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from human placental cytosol: one enzyme with two activities? Steroids. 1980 Aug;36(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(80)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P., DOBSON M. M., TAPLEY D. F. Oxidative degradation of testosterone by adaptive enzymes. Nature. 1952 Oct 11;170(4328):620–621. doi: 10.1038/170620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. Z., FORCHIELLI E., DORFMAN R. I. The reduction in vitro of 17 alpha-hydroxypregnenolone (3 beta, 17 alpha-dihydroxy-delta 5-pregnen-20-one) by rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235:2797–2800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broek W. J., Veeger C. Pyridine-nucleotide transhydrogenase. 5. Kinetic studies on transhydrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):72–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEST W. G., WILCOX R. B. Purification and properties of rat ovarian 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2425–2428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein Y., Lindner H. R., Eckstein B. Thymus metabolises progesterone- possible enzymatic marker for T lymphocytes. Nature. 1977 Apr 14;266(5603):632–633. doi: 10.1038/266632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter J., Morris G. N., O'Rourke-Locascio S., Bokkenheuser V. D., Mosbach E. H., Cohen B. I., Hylemon P. B. Mode of action of steroid desmolase and reductases synthesized by Clostridium "scindens" (formerly Clostridium strain 19). J Lipid Res. 1984 Oct;25(10):1124–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]