Abstract
A cloned 16S rRNA gene from the extreme thermophilic eubacterium Thermus thermophilus HB8 was used to characterize the in vivo expression of the 16S rRNA genes in this organism by nuclease S1 mapping. The gene represents an isolated transcription unit encoding solely 16S rRNA. Under exponential growth conditions, transcription was initiated at a single promoter, which represents the structural equivalent of Escherichia coli rrn P2 promoters. The promoter-leader region was very similar to the E. coli rrn P2 promoter-leader segment that is responsible for antitermination. The T. thermophilus leader region was approximately 85 nucleotides shorter than its E. coli P2 counterpart. Potential processing intermediates were correlated with a proposed secondary structure of T. thermophilus pre-16S rRNA.
Full text
PDF


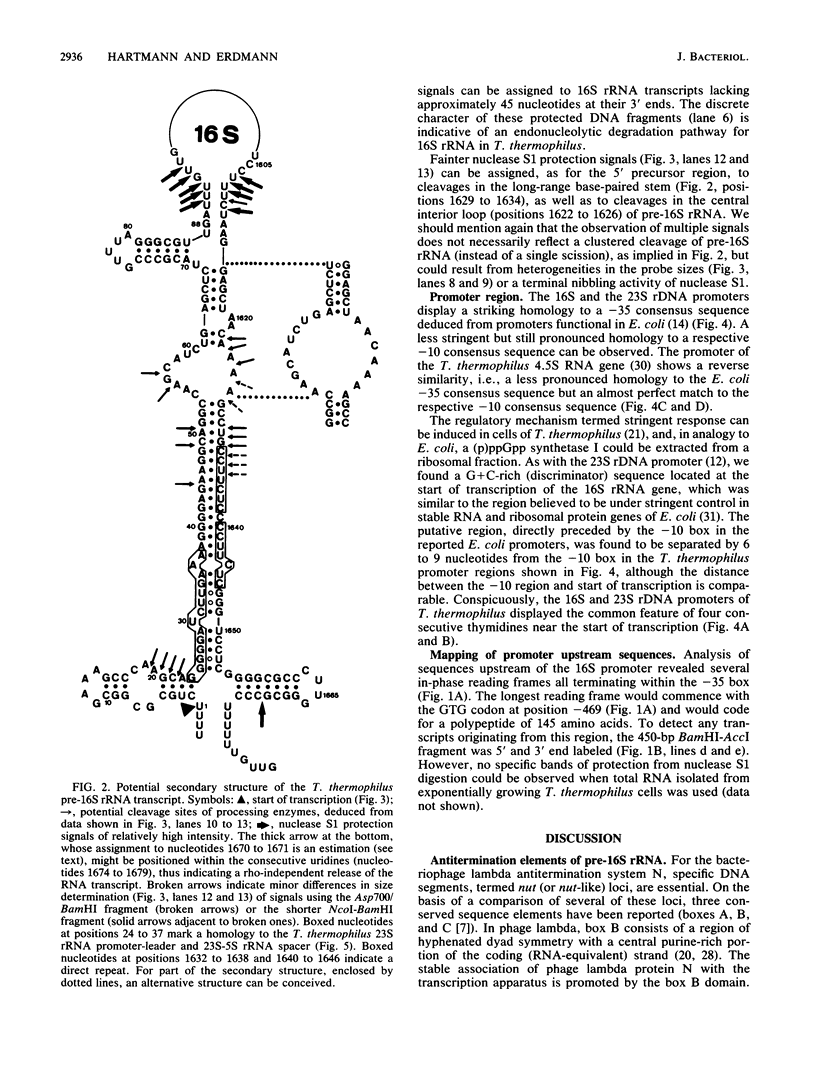
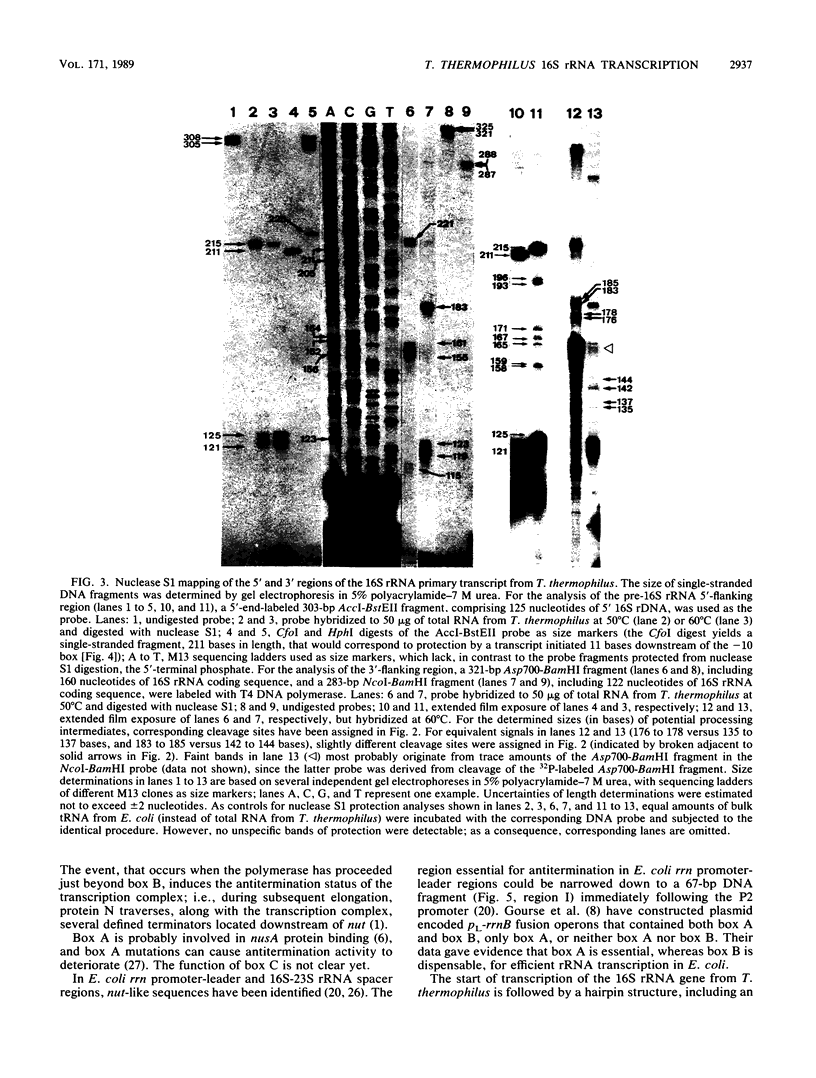




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barik S., Ghosh B., Whalen W., Lazinski D., Das A. An antitermination protein engages the elongating transcription apparatus at a promoter-proximal recognition site. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):885–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Garber R. L., Altman S. Nucleotide sequence and in vitro processing of a precursor molecule to Escherichia coli 4.5 S RNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7709–7716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Young R. A., Steitz J. A. The ribonuclease III site flanking 23S sequences in the 30S ribosomal precursor RNA of E. coli. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90513-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castenholz R. W. Thermophilic blue-green algae and the thermal environment. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Dec;33(4):476–504. doi: 10.1128/br.33.4.476-504.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. R. Evidence that a nucleotide sequence, "boxA," is involved in the action of the NusA protein. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. K., Toschka H. Y., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. Genomic organization of rDNA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. K., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. An unusual rRNA operon constellation: in Thermus thermophilus HB8 the 23S/5S rRNA operon is a separate entity from the 16S rRNA operon. Biochimie. 1987 Oct;69(10):1097–1104. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. K., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. Sequences implicated in the processing of Thermus thermophilus HB8 23S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7735–7747. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. C., Schlessinger D. S1 nuclease mapping analysis of ribosomal RNA processing in wild type and processing deficient Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):12034–12042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. C., Sirdeshmukh R., Schlessinger D. RNase III cleavage is obligate for maturation but not for function of Escherichia coli pre-23S rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):185–188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Chamberlin M. J. Pausing and attenuation of in vitro transcription in the rrnB operon of E. coli. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):523–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90394-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krych M., Sirdeshmukh R., Gourse R., Schlessinger D. Processing of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA with bacteriophage lambda leader sequences. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5523–5529. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5523-5529.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Squires C. L., Squires C. Antitermination of E. coli rRNA transcription is caused by a control region segment containing lambda nut-like sequences. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. A. Antitermination mechanisms in rRNA operons of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.1-5.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. R., Tomich C. S., Friedman D. I. The nusA recognition site. Alteration in its sequence or position relative to upstream translation interferes with the action of the N antitermination function of phage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90270-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salstrom J. S., Szybalski W. Coliphage lambdanutL-: a unique class of mutants defective in the site of gene N product utilization for antitermination of leftward transcription. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):195–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Toschka H. Y., Erdmann V. A. Nucleotide sequence of the 4.5S RNA gene from Thermus thermophilus HB8. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):9042–9042. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.9042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Conserved features of coordinately regulated E. coli promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2605–2618. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Complementary sequences 1700 nucleotides apart form a ribonuclease III cleavage site in Escherichia coli ribosomal precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3593–3597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]