Abstract
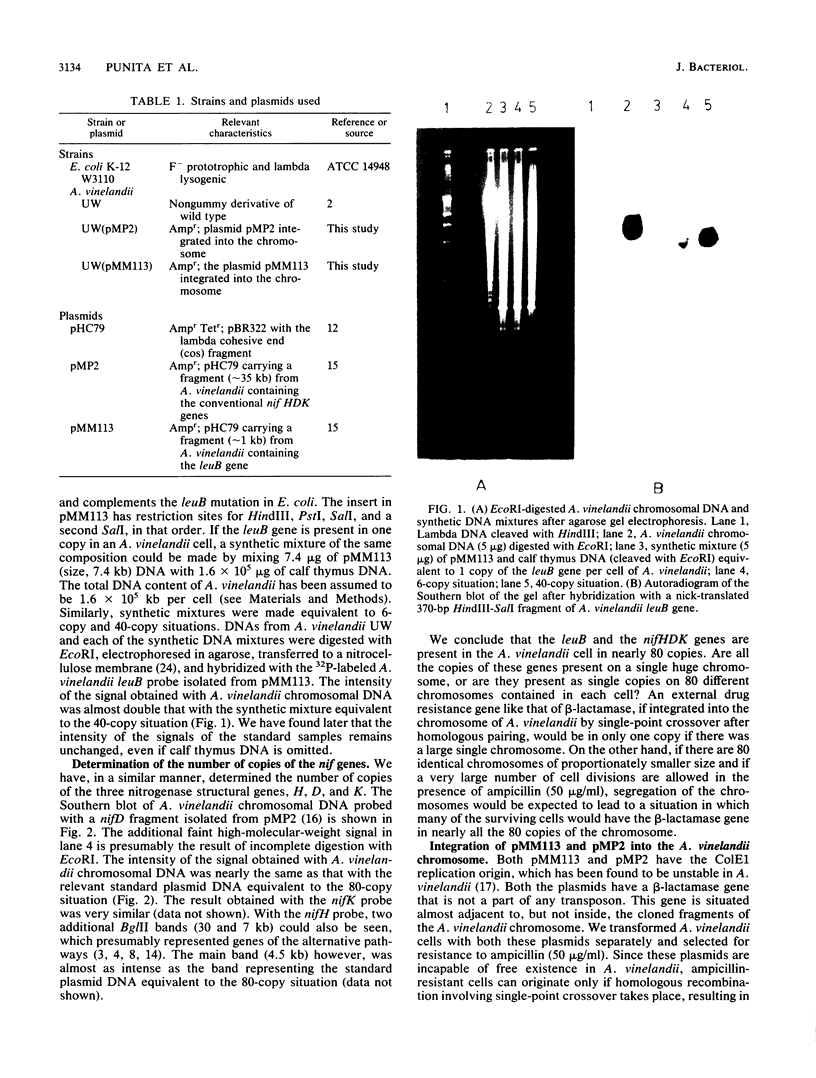
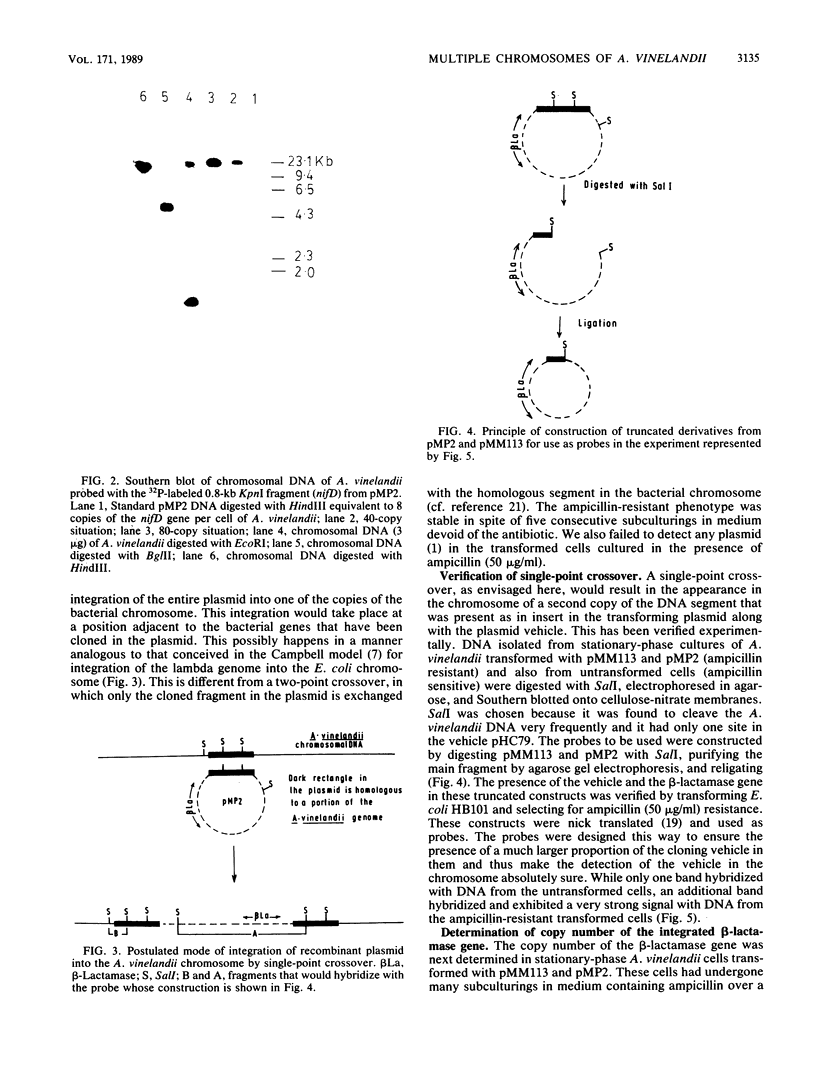
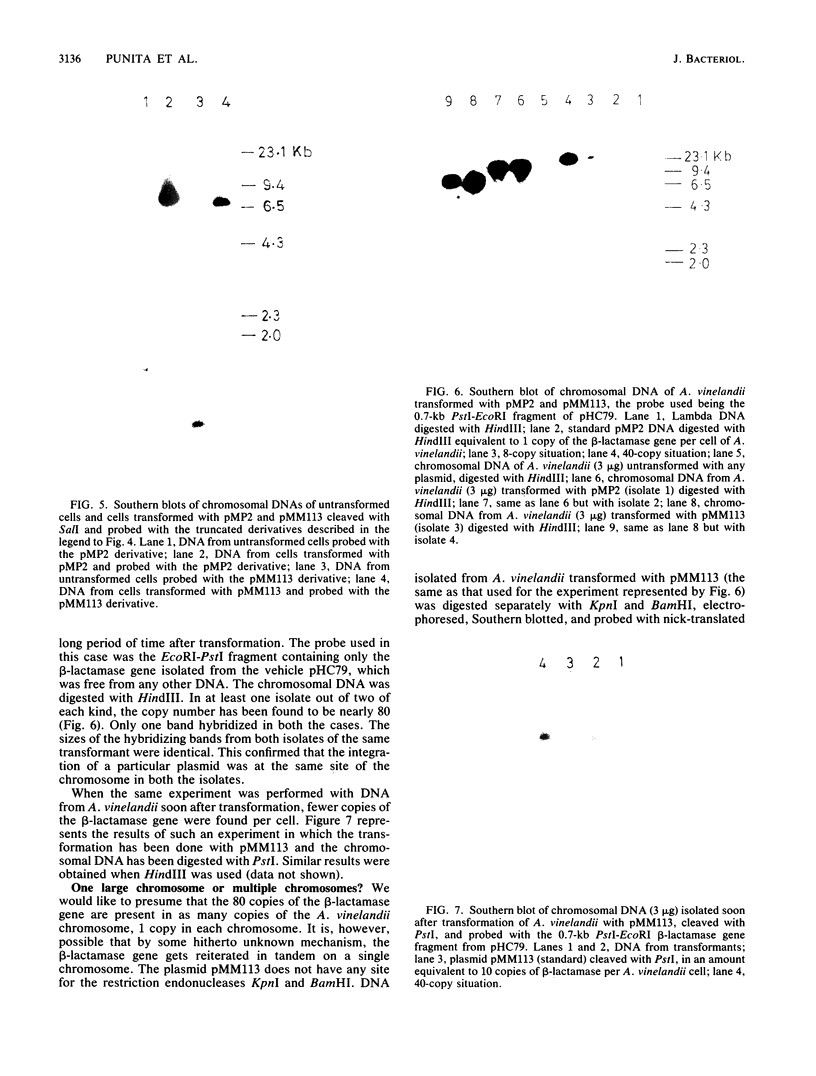
The number of copies of the genes leuB, nifH, nifD, and nifK per cell of Azotobacter vinelandii has been determined to be about 80. A beta-lactamase gene was integrated into the A. vinelandii chromosome by single-point crossover. Subsequently, we have been able to detect nearly 80 copies of this beta-lactamase gene per cell of A. vinelandii when cultured for a large number of generations in the presence of ampicillin. The multiple copies of the beta-lactamase gene do not seem to be present on a single chromosome, as evident from the fragment obtained by digestion of cellular DNA with the appropriate restriction endonuclease. The kinetics of renaturation of DNA of A. vinelandii is suggestive of complexity similar to that of Escherichia coli. The DNA content of A. vinelandii, however, is 40 times that of E. coli. All these indicate the presence of multiple chromosomes, possibly as many as 80, in A. vinelandii.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Brill W. J. Genetic analysis of Azotobacter vinelandii mutant strains unable to fix nitrogen. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):954–956. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.954-956.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Evidence for an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7342–7346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Premakumar R., Dean D. R., Jacobson M. R., Chisnell J. R., Rizzo T. M., Kopczynski J. Nitrogen Fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii Strains Having Deletions in Structural Genes for Nitrogenase. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):92–94. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4746.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. The arrangement of simian virus 40 sequences in the DNA of transformed cells. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):269–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. R., Brooks H. E., Pasternak J. J. Transformation of Azotobacter vinelandii with plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):276–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.276-279.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock B. A., Jones C. W. Bacterial respiration. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):47–99. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.47-99.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Toukdarian A. Genetics of azotobacters: applications to nitrogen fixation and related aspects of metabolism. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:227–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medhora M., Phadnis S. H., Das H. K. Construction of a gene library from the nitrogen-fixing aerobe Azotobacter vinelandii. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. L., Chesshyre J. A., Wheeler C., Jones R., Woodley P. R., Postgate J. R. Genome size and complexity in Azotobacter chroococcum. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1603–1612. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoff H. L., Berke E., Loperfido B. Physiological studies of encystment in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):185–189. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.185-189.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoff H. L., Shimel B., Ellis S. Characterization of Azotobacter vinelandii deoxyribonucleic acid and folded chromosomes. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):871–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.871-877.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg G. W., Wilson P. W. Formation of the nitrogen-fixing enzyme system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):25–31. doi: 10.1139/m68-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]