Abstract
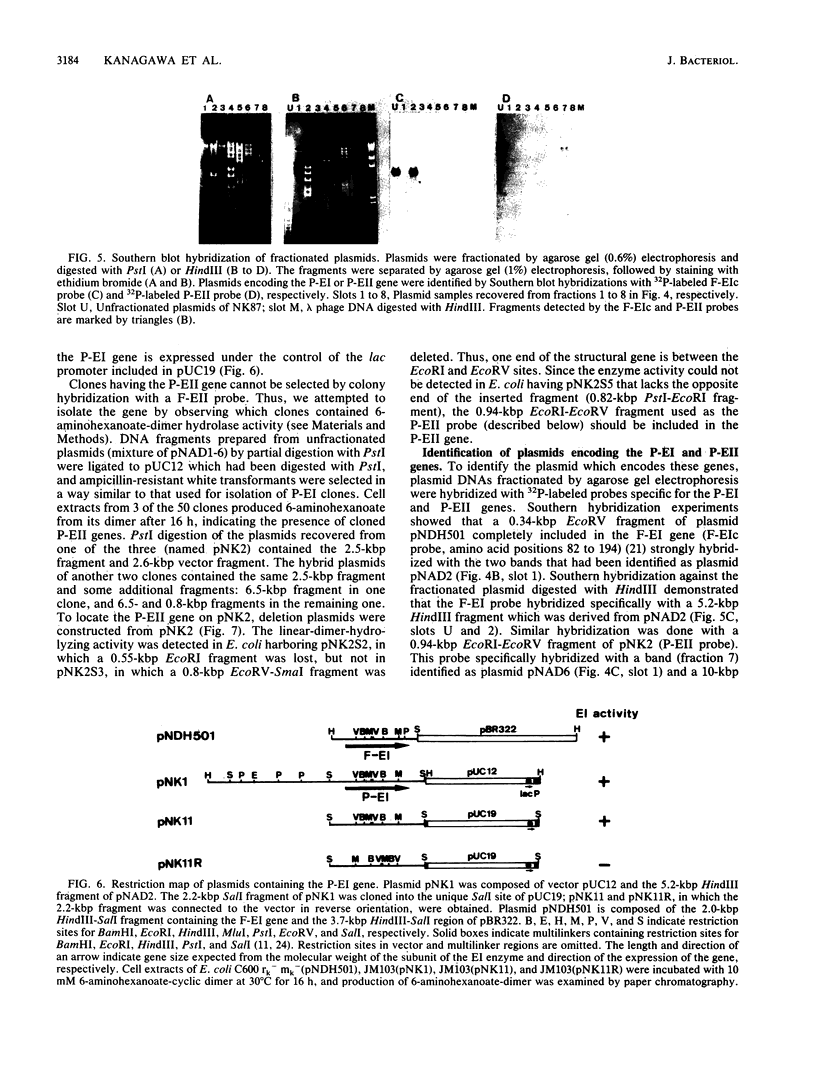
A bacterial strain, Pseudomonas sp. strain NK87, that can use 6-aminohexanoate-cyclic dimer as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen was newly isolated from wastewater of a factory which produces nylon-6. Two responsible enzymes, 6-aminohexanoate-cyclic-dimer hydrolase (P-EI) and 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase (P-EII), were found in the NK87 strain, as is the case with Flavobacterium sp. strain KI72, another 6-aminohexanoate-cyclic-dimer-metabolizing bacterium (H. Okada, S. Negoro, H. Kimura, and S. Nakamura, Nature [London] 306:203-206, 1983). The P-EI enzyme is immunologically identical to the 6-aminohexanoate-cyclic-dimer hydrolase of KI72 (F-EI). However, antiserum against the 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase purified from KI72 (F-EII) did not react with cell extracts of NK87, indicating that the F-EII and P-EII enzymes are immunologically different. Restriction endonuclease analyses show that the NK87 strain harbors at least six plasmids ranging in size from 20 to 80 kilobase pairs (kbp). The P-EI and P-EII genes were cloned in Escherichia coli. Both the P-EI and F-EI probes strongly hybridized with a 23-kbp plasmid in Southern hybridization analyses. The P-EII probe hybridized specifically with an 80-kbp plasmid, but the F-EII probe hybridized with none of the plasmids harbored in NK87. These results indicate that the P-EI gene and P-EII gene are encoded on the 23-kbp and 80-kbp plasmids, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of Lambda Lysogenicity during Bacterial Recombination in Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):429–439. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita S., Negoro S., Muramatsu M., Bisaria V. S., Sawada S., Okada H. 6-Aminohexanoic acid cyclic dimer hydrolase. A new cyclic amide hydrolase produced by Achromobacter guttatus KI74. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 1;80(2):489–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita S., Terada T., Taniguchi T., Takene Y., Masuda S., Matsunaga N., Okada H. Purification and characterization of 6-aminohexanoic-acid-oligomer hydrolase of Flavobacterium sp. Ki72. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun 1;116(3):547–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro S., Nakamura S., Kimura H., Fujiyama K., Zhang Y. Z., Kanzaki N., Okada H. Construction of hybrid genes of 6-aminohexanoic acid-oligomer hydrolase and its analogous enzyme. Estimation of the intramolecular regions important for the enzyme evolution. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13648–13651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro S., Nakamura S., Okada H. DNA-DNA hybridization analysis of nylon oligomer-degradative plasmid pOAD2: identification of the DNA region analogous to the nylon oligomer degradation gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):419–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.419-424.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro S., Shinagawa H., Nakata A., Kinoshita S., Hatozaki T., Okada H. Plasmid control of 6-aminohexanoic acid cyclic dimer degradation enzymes of Flavobacterium sp. KI72. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):238–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.238-245.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro S., Taniguchi T., Kanaoka M., Kimura H., Okada H. Plasmid-determined enzymatic degradation of nylon oligomers. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):22–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.22-31.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Negoro S., Kimura H., Nakamura S. Evolutionary adaptation of plasmid-encoded enzymes for degrading nylon oligomers. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):203–206. doi: 10.1038/306203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Fukuyama S., Kanzaki N., Kanagawa K., Negoro S., Okada H. High homology between 6-aminohexanoate-cyclic-dimer hydrolases of Flavobacterium and Pseudomonas strains. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3187–3191. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3187-3191.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]