Abstract
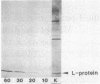
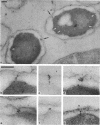
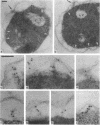
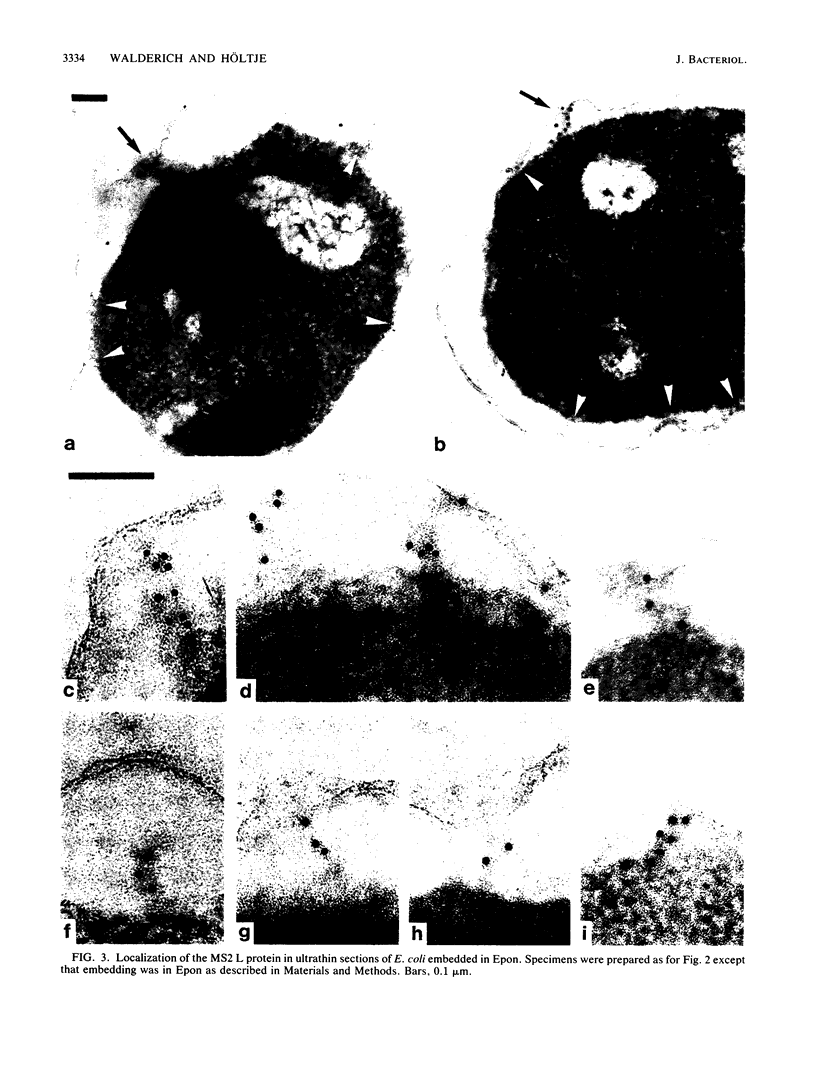
Specific localization of the lysis (L) protein of bacteriophage MS2 in the cell wall of Escherichia coli was determined by immunoelectron microscopy. After induction of the cloned lysis gene, the cells were plasmolyzed, fixed, and embedded in either Epon or Lowicryl K4M. Polyclonal L-protein-specific antiserum was purified by preabsorption to membranes from cells harboring a control plasmid. Protein A-gold was used to label the protein-antibody complexes. Between 42.8% (Lowicryl) and 33.8% (Epon) of the label was found in inner and outer membranes, but 30.3% (Lowicryl) and 32.8% (Epon) was present mostly in clusters in the adhesion sites visible after plasmolysis. The remaining label (26.9 and 33.4%, respectively) appeared to be present in the periplasmic space but may also have been part of membrane junctions not visible because of poor contrast of the specimen. In contrast, a quite different distribution of the L protein was found in cells grown under conditions of penicillin tolerance, i.e., at pH 5, a condition that had previously been shown to protect cells from L-protein-induced lysis. At tolerant conditions, only 21.0% of the L protein was in the adhesion sites; most of the protein (68.2%) was found in inner and outer membranes. It is concluded that lysis of the host, E. coli, was a result of the formation of specific L-protein-mediated membrane adhesion sites.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E. Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Bayer M. H. Effects of bacteriophage fd infection on Escherichia coli HB11 envelope: a morphological and biochemical study. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):258–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.258-266.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Bayer M. H., Lunn C. A., Pigiet V. Association of thioredoxin with the inner membrane and adhesion sites in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2659–2666. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2659-2666.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beremand M. N., Blumenthal T. Overlapping genes in RNA phage: a new protein implicated in lysis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Inouye M., Atkins J. Bacteriophage MS2 lysis protein does not require coat protein to mediate cell lysis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1098–1100. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1098-1100.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Barrell B. G., Staden R., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage G4 DNA. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):236–247. doi: 10.1038/276236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goessens W. H., Driessen A. J., Wilschut J., van Duin J. A synthetic peptide corresponding to the C-terminal 25 residues of phage MS2 coded lysis protein dissipates the protonmotive force in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles by generating hydrophilic pores. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):867–873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Lopez R., Tomasz A. Suppression of lytic effect of beta lactams on Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3293–3297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich B., Lubitz W., Plapp R. Lysis of Escherichia coli by induction of cloned phi X174 genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):493–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00334146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Kellenberger E. Periplasmic gel: new concept resulting from the reinvestigation of bacterial cell envelope ultrastructure by new methods. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.143-152.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horabin J. I., Webster R. E. An amino acid sequence which directs membrane insertion causes loss of membrane potential. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11575–11583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Fiedler W., Rotering H., Walderich B., van Duin J. Lysis induction of Escherichia coli by the cloned lysis protein of the phage MS2 depends on the presence of osmoregulatory membrane-derived oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3539–3541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelein R. A., Remaut E., Fiers W., van Duin J. Lysis gene expression of RNA phage MS2 depends on a frameshift during translation of the overlapping coat protein gene. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):35–41. doi: 10.1038/295035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J., Webster R. E. Assembly site of bacteriophage f1 corresponds to adhesion zones between the inner and outer membranes of the host cell. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1270–1274. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1270-1274.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Stanssens P., Fiers W. Plasmid vectors for high-efficiency expression controlled by the PL promoter of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Leunissen J., van Damme-Jongsten M., Overduin P. Failure of E. coli K-12 to transport PhoE-LacZ hybrid proteins out of the cytoplasm. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walderich B., Ursinus-Wössner A., van Duin J., Höltje J. V. Induction of the autolytic system of Escherichia coli by specific insertion of bacteriophage MS2 lysis protein into the bacterial cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5027–5033. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5027-5033.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. D., Young R. Lytic action of cloned phi X174 gene E. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):993–1002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.993-1002.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]