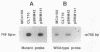Abstract
Expression of the pyrBI operon of Escherichia coli K-12, which encodes the subunits of the pyrimidine biosynthetic enzyme aspartate transcarbamylase, is negatively regulated over a several-hundredfold range by pyrimidine availability. This regulation occurs, at least in large part, through a UTP-sensitive attenuation control mechanism in which transcriptional termination at the pyrBI attenuator, a rho-independent transcriptional terminator located immediately upstream of the pyrB structural gene, is regulated by the relative rates of transcription and translation within the pyrBI leader region. There is suggestive evidence that an additional, attenuator-independent control mechanism also contributes to this regulation. To measure the level of regulation that occurs through the attenuation and attenuator-independent control mechanisms, we constructed a mutant strain in which a 9-base-pair deletion was introduced into the attenuator of the chromosomal pyrBI operon. This deletion, which removes the run of thymidine residues at the end of the attenuator, completely abolishes rho-independent transcriptional termination activity. When the mutant strain was grown under conditions of pyrimidine excess, the level of operon expression was 51-fold greater than that of an isogenic pyrBI+ strain. Under conditions of pyrimidine limitation, operon expression was increased an additional 6.5-fold in the mutant. These results demonstrate that the attenuation control mechanism is primarily responsible for pyrimidine-mediated regulation but that there is a significant contribution by an attenuator-independent control mechanism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper M. D., Ames B. N. Transport of antibiotics and metabolite analogs by systems under cyclic AMP control: positive selection of Salmonella typhimurium cya and crp mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):149–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.149-157.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. E., Hesse S. D., Waechter-Brulla D. A., Lynn S. P., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. A genetic enrichment for mutations constructed by oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonekamp F., Clemmesen K., Karlström O., Jensen K. F. Mechanism of UTP-modulated attenuation at the pyrE gene of Escherichia coli: an example of operon polarity control through the coupling of translation to transcription. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2857–2861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02220.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmesen K., Bonekamp F., Karlström O., Jensen K. F. Role of translation in the UTP-modulated attenuation at the pyrBI operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(2):247–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00425666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Fast R., Karlström O., Larsen J. N. Association of RNA polymerase having increased Km for ATP and UTP with hyperexpression of the pyrB and pyrE genes of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):857–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.857-865.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin H. L., Schachman H. K. Regulation of aspartate transcarbamoylase synthesis in Escherichia coli: analysis of deletion mutations in the promoter region of the pyrBI operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4643–4647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn S. P., Kasper L. M., Gardner J. F. Contributions of RNA secondary structure and length of the thymidine tract to transcription termination at the thr operon attenuator. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):472–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen P., Jensen K. F. Effect of UTP and GTP pools on attenuation at the pyrE gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):152–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00330436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland K. L., Liu C. G., Turnbough C. L., Jr Role of the ribosome in suppressing transcriptional termination at the pyrBI attenuator of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7149–7153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland K. L., Powell F. E., Turnbough C. L., Jr Role of translation and attenuation in the control of pyrBI operon expression in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):991–999. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.991-999.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Neuhard J. Control of expression of the pyr genes in Salmonella typhimurium: effects of variations in uridine and cytidine nucleotide pools. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):814–822. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.814-822.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
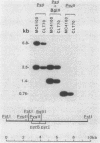
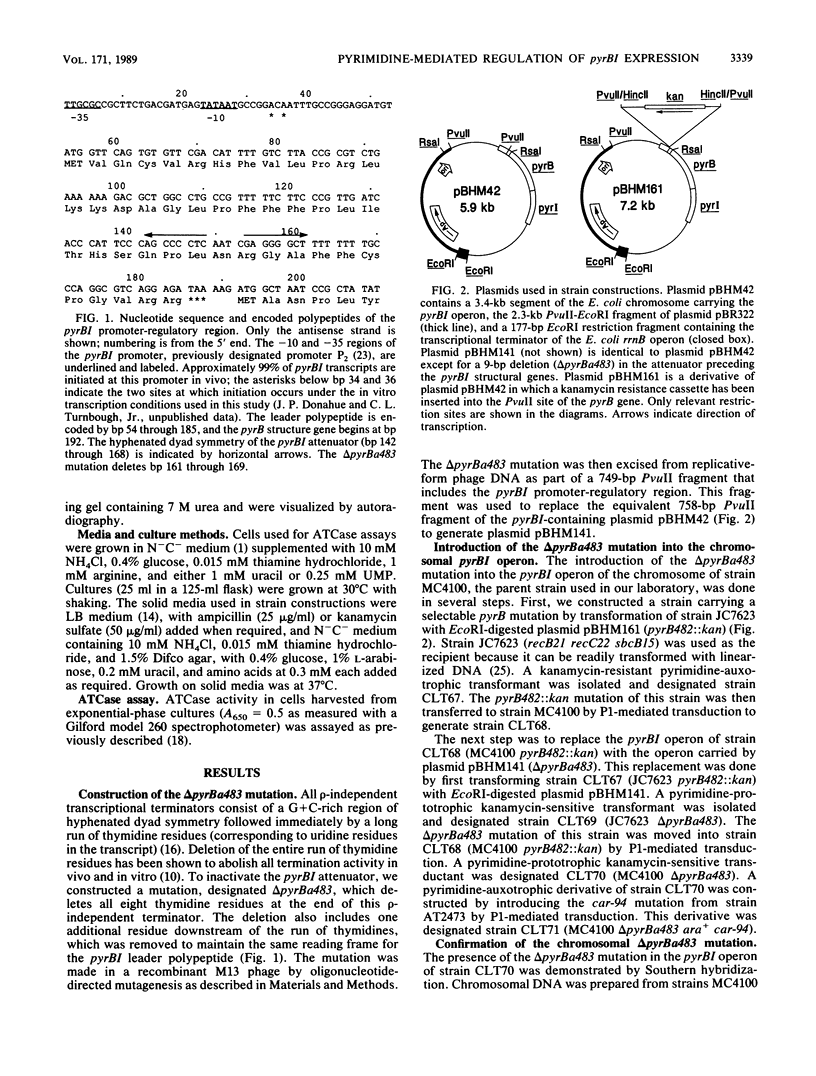
- Turnbough C. L., Jr, Hicks K. L., Donahue J. P. Attenuation control of pyrBI operon expression in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):368–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbough C. L., Jr, Kerr K. H., Funderburg W. R., Donahue J. P., Powell F. E. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the pyrF operon of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10239–10245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbough C. L., Jr Regulation of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase synthesis by guanosine tetraphosphate and pyrimidine ribonucleoside triphosphates. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):998–1007. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.998-1007.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C., Elledge S. J., Krueger J. H., Walker G. C. Site-directed insertion and deletion mutagenesis with cloned fragments in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1219–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1219-1221.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]