Abstract
Previous work identified the dsg gene as necessary for cell-cell interaction in Myxococcus xanthus. Point mutations of this gene, such as dsg-439, are viable, but insertions of Tn5 within the dsg gene (dsg::Tn5) are lethal. Partial diploids, dsg::Tn5/dsg+ or dsg::Tn5/dsg-429 or dsg::Tn5/dsg-439, are also viable, showing that the lethal effect of the haploid insertions is due to loss of function. Thus the evidence implies that the dsg gene is essential for viability as well as development, but its essential quality differs between growth and development because dsg-429 and dsg-439 mutants grow normally, but are unable to develop.
Full text
PDF
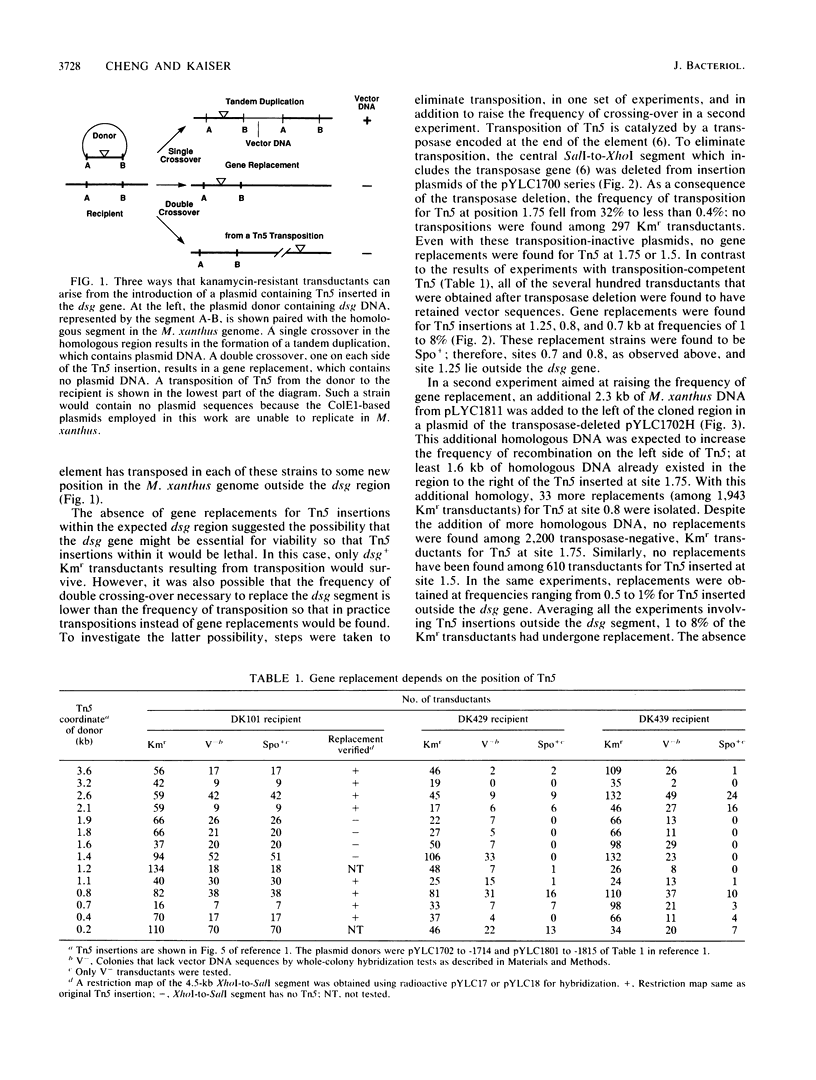
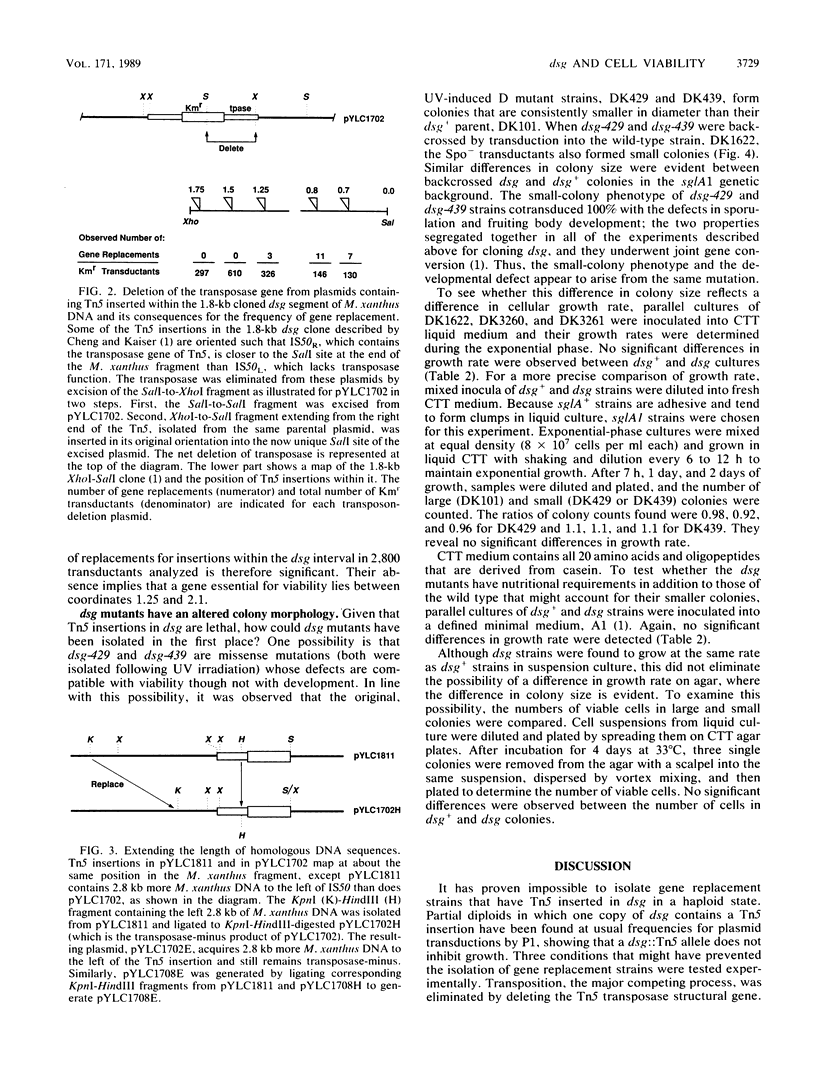


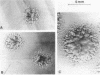
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng Y., Kaiser D. dsg, a gene required for cell-cell interaction early in Myxococcus development. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3719–3726. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3719-3726.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Coliphage P1-mediated transduction of cloned DNA from Escherichia coli to Myxococcus xanthus: use for complementation and recombinational analyses. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):317–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.317-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein S. J., Jorgensen R. A., Postle K., Reznikoff W. S. The inverted repeats of Tn5 are functionally different. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):795–805. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]