Abstract
Ferric reductase activity was examined in Azotobacter vinelandii and was found to be located in the cytoplasm. The specific activities of soluble cell extracts were not affected by the iron concentration of the growth medium; however, activity was inhibited by the presence of Zn2+ during cell growth and also by the addition of Zn2+ to the enzyme assays. Intracellular Fe2+ levels were lower and siderophore production was increased in Zn2+-grown cells. The ferric reductase was active under aerobic conditions, had an optimal pH of approximately 7.5, and required flavin mononucleotide and Mg2+ for maximum activity. The enzyme utilized NADH to reduce iron supplied as a variety of iron chelates, including the ferrisiderophores of A. vinelandii. The enzyme was purified by conventional protein purification techniques, and the final preparation consisted of two major proteins with molecular weights of 44,600 and 69,000. The apparent Km values of the ferric reductase for Fe3+ (supplied as ferric citrate) and NADH were 10 and 15.8 microM, respectively, and the data for the enzyme reaction were consistent with Ping Pong Bi Bi kinetics. The approximate Ki values resulting from inhibition of the enzyme by Zn2+, which was a hyperbolic (partial) mixed-type inhibitor, were 25 microM with respect to iron and 1.7 microM with respect to NADH. These results suggested that ferric reductase activity may have a regulatory role in the processes of iron assimilation in A. vinelandii.
Full text
PDF



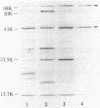
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Ferrisiderophore reductase activity in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):715–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.715-721.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. A., Ratledge C. Iron transport in Mycobacterium smegmatis: ferrimycobactin reductase (nad(p)h:ferrimycobactin oxidoreductase), the enzyme releasing iron from its carrier. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 1;53(2):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Roy S. C. Effect of trace elements on the production of pigments by a pseudomonad. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):228–231. doi: 10.1042/bj0930228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. L., Bulen W. A. The isolation and identification of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid and 2-N,6-N-di-92,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)-L-lysine formed by iron-deficient Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):757–762. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Iron reductases from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):199–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.199-204.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crichton R. R., Charloteaux-Wauters M. Iron transport and storage. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):485–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey H. A., Jr, Lascelles J. Reduction of iron and synthesis of protoheme by Spirillum itersonii and other organisms. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):815–820. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.815-820.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst J. F., Winkelmann G. Enzymatic release of iron from sideramines in fungi. NADH:sideramine oxidoreductase in Neurospora crassa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 7;500(1):27–41. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines C. G., Lodge J. S., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Ferrisiderophore reductase activity associated with an aromatic biosynthetic enzyme complex in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):527–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.527-533.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huyer M., Page W. J. Zn Increases Siderophore Production in Azotobacter vinelandii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2625–2631. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2625-2631.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knosp O., von Tigerstrom M., Page W. J. Siderophore-mediated uptake of iron in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.341-347.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. S., Gaines C. G., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Ferrisiderophore reductase activity in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):771–774. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.771-774.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. S., Gaines C. G., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Non-hydrolytic release of iron from ferrienterobactin analogs by extracts of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 31;97(4):1291–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. D., Dailey H. A. Aerobic ferrisiderophore reductase assay and activity stain for native polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Oct 1;134(1):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. D., Dailey H. A. Ferric iron reductase of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1120–1125. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1120-1125.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osaki S., Johnson D. A., Frieden E. The mobilization of iron from the perfused mammalian liver by a serum copper enzyme, ferroxidase I. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):3018–3023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page W. J., Huyer M. Derepression of the Azotobacter vinelandii siderophore system, using iron-containing minerals to limit iron repletion. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):496–502. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.496-502.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page W. J., Sadoff H. L. Physiological factors affecting transformation of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1080–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1080-1087.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page W. J., von Tigerstrom M. Iron- and molybdenum-repressible outer membrane proteins in competent Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):237–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.237-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broek W. J., Santema J. S., Wassink J. H., Veeger C. Pyridine-nucleotide transhydrogenase. 1. Isolation, purification and characterisation of the transhydrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):31–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broek W. J., Van Breemen J. F., Van Bruggen E. F., Veeger C. Pyridine-nucleotide transhydrogenase. 2. Electron-microscopic studies on the transhydrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):46–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J. Free manganese (II) and iron (II) cations can act as intracellular cell controls. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 5;140(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80508-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Wee S., Herrero M., Neilands J. B. Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColV-K30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2624–2630. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2624-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]