Abstract
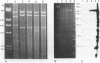
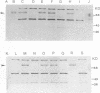
A 14-kilobase-pair (kbp) EcoRI DNA fragment that encodes an enzyme capable of rapid hydrolysis of N-methylcarbamate insecticides (carbofuran hydrolase) was cloned from carbofuran-degrading Achromobacter sp. strain WM111. When used to probe Southern blots containing plasmid and total DNAs from WM111, this 14-kbp fragment hybridized strongly to a 14-kbp EcoRI fragment from the greater than 100-kbp plasmid harbored by this strain but weakly to EcoRI-digested total DNA from Achromobacter sp. strain WM111, indicating that the gene for N-methylcarbamate degradation (mcd) is plasmid encoded. Further subcloning localized the mcd gene on a 3-kbp ScaI-ClaI fragment. There was little or no expression of this gene in the alternative gram-negative hosts Pseudomonas putida, Alcaligenes eutrophus, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, and Achromobacter pestifer. Western blotting (immunoblotting) of the protein products produced by low-level expression in P. putida confirmed that this 3-kbp fragment encodes the two 70+-kilodalton protein products seen in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of purified carbofuran hydrolase.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amy P. S., Schulke J. W., Frazier L. M., Seidler R. J. Characterization of aquatic bacteria and cloning of genes specifying partial degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1237–1245. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1237-1245.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper N. D., Fleming M. M., Skipper H. D. Biodegradation of carbofuran in pretreated and non-pretreated soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1987 Oct;39(4):571–578. doi: 10.1007/BF01698447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic homology between independently isolated chlorobenzoate-degradative plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):532–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.532-534.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry G. R., Ali A. N. Bacterial metabolism of carbofuran. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1414–1419. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1414-1419.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connors M. A., Barnsley E. A. Naphthalene plasmids in pseudomonads. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1096–1101. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1096-1101.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Chandrasekharappa S., Gill J. F., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. A set of cassettes and improved vectors for genetic and biochemical characterization of Pseudomonas genes. Gene. 1987;57(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90177-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Tomasek P., Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Gene amplification induces mucoid phenotype in rec-2 Pseudomonas aeruginosa exposed to kanamycin. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):510–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.510-516.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Properties of six pesticide degradation plasmids isolated from Alcaligenes paradoxus and Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.681-686.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby C. J., Bayley S. A., Worsey M. J., Williams P. A., Broda P. Molecular sizes and relationships of TOL plasmids in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1274–1280. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1274-1280.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn N. W., Gunsalus I. C. Transmissible plasmid coding early enzymes of naphthalene oxidation in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):974–979. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.974-979.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsot A., Maddox J. V., Bruce W. Enhanced microbial degradation of carbofuran in soils with histories of Furadan use. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1981 Jun;26(6):781–788. doi: 10.1007/BF01622171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman D. J., Gowland P. C., Slater J. H. Large plasmids from soil bacteria enriched on halogenated alkanoic acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):44–51. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.44-51.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E., Janik A. Transformation of Acinetobacter calco-aceticus (Bacterium anitratum). J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.281-288.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karns J. S., Kilbane J. J., Duttagupta S., Chakrabarty A. M. Metabolism of Halophenols by 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading Pseudomonas cepacia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1176–1181. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1176-1181.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbane J. J., Chatterjee D. K., Karns J. S., Kellogg S. T., Chakrabarty A. M. Biodegradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid by a pure culture of Pseudomonas cepacia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.72-78.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Pignatello J. J., Crawford R. L. Degradation of chlorinated phenols by a pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):907–910. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.907-910.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelis M. L., Ornston L. N. Genetic control of enzyme induction in the -ketoadipate pathway of Pseudomonas putida: deletion mapping of cat mutations. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):790–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.790-795.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Worsey M. J. Ubiquity of plasmids in coding for toluene and xylene metabolism in soil bacteria: evidence for the existence of new TOL plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):818–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.818-828.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]