Abstract
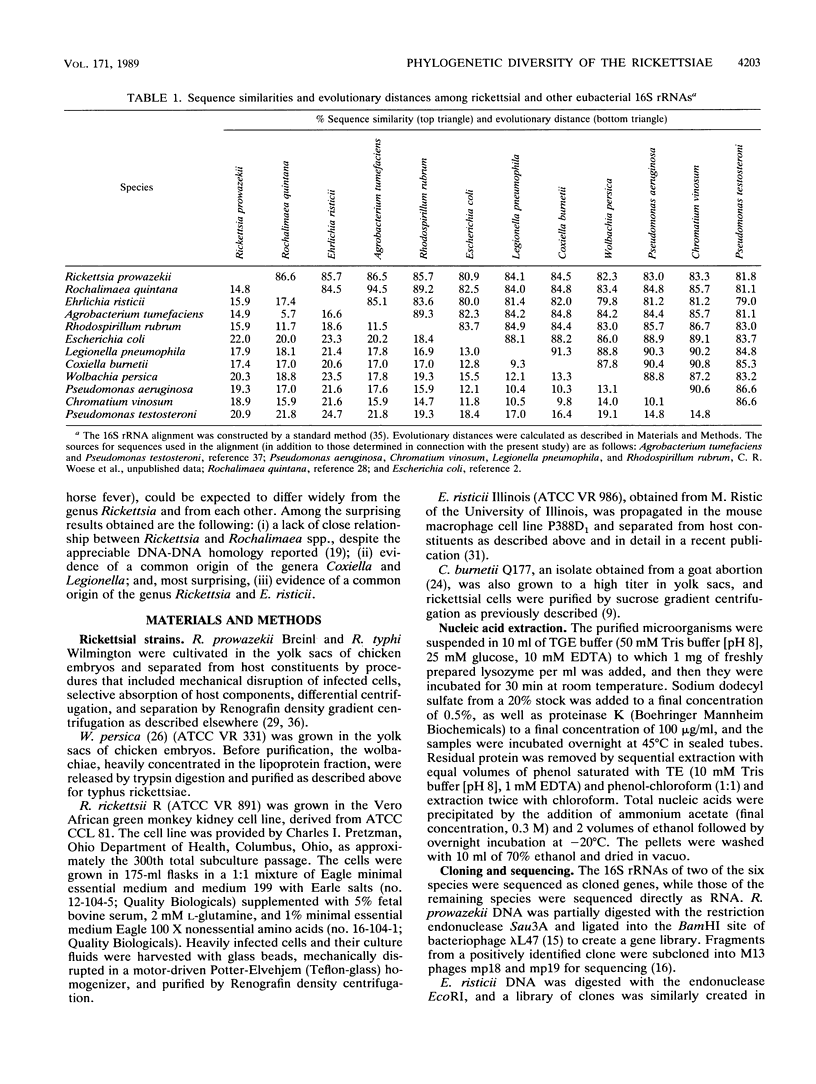
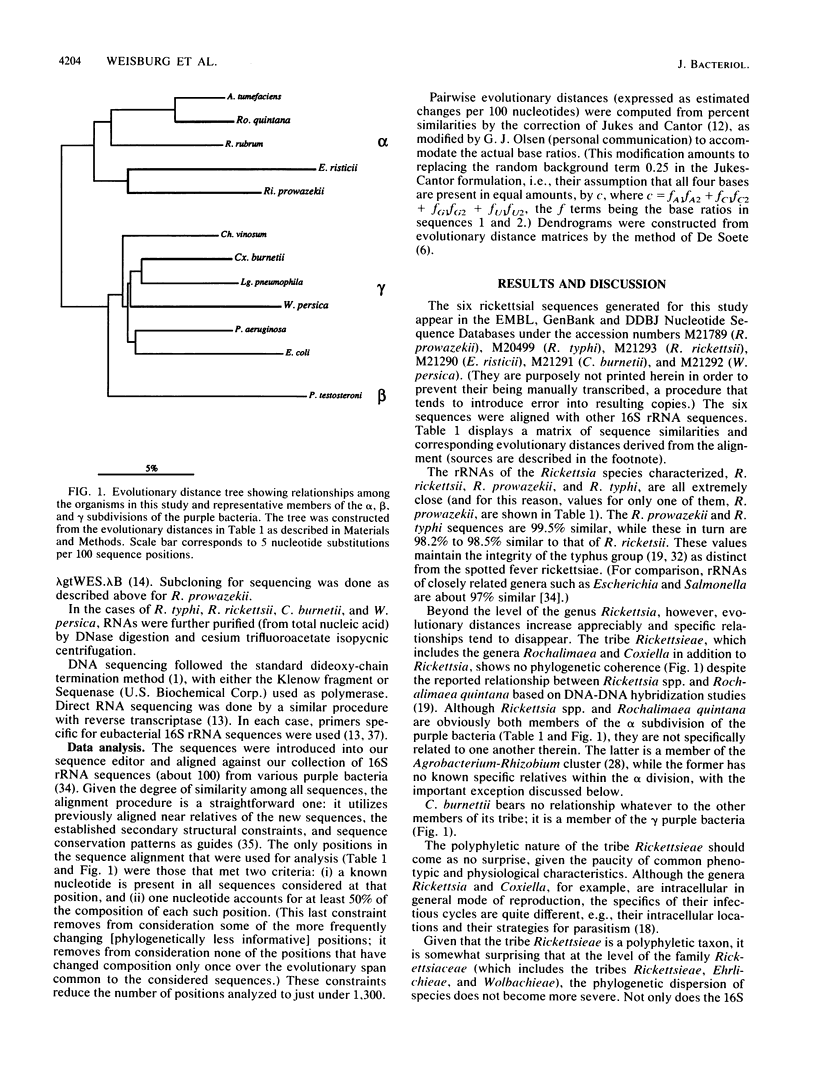
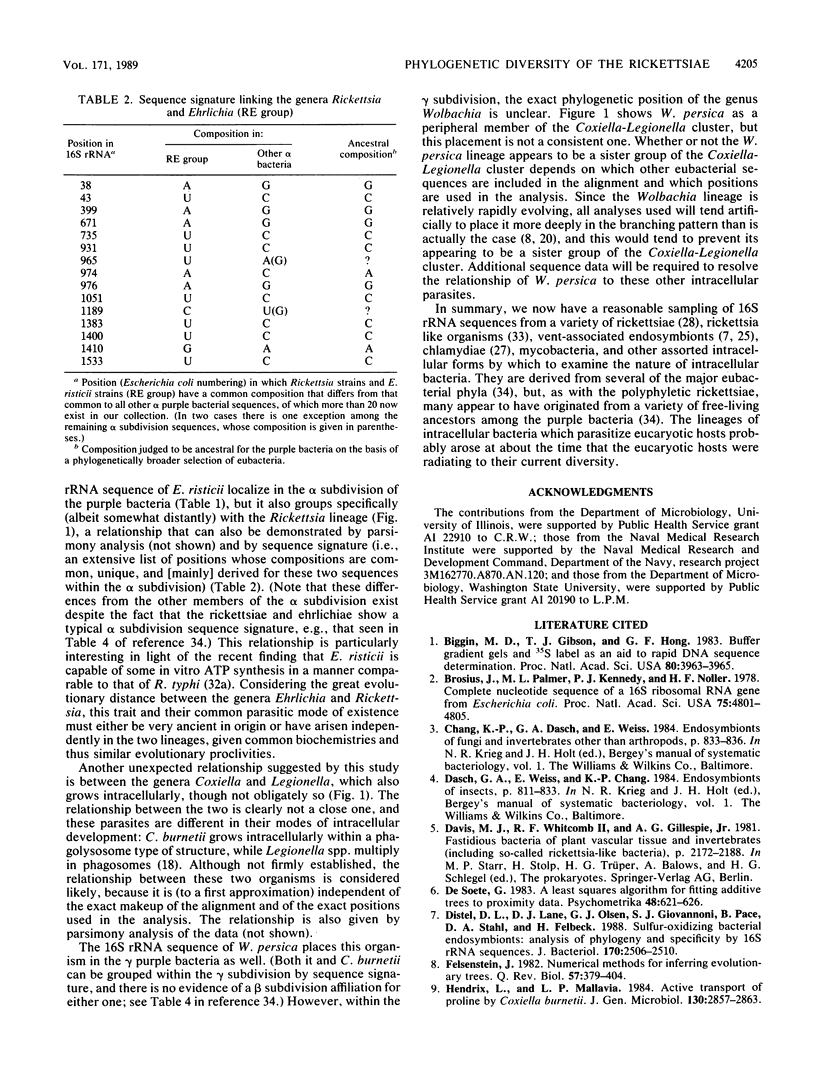
Small subunit rRNA sequences have been determined for representative strains of six species of the family Rickettsiaceae: Rickettsia rickettsii, Rickettsia prowazekii, Rickettsia typhi, Coxiella burnetii, Ehrlichia risticii, and Wolbachia persica. The relationships among these sequences and those of other eubacteria show that all members of the family Rickettsiaceae belong to the so-called purple bacterial phylum. The three representatives of the genus Rickettsia form a tight monophyletic cluster within the alpha subdivision of the purple bacteria. E. risticii also belongs to the alpha subdivision and shows a distant yet specific relationship to the genus Rickettsia. However, the family as a whole is not monophyletic, in that C. burnetii and W. persica are members of the gamma subdivision. The former appears to show a specific, but rather distant, relationship to the genus Legionella.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Weiss E. Characterization of the Madrid E strain of Rickettsia prowazekii purified by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):280–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.280-286.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel D. L., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace B., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A., Felbeck H. Sulfur-oxidizing bacterial endosymbionts: analysis of phylogeny and specificity by 16S rRNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2506–2510. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2506-2510.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix L., Mallavia L. P. Active transport of proline by Coxiella burnetii. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2857–2863. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. J., Ristic M., Cole A. I., Johnson P., Baker G., Goetz T. Isolation, experimental transmission, and characterization of causative agent of Potomac horse fever. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.3880925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Brammar W. J. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning large DNA fragments made with several restriction enzymes. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J. Earliest phylogenetic branchings: comparing rRNA-based evolutionary trees inferred with various techniques. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:825–837. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. E., Frazier M. E., Mallavia L. P. Correlation of plasmid type and disease caused by Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.775-779.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Analysis of hydrothermal vent-associated symbionts by ribosomal RNA sequences. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):409–411. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4647.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Hatch T. P., Woese C. R. Eubacterial origin of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):570–574. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.570-574.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Woese C. R., Dobson M. E., Weiss E. A common origin of rickettsiae and certain plant pathogens. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):556–558. doi: 10.1126/science.3931222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Coolbaugh J. C., Williams J. C. Separation of viable Rickettsia typhi from yolk sac and L cell host components by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):456–463. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.456-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Dasch G. A., Kang Y. H., Westfall H. N. Substrate utilization by Ehrlichia sennetsu and Ehrlichia risticii separated from host constituents by renografin gradient centrifugation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5012–5017. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5012-5017.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Williams J. C., Dasch G. A., Kang Y. H. Energy metabolism of monocytic Ehrlichia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1674–1678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D., Oyaizu Y., Oyaizu H., Olsen G. J., Woese C. R. Mitochondrial origins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4443–4447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


