Abstract
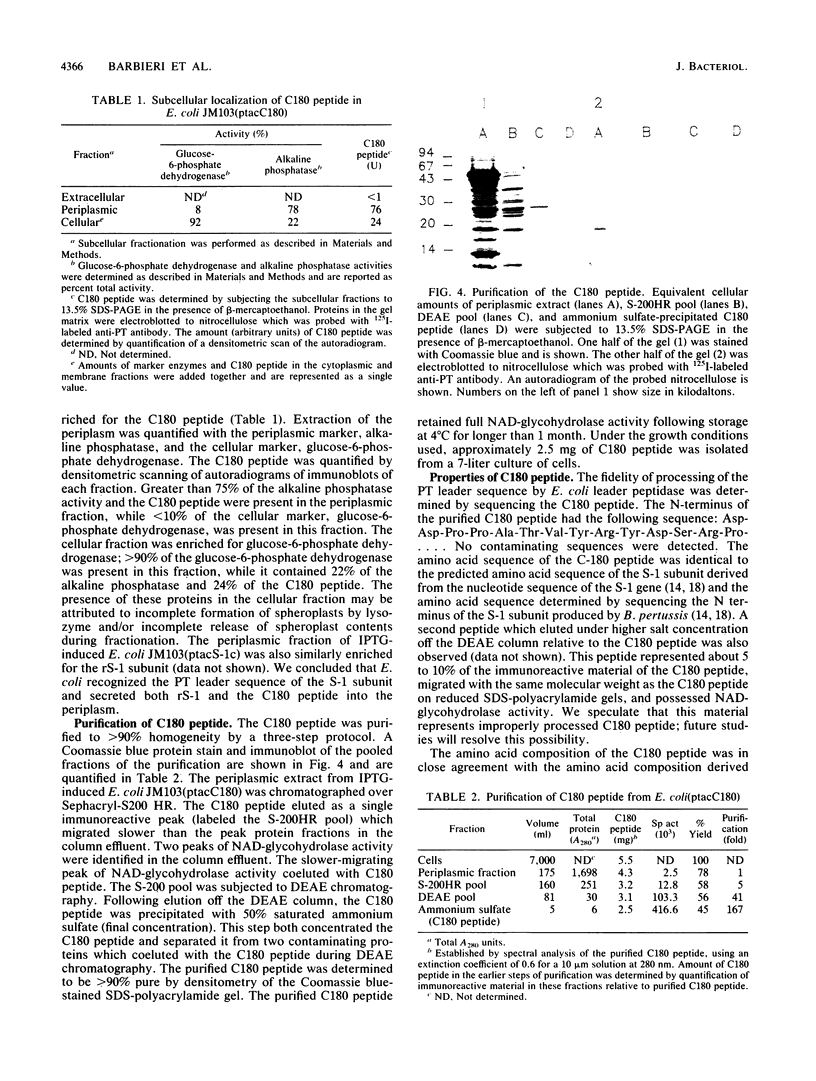
The structural gene of the S-1 subunit of pertussis toxin (rS-1) and the catalytic C180 peptide of the S-1 subunit (C180 peptide) were independently subcloned downstream of the tac promoter in Escherichia coli. Both constructions included DNA encoding for the predicted leader sequence of the S-1 subunit which was inserted between the tac promoter and the structural gene. E. coli containing the plasmids encoding for rS-1 and C180 peptide produced a peptide that reacted with anti-pertussis toxin antibody and had a molecular weight corresponding to that of the cloned gene; some degradation of rS-1 was observed. Extracts of E. coli containing plasmids encoding for rS-1 and the C180 peptide possessed ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Subcellular fractionation showed that both rS-1 and the C180 peptide were present in the periplasm, indicating that E. coli recognized the pertussis toxin peptide leader sequence. The protein sequence of the amino terminus of the C180 peptide was identical to that of authentic S-1 subunit produced by Bordetella pertussis, which showed that E. coli leader peptidase correctly processed the pertussis toxin peptide leader sequence. Two single amino acid substitutions at residue 26 (C180I-26) and residue 139 (C180S-139) which were previously shown to reduce ADP-ribosyltransferase activity were introduced into the C180 peptide. C180I-26 possessed approximately 1% of the NAD-glycohydrolase activity of the C180 peptide, suggesting that tryptophan 26 functions in the interaction of NAD with the C180 peptide. In contrast, C180S-139 possessed essentially the same level of NAD-glycohydrolase activity as the C180 peptide, suggesting that glutamic acid 139 does not function in the interaction of NAD but plays a role in a later step in the ADP-ribosyltransferase reaction.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbieri J. T., Cortina G. ADP-ribosyltransferase mutations in the catalytic S-1 subunit of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1934–1941. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1934-1941.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri J. T., Rappuoli R., Collier R. J. Expression of the S-1 catalytic subunit of pertussis toxin in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1321–1323. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1321-1323.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Chang C. P., Robinson R. R., Horwitz A. H. Escherichia coli secretion of an active chimeric antibody fragment. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1041–1043. doi: 10.1126/science.3285471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. J., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of Bordetella pertussis toxin mutants. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2465–2470. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2465-2470.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N., Cieplak W., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Sato H., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin S1 mutant with reduced enzyme activity and a conserved protective epitope. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2459776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. L., Hausman S. Z., Lindner W., Robey F. A., Manclark C. R. Structural characterization of pertussis toxin A subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17677–17682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. M., Collier R. J. Interaction of diphtheria toxin with adenylyl-(3',5')-uridine 3'-monophosphate. II. The NAD-binding site and determinants of dinucleotide affinity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15159–15162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. M., Guidi-Rontani C., Collier R. J. Exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: active, cloned toxin is secreted into the periplasmic space of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4962–4966. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4962-4966.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Sato T., Yura T. Synthesis and assembly of the membrane proteins in E. coli. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Amano T., Ui M. Modulation by islet-activating protein of adenylate cyclase activity in C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3739–3746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Cieplak W., Marchitto K. S., Sato H., Keith J. M. Activities of complete and truncated forms of pertussis toxin subunits S1 and S2 synthesized by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2546–2553. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2546-2553.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Bartoloni A., Perugini M., Rappuoli R. Expression and immunological properties of the five subunits of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):963–967. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.963-967.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Rappuoli R. Promoter of the pertussis toxin operon and production of pertussis toxin. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2843–2846. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2843-2846.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Bartoloni A., Prugnola A., Silvestri S., Rappuoli R. Subunit S1 of pertussis toxin: mapping of the regions essential for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7521–7525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runeberg-Nyman K., Engström O., Löfdahl S., Ylöstalo S., Sarvas M. Expression and secretion of pertussis toxin subunit S1 in Bacillus subtilis. Microb Pathog. 1987 Dec;3(6):461–468. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Izumiya K., Sato H., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Role of antibody to leukocytosis-promoting factor hemagglutinin and to filamentous hemagglutinin in immunity to pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1223–1231. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1223-1231.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerra A., Plückthun A. Assembly of a functional immunoglobulin Fv fragment in Escherichia coli. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1038–1041. doi: 10.1126/science.3285470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]