Abstract
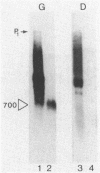
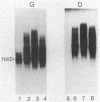
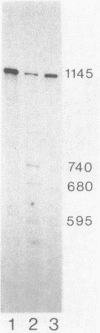
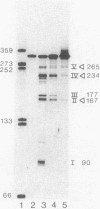
Previous genetic analysis showed that the polar effects of mutations in the hisG cistron of Salmonella typhimurium are dependent on the presence of a single putative transcription termination element within the hisG gene. In fact, all proximal mutations causing translation termination are strongly polar, whereas distal ones are not. The element was mapped by isolating mutations able to relieve the polar phenotype, and they were found to be small deletions in the region downstream of the translational stop codon (M. S. Ciampi and J. R. Roth, Genetics 118:193-202, 1988). In this study, we analyzed the his-specific RNAs synthesized in vivo in different strains harboring the polar frameshift hisG2148 mutation. The nature of the polarity effects is clearly transcriptional, since shorter RNA molecules were produced. When the hisG2148 mutation was transferred in a rho background or in strains harboring the small distal deletions, an increase in readthrough transcription was observed. The transcriptional termination element was characterized in more detail by performing high-resolution S1 nuclease mapping experiments. This analysis showed that (i) termination or exonucleolytic degradation following termination produced transcripts with heterogeneous 3' ends; (ii) this process is dependent on the transcription termination factor Rho, since relief of termination occurs in a rho background; and (iii) the element appears to function as a transcription terminator, at least to some extent, even in the course of active translation of the hisG cistron.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alifano P., Ciampi M. S., Nappo A. G., Bruni C. B., Carlomagno M. S. In vivo analysis of the mechanisms responsible for strong transcriptional polarity in a "sense" mutant within an intercistronic region. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Gross C. A., Watanabe K. K., Burgess R. R. The operon that encodes the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase also encodes ribosomal protein S21 and DNA primase in E. coli K12. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):335–349. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90453-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno M. S., Blasi F., Bruni C. B. Gene organization in the distal part of the Salmonella typhimurium histidine operon and determination and sequence of the operon transcription terminator. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00425756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno M. S., Chiariotti L., Alifano P., Nappo A. G., Bruni C. B. Structure and function of the Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli K-12 histidine operons. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):585–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampi M. S., Roth J. R. Polarity effects in the hisG gene of salmonella require a site within the coding sequence. Genetics. 1988 Feb;118(2):193–202. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.2.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampi M. S., Schmid M. B., Roth J. R. Transposon Tn10 provides a promoter for transcription of adjacent sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Wolska K. Transcription antitermination in vitro by lambda N gene product: requirement for a phage nut site and the products of host nusA, nusB, and nusE genes. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90537-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Adhya S., Gottesman M., Pastan I. Effect of Rho on transcription of bacterial operons. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):260–264. doi: 10.1038/newbio241260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink G. R., Martin R. G. Translation and polarity in the histidine operon. II. Polarity in the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90246-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. R. Evidence that a nucleotide sequence, "boxA," is involved in the action of the NusA protein. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. R., Georgopoulos C., Tilly K., Herskowitz I., Banuett F. Interactions of bacteriophage and host macromolecules in the growth of bacteriophage lambda. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):299–325. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.299-325.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M. Repair of overlapping DNA termini. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):63–64. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., McLimont M., Hanly S. Termination of transcription by nusA gene protein of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):215–220. doi: 10.1038/292215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisolia V., Carlomagno M. S., Bruni C. B. Cloning and expression of the distal portion of the histidine operon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):692–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.692-700.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. E., Hartman Z., Stahl R. C. Classification and mapping of spontaneous and induced mutations in the histidine operon of Salmonella. Adv Genet. 1971;16:1–34. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60352-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe I., Johnston H. M., Biek D., Roth J. R. A refined map of the hisG gene of Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1979 May;92(1):17–26. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housley P. R., Leavitt A. D., Whitfield H. J. Genetic analysis of a temperature-sensitive Salmonella typhimurium rho mutant with an altered rho-associated polycytidylate-dependent adenosine triphosphatase activity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):13–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.13-24.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Roth J. R. DNA sequence changes of mutations altering attenuation control of the histidine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):735–756. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Roth J. R. Histidine mutants requiring adenine: selection of mutants with reduced hisG expression in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1979 May;92(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Silbert D. F., Smith W. E., Whitfield H. J., Jr Polarity in the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Talal N. Translation and polarity in the histidine operon. IV. Relation of polarity to map position in hisC. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 14;36(2):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B., Hans Hopschneider P. Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Bear D. G., Litchman B. L., von Hippel P. H. RNA sequence and secondary structure requirements for rho-dependent transcription termination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3739–3754. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton W. A., Beckwith J. R., Zipser D., Brenner S. Nonsense mutants and polarity in the lac operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):290–296. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Bruni C. B., Martin R. G., Terry W. An intercistronic region in the histidine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 28;69(3):427–452. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. Phage P22-mutants with increased or decreased transduction abilities. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00270447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Remaut E., Fiers W. Inefficient translation initiation causes premature transcription termination in the lacZ gene. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):711–718. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90837-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]