Abstract
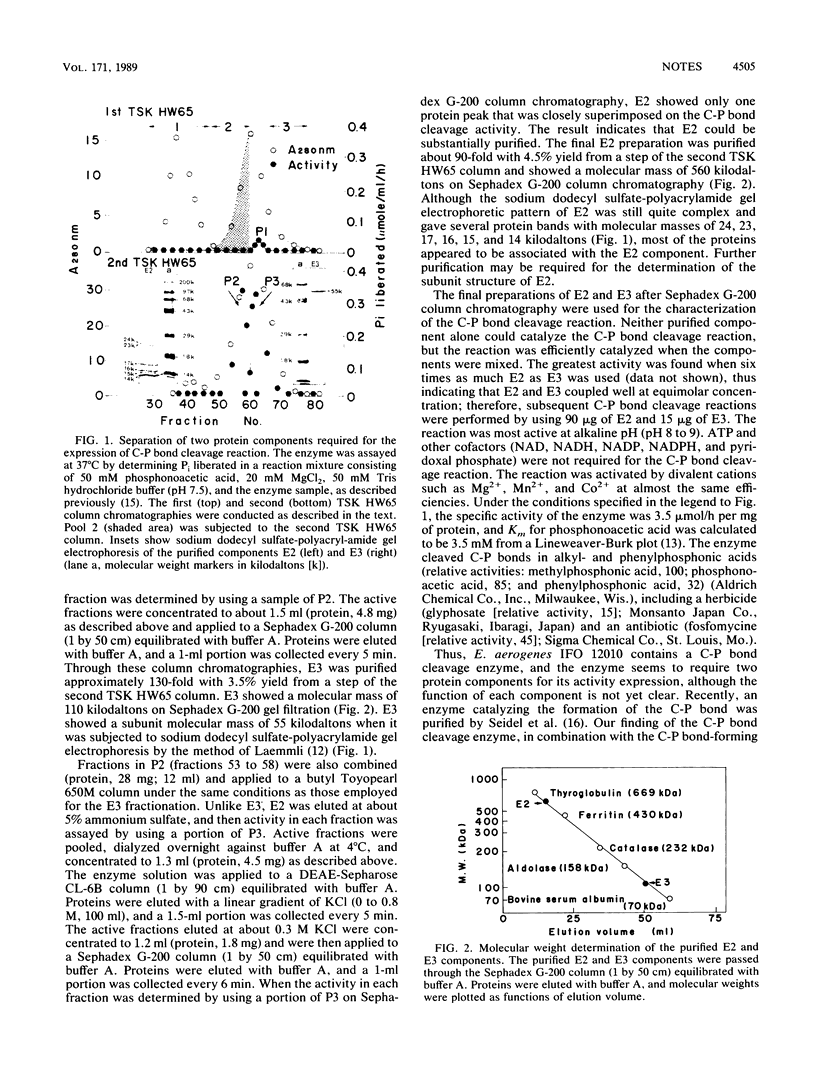
Enterobacter aerogenes IFO 12010 contains a carbon-phosphorus (C-P) bond cleavage enzyme catalyzing the liberation of inorganic phosphate from various alkyl- and phenylphosphonic acids. The enzyme in the bacterium was found to be composed of two physically different protein components, E2 and E3. The molecular weights of E2 and E3 were 560,000 and 110,000, respectively, and E3 was resolved into two apparently homogeneous subunits. Neither component alone could catalyze the C-P bond cleavage reaction, but the reaction was efficiently catalyzed when the components were mixed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balthazor T. M., Hallas L. E. Glyphosate-degrading microorganisms from industrial activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):432–434. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.432-434.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. M., Daughton C. G., Alexander M. Benzene from bacterial cleavage of the carbon-phosphorus bond of phenylphosphonates. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):453–455. doi: 10.1042/bj1840453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. M., Daughton C. G., Alexander M. Phosphonate utilization by bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):85–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.85-90.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughton C. G., Cook A. M., Alexander M. Phosphate and soil binding: factors limiting bacterial degradation of ionic phosphorus-containing pesticide metabolites. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):605–609. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.605-609.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORIGUCHI M., KANDATSU M. Isolation of 2-aminoethane phosphonic acid from rumen protozoa. Nature. 1959 Sep 19;184(Suppl 12):901–902. doi: 10.1038/184901b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Nauze J. M., Coggins J. R., Dixon H. B. Aldolase-like imine formation in the mechanism of action of phosphonoacetaldehyde hydrolase. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):409–411. doi: 10.1042/bj1650409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Nauze J. M., Rosenberg H., Shaw D. C. The enzymic cleavage of the carbon-phosphorus bond: purification and properties of phosphonatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 15;212(2):332–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Nauze J. M., Rosenberg H. The identification of 2-phosphonoacetaldehyde as an intermediate in the degradation of 2-aminoethylphosphonate by Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 15;165(3):438–447. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTALERZ P., WIECZOREK Z., KOCHMAN M. UTILIZATION OF CARBON-BOUND PHOSPHORUS BY MICROORGANISMS. Acta Biochim Pol. 1965;12:151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata K., Higaki N., Kimura A. Detection of carbon-phosphorus lyase activity in cell free extracts of Enterobacter aerogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):190–195. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel H. M., Freeman S., Seto H., Knowles J. R. Phosphonate biosynthesis: isolation of the enzyme responsible for the formation of a carbon-phosphorus bond. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):457–458. doi: 10.1038/335457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Shames S. L., Venditti C. P., Walsh C. T. Bacterial carbon-phosphorus lyase: products, rates, and regulation of phosphonic and phosphinic acid metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):710–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.710-717.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELEZNICK L. D., MYERS T. C., TITCHENER E. B. GROWTH OF ESCHERICHIA COLI ON METHYL- AND ETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACIDS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 15;78:546–547. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90921-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




