Abstract
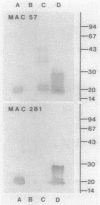
Monoclonal antibody AFRC MAC 203 recognizes a developmentally regulated lipopolysaccharide antigen in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae 3841. Transposon-induced mutants that constitutively expressed MAC 203 antigen were isolated. These strains were morphologically normal, showed no gross abnormalities in lipopolysaccharide size distribution on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, and induced normal nitrogen-fixing nodules. However, the mutants lacked lipopolysaccharide epitopes recognized by another rat monoclonal antibody, AFRC MAC 281, suggesting that the corresponding epitopes may be interconverted or share a common precursor. In conjugational crosses, the transposon insertion associated with both the loss of MAC 281 antigen and the constitutive expression of MAC 203 antigen showed linkage to the chromosomal rif allele. A derivative of strain 3841 with a deletion spanning the nod-fix region of the symbiotic plasmid showed no altered expression pattern for MAC 203 antigen, suggesting that the relevant genetic determinants map to genomic sites that are not associated with nifA or any known genes on the symbiotic plasmid.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Butcher G. W., Galfre G., Wood E. A., Brewin N. J. Physical association between the peribacteroid membrane and lipopolysaccharide from the bacteroid outer membrane in Rhizobium-infected pea root nodule cells. J Cell Sci. 1986 Sep;85:47–61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.85.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W. Heterogeneity of Rhizobium lipopolysaccharides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1012–1017. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1012-1017.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Hollingsworth R. L., Dazzo F. B. A core oligosaccharide component from the lipopolysaccharide of Rhizobium trifolii ANU843. Carbohydr Res. 1988 May 1;176(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(88)84064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Kalembasa S., Turowski D., Pachori P., Noel K. D. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from a Rhizobium phaseoli mutant that is defective in infection thread development. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4923–4928. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4923-4928.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Sanders R. E., Napoli C., Albersheim P. Host-Symbiont Interactions: III. Purification and Partial Characterization of Rhizobium Lipopolysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1978 Dec;62(6):912–917. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.6.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cava J. R., Elias P. M., Turowski D. A., Noel K. D. Rhizobium leguminosarum CFN42 genetic regions encoding lipopolysaccharide structures essential for complete nodule development on bean plants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.8-15.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Truchet G. L., Sherwood J. E., Hrabak E. M., Abe M., Pankratz S. H. Specific phases of root hair attachment in the Rhizobium trifolii-clover symbiosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1140–1150. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1140-1150.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Virts E., Palomares A., Kim C. H. The nifA gene of Rhizobium meliloti is oxygen regulated. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3217–3223. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3217-3223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie J. A., Ma Q. S., Knight C. D., Hombrecher G., Johnston A. W. Cloning of the symbiotic region of Rhizobium leguminosarum: the nodulation genes are between the nitrogenase genes and a nifA-like gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):947–952. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geremia R. A., Cavaignac S., Zorreguieta A., Toro N., Olivares J., Ugalde R. A. A Rhizobium meliloti mutant that forms ineffective pseudonodules in alfalfa produces exopolysaccharide but fails to form beta-(1----2) glucan. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):880–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.880-884.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C. Removal of gram-negative endotoxin from solutions by affinity chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 29;61(3):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Schmidt J., Wieneke U., Krüssmann H. D., Schell J. Transmembrane orientation and receptor-like structure of the Rhizobium meliloti common nodulation protein NodC. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):583–588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston A. W., Beringer J. E. Identification of the rhizobium strains in pea root nodules using genetic markers. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):343–350. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannenberg E. L., Brewin N. J. Expression of a cell surface antigen from Rhizobium leguminosarum 3841 is regulated by oxygen and pH. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4543–4548. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4543-4548.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijne J. W., Smit G., Díaz C. L., Lugtenberg B. J. Lectin-enhanced accumulation of manganese-limited Rhizobium leguminosarum cells on pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2994–3000. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2994-3000.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Signer E. R., Walker G. C. Exopolysaccharide-deficient mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that form ineffective nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6231–6235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N. Osmotic adaptation by gram-negative bacteria: possible role for periplasmic oligosaccharides. Science. 1986 Jan 3;231(4733):48–51. doi: 10.1126/science.3941890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Sanchez A., Fernandez L., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A. Rhizobium phaseoli symbiotic mutants with transposon Tn5 insertions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.148-155.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Vandenbosch K. A., Kulpaca B. Mutations in Rhizobium phaseoli that lead to arrested development of infection threads. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1392–1401. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1392-1401.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. G., Wells B., Brewin N. J., Wood E., Knight C. D., Downie J. A. The legume-Rhizobium symbiosis: a cell surface interaction. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1985;2:317–331. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1985.supplement_2.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonejans E., Expert D., Toussaint A. Characterization and virulence properties of Erwinia chrysanthemi lipopolysaccharide-defective, phi EC2-resistant mutants. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4011–4017. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4011-4017.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R., O'Connell M., Labes M., Pühler A. Plasmid vectors for the genetic analysis and manipulation of rhizobia and other gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1986;118:640–659. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)18106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit G., Kijne J. W., Lugtenberg B. J. Involvement of both cellulose fibrils and a Ca2+-dependent adhesin in the attachment of Rhizobium leguminosarum to pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4294–4301. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4294-4301.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VandenBosch K. A., Brewin N. J., Kannenberg E. L. Developmental regulation of a Rhizobium cell surface antigen during growth of pea root nodules. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4537–4542. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4537-4542.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virts E. L., Stanfield S. W., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. S. Common regulatory elements control symbiotic and microaerobic induction of nifA in Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3062–3065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]