Abstract
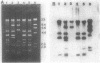
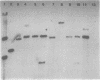
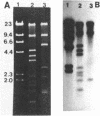
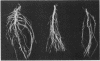
Ten independently generated mutants of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar phaseoli CFN42 isolated after Tn5 mutagenesis formed nonmucoid colonies on all agar media tested and lacked detectable production of the normal acidic exopolysaccharide in liquid culture. The mutants were classified into three groups. Three mutants harbored Tn5 insertions on a 3.6-kilobase-pair EcoRI fragment and were complemented to have normal exopolysaccharide production by cosmids that shared an EcoRI fragment of this size from the CFN42 genome. The Tn5 inserts of five other mutants appeared to be located on a second, slightly smaller EcoRI fragment. Attempts to complement mutants of this second group with cloned DNA were unsuccessful. The mutations of the other two mutants were located in apparently adjacent EcoRI fragments carried on two cosmids that complemented those two mutants. The latter two mutants also lacked O-antigen-containing lipopolysaccharides and induced underdeveloped nodules that lacked nitrogenase activity on bean plants. The other eight mutants had normal lipopolysaccharides and wild-type symbiotic proficiencies on bean plants. Mutants in each of these groups were mated with R. leguminosarum strains that nodulated peas (R. leguminosarum biovar viciae) or clovers (R. leguminosarum biovar trifolii). Transfer of the Tn5 mutations resulted in exopolysaccharide-deficient R. leguminosarum biovar viciae or R. leguminosarum biovar trifolii transconjugants that were symbiotically deficient in all cases. These results support earlier suggestions that successful symbiosis with peas or clovers requires that rhizobia be capable of acidic exopolysaccharide production, whereas symbiosis with beans does not have this requirement.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum E. R., Thompson D. V., Idler K., Chartrain N. Rhizobium japonicum USDA 191 has two nodD genes that differ in primary structure and function. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):12–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.12-20.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthakur D., Barker R. F., Latchford J. W., Rossen L., Johnston A. W. Analysis of pss genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum required for exopolysaccharide synthesis and nodulation of peas: their primary structure and their interaction with psi and other nodulation genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):155–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00333413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthakur D., Johnston A. W. Sequence of psi, a gene on the symbiotic plasmid of Rhizobium phaseoli which inhibits exopolysaccharide synthesis and nodulation and demonstration that its transcription is inhibited by psr, another gene on the symbiotic plasmid. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):149–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00331502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Kalembasa S., Turowski D., Pachori P., Noel K. D. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from a Rhizobium phaseoli mutant that is defective in infection thread development. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4923–4928. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4923-4928.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Lee R. P. A Comparison of the Surface Polysaccharides from Rhizobium leguminosarum 128C53 smrif with the Surface Polysaccharides from Its Exo Mutant. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):223–228. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cava J. R., Elias P. M., Turowski D. A., Noel K. D. Rhizobium leguminosarum CFN42 genetic regions encoding lipopolysaccharide structures essential for complete nodule development on bean plants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.8-15.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic S. P., Chen H., Batley M., Redmond J. W., Rolfe B. G. Nitrogen fixation ability of exopolysaccharide synthesis mutants of Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 and Rhizobium trifolii is restored by the addition of homologous exopolysaccharides. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):53–60. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.53-60.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Hirsch A. M., Leigh J. A., Johansen E., Kuldau G. A., Deegan S., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. Symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that uncouple plant from bacterial differentiation. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazebrook J., Walker G. C. A novel exopolysaccharide can function in place of the calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide in nodulation of alfalfa by Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):661–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90588-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Reed J. W., Hanks J. F., Hirsch A. M., Walker G. C. Rhizobium meliloti mutants that fail to succinylate their calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide are defective in nodule invasion. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Signer E. R., Walker G. C. Exopolysaccharide-deficient mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that form ineffective nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6231–6235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S., Reed J. W., Himawan J., Walker G. C. Genetic analysis of a cluster of genes required for synthesis of the calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4239–4248. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4239-4248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Rick P. D. Size heterogeneity of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides in outer membranes and culture supernatant membrane fragments. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.630-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Brill W. J. Diversity and Dynamics of Indigenous Rhizobium japonicum Populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):931–938. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.931-938.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Stacey G., Tandon S. R., Silver L. E., Brill W. J. Rhizobium japonicum mutants defective in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):485–494. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.485-494.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Vandenbosch K. A., Kulpaca B. Mutations in Rhizobium phaseoli that lead to arrested development of infection threads. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1392–1401. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1392-1401.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plazinski J., Cen Y. H., Rolfe B. G. General method for the identification of plasmid species in fast-growing soil microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):1001–1003. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.1001-1003.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnoky P., Grosskopf E., Ha D. T., Kiss G. B., Kondorosi A. Rhizobium fix genes mediate at least two communication steps in symbiotic nodule development. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):597–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Signer E. R. Positive selection of nodulation-deficient Rhizobium phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):83–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.83-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne L., Tansey L., Pollock T. J. Clustering of mutations blocking synthesis of xanthan gum by Xanthomonas campestris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3593–3600. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3593-3600.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbosch K. A., Noel K. D., Kaneko Y., Newcomb E. H. Nodule initiation elicited by noninfective mutants of Rhizobium phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):950–959. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.950-959.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan H. J., Levery S. B., Lee C. C., Leigh J. A. A second exopolysaccharide of Rhizobium meliloti strain SU47 that can function in root nodule invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3055–3059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]