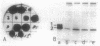Abstract
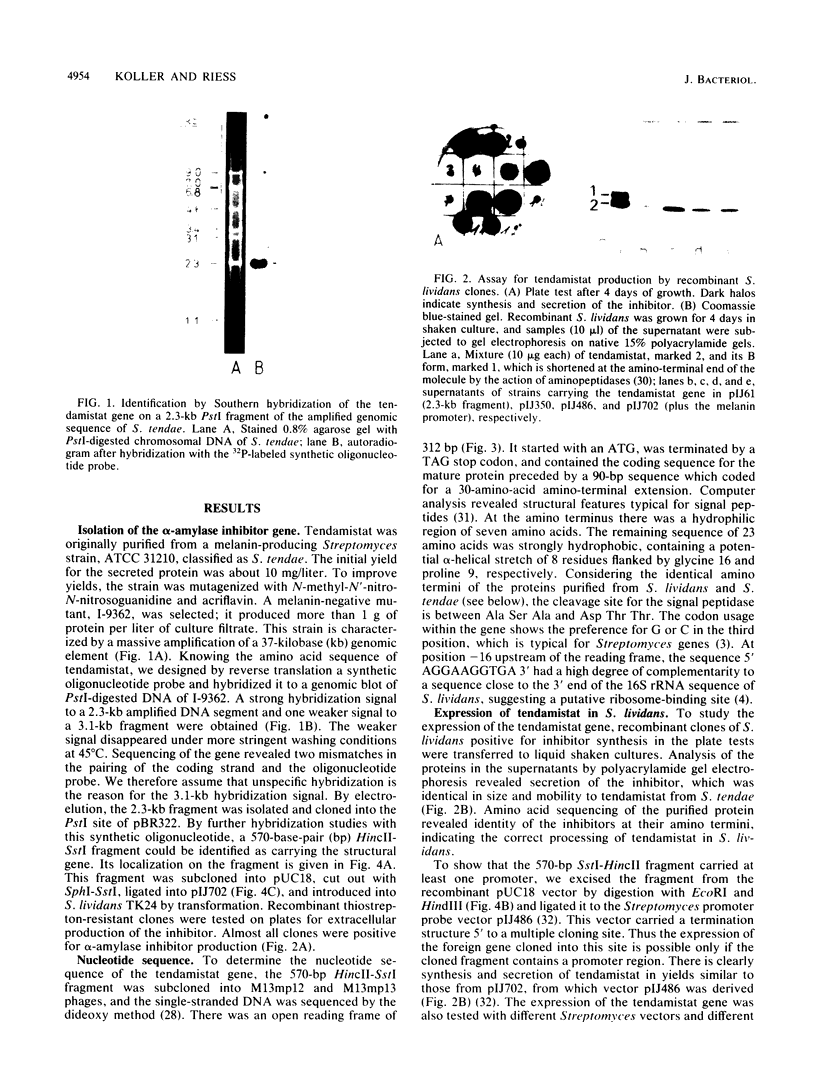
The coding region for a secreted proteinaceous inhibitor of the human alpha-amylase (tendamistat; HOE 467) was identified by using a synthetic oligonucleotide probe. The gene is part of a 37-kilobase amplified genomic sequence found in an overproducing mutant of Streptomyces tendae. After subcloning, sequence analysis revealed an open reading frame of 312 base pairs preceded by a putative ribosome-binding site. The reading frame is 30 codons longer than necessary for the mature protein. This sequence coded for an amino-terminal extension of tendamistat and shows typical features of a signal peptide. After being cloned into Streptomyces vector plasmids and transformed to the heterologous host, Streptomyces lividans TK24, the gene was expressed, and the alpha-amylase inhibitor was correctly processed and secreted into the culture medium. The amount of secreted protein was dependent on the gene dosage and on the promoter arrangement.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aschauer H., Vértesy L., Braunitzer G. Die Sequenz des alpha-Amylaseinhibitors Hoe-467 A (alphs-Amylaseinaktivator Hoe-467 A) aus Streptomyces tendae 4158. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Apr;362(4):465–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R., Sukatsch D. A. Continuous-flow determination of an alpha-amylase inactivator in fermentation samples using a ferricyanide reagent. Anal Biochem. 1984 Mar;137(2):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Cohen S. N. Gene expression in Streptomyces: construction and application of promoter-probe plasmid vectors in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(2):265–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00331128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttner M J, Fearnley I M, Bibb M J. The agarase gene (dagA) of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):101–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00329843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann O., Vértesy L., Braunitzer G. The primary structure of alpha-amylase inhibitor Z-2685 from Streptomyces parvullus FH-1641. Sequence homology between inhibitor and alpha-amylase. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Dec;366(12):1161–1168. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Bibb M. J., Chater K. F., Kieser T. Plasmid and phage vectors for gene cloning and analysis in Streptomyces. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:116–166. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshiko S., Makabe O., Nojiri C., Katsumata K., Satoh E., Nagaoka K. Molecular cloning and characterization of the Streptomyces hygroscopicus alpha-amylase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1029–1036. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1029-1036.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline A. D., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Studies by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry of the solution conformation of the alpha-amylase inhibitor tendamistat. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 20;189(2):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. M., Virolle M. J., Chang S. Y., Chang S., Bibb M. J. alpha-Amylase gene of Streptomyces limosus: nucleotide sequence, expression motifs, and amino acid sequence homology to mammalian and invertebrate alpha-amylases. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5745–5754. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5745-5754.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai H., Hara S., Ikenaka T., Goto A., Arai M., Murao S. Amino acid sequence of protein alpha-amylase inhibitor from Streptomyces griseosporeus YM-25. J Biochem. 1985 Apr;97(4):1129–1133. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaso H., Saito S., Saito H., Takahashi H. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a Streptomyces griseosporeus proteinaceous alpha-amylase inhibitor (HaimII) gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4451–4457. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4451-4457.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pflugrath J. W., Wiegand G., Huber R., Vértesy L. Crystal structure determination, refinement and the molecular model of the alpha-amylase inhibitor Hoe-467A. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 20;189(2):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90520-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Wirth D. F., Hering C. Expression of the Streptomyces enzyme endoglycosidase H in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10640–10644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vértesy L., Oeding V., Bender R., Zepf K., Nesemann G. Tendamistat (HOE 467), a tight-binding alpha-amylase inhibitor from Streptomyces tendae 4158. Isolation, biochemical properties. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):505–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Janssen G. R., Kieser T., Bibb M. J., Buttner M. J., Bibb M. J. Construction and characterisation of a series of multi-copy promoter-probe plasmid vectors for Streptomyces using the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene from Tn5 as indicator. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):468–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00422072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. How signal sequences maintain cleavage specificity. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]