Abstract
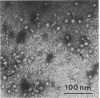
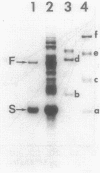
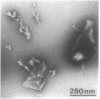
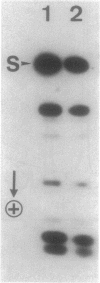
Of the 51 polypeptides detected by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the plasma membrane of the helical mollicute Spiroplasma melliferum, 21 are acylated, predominantly with myristic (14:0) and palmitic (16:0) chains. This is notably the case for spiralin, the major membrane protein of this bacterium, which contains an average of 0.7 acyl chains per polypeptide, attached very probably by ester bonds to alcohol amino acids. The amphiphilicity of spiralin was demonstrated by the behavior of the protein in charge-shift electrophoresis, its incorporation into liposomes, and its ability to form in the absence of lipids and detergents, globular protein micelles (diameter, approximately 15 nm). The presence of epitopes on the two faces of the cell membrane, as probed by antibody adsorption and crossed immunoelectrophoresis, and the strong interaction between spiralin and the intracytoplasmic fibrils show that spiralin is a transmembrane protein. The mean hydropathy of the amino acid composition of spiralin (-0.30) is on the hydrophilic side of the scale. Surprisingly, the water-insoluble core of spiralin micelles, which is the putative membrane anchor, has a still more hydrophilic amino acid composition (mean hydropathy, -0.70) and is enriched in glycine and serine residues. Taking into account all these properties, we propose a topological model for spiralin featuring a transbilayer localization with hydrophilic domains protruding on the two faces of the membrane and connected by a small domain embedded within the apolar region of the lipid bilayer. In this model, the membrane anchoring of the protein is strengthened by a covalently bound acyl chain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berzofsky J. A. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors in protein antigenic structure. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):932–940. doi: 10.1126/science.2410982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard A., Wroblewski H., Barroso G. Localization of spiralin in Escherichia coli cells transformed with the recombinant plasmid pESI. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):414–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricker T. M., Boyer M. J., Keith J., Watson-McKown R., Wise K. S. Association of lipids with integral membrane surface proteins of Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):295–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.295-301.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément J. M., Hofnung M. Gene sequence of the lambda receptor, an outer membrane protein of E. coli K12. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90392-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. M., Tully J. G., Popkin T. J., Bové J. M. Morphology, ultrastructure, and bacteriophage infection of the helical mycoplasma-like organism (Spiroplasma citri gen. nov., sp. nov.) cultured from "stubborn" disease of citrus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):367–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.367-386.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl C. E., Dahl J. S., Bloch K. Proteolipid formation in Mycoplasma capricolum. Influence of cholesterol on unsaturated fatty acid acylation of membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11814–11818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl C. E., Dahl J. S. Phospholipids as acyl donors to membrane proteins of Mycoplasma capricolum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10771–10776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl C. E., Sacktor N. C., Dahl J. S. Acylated proteins in Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):445–447. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.445-447.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. J., Katznel A., Razin S., Rottem S. Spiroplasma membrane lipids. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):118–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.118-122.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Sissenstein R., McManus T. T., Woodward J. E., Lee I. M., Mudd J. B. Lipid composition and lipid metabolism of Spiroplasma citri. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):946–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.946-954.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Smith K. J., Gallimore P. H. Purification and characterisation of the protein encoded by the activated human N-ras gene and its membrane localisation. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallen R. M. Colorimetric estimation of phospholipids in aqueous dispersions: addendum. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1981 Mar;4(3-4):241–242. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(81)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Hara H., Suzuki H., Hirota Y. Lipid modification of Escherichia coli penicillin-binding protein 3. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5392–5395. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5392-5395.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Sarvas M., Simons K. Asymmetric and symmetric membrane reconstitution by detergent elimination. Studies with Semliki-Forest-virus spike glycoprotein and penicillinase from the membrane of Bacillus licheniformis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Charge shift electrophoresis: simple method for distinguishing between amphiphilic and hydrophilic proteins in detergent solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):529–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Hjertén S. Localization of the Tween 20-soluble membrane proteins of Acholeplasma laidlawii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G., Gerber G. E., Herlihy W. C., Gray C. P., Anderegg R. J., Nihei K., Biemann K. Amino acid sequence of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Gutierrez L., McKay I. A., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Dynamic fatty acylation of p21N-ras. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3353–3357. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02656.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo A. K., Edelman M. Intramembrane translocation and posttranslational palmitoylation of the chloroplast 32-kDa herbicide-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1497–1501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström S., Johansson K. E., Wieslander A. Selective acylation of membrane proteins in Acholeplasma laidlawii. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):85–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Bergmans H., van Mansfeld F., Lugtenberg B. Complete nucleotide sequence of phoE, the structural gene for the phosphate limitation inducible outer membrane pore protein of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):513–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Hasin M., Ne'eman Z., Rottem S. Isolation, chemical composition, and ultrastructural features of the cell membrane of the mycoplasma-like organism Spiroplasma citri. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1421–1435. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1421-1435.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Molecular biology and genetics of mycoplasmas (Mollicutes). Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):419–455. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.419-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The mycoplasmas. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):414–470. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.414-470.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Adar L., Gross Z., Ne'eman Z., Davis P. J. Incorporation and modification of exogenous phosphatidylcholines by mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):299–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.299-304.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Hasin M., Razin S. Binding of proteins to mycoplasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 16;298(4):876–886. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Helenius A., Leonard K., Sarvas M., Gething M. J. Formation of protein micelles from amphiphilic membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5306–5310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck G., Leuthard P., Bürk R. R. Detection of basic proteins and low molecular weight peptides in polyacrylamide gels by formaldehyde fixation. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90486-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Characterization of membrane proteins in detergent solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):133–170. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegman V., Wallbrandt P., Nyström S., Johansson K. E., Jonsson B. H., Wieslander A. Cloning and expression of Acholeplasma laidlawii membrane acyl proteins in Escherichia coli. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):408–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend R., Archer D. B., Plaskitt K. A. Purification and preliminary characterization of Spiroplasma fibrils. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):694–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.694-700.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallevik K., Jensenius J. C. A simple and reliable method for the drying of polyacrylamide slab gels. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1982 Apr;6(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(82)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewski H., Burlot R., Thomas D. Adsorption of proteins from the Spiroplasma citri cell membrane by magnesium lauroyl-sarcosinate crystals. Biochimie. 1981 Mar;63(3):177–186. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewski H., Johansson K. E., Hjérten S. Purification and characterization of spiralin, the main protein of the Spiroplasma citri membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewski H., Robic D., Thomas D., Blanchard A. Comparison of the amino acid compositions and antigenic properties of spiralins purified from the plasma membranes of different spiroplasmas. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Jan-Feb;135A(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Tokunaga M. Biogenesis of lipoproteins in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:127–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]