Abstract
A new mutant of Escherichia coli K-12 unable to grow with L-serine, glycine, and L-leucine has been isolated by lambda plac Mu insertion and shown to be deficient in L-serine deaminase activity. The corresponding gene, sdaA, has been cloned from a prototrophic strain, and the clone has been characterized and sequenced. The evidence is consistent with the hypothesis that sdaA is the structural gene for L-serine deaminase. However, other possibilities are also considered. No significant homology with previously reported DNA or protein sequences was detected.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson B. D., Ravnikar P. D., Somerville R. L. Nucleotide sequence of the 2-amino-3-ketobutyrate coenzyme A ligase (kbl) gene of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3586–3586. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer E., Silhavy T. J., Weinstock G. M. Transposable lambda placMu bacteriophages for creating lacZ operon fusions and kanamycin resistance insertions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1092–1099. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1092-1099.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. T., Newman E. B. Threonine as a carbon source for Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1150–1153. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1150-1153.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowing D. W., Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A., Woolford C., Hendrix R. W., Gross C. A. Consensus sequence for Escherichia coli heat shock gene promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J., Newman E. B. Derivation of glycine from threonine in Escherichia coli K-12 mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):810–817. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.810-817.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Gautier C. Codon usage in bacteria: correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7055–7074. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Casadaban M. J. Mini-mu bacteriophage with plasmid replicons for in vivo cloning and lac gene fusing. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):357–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.357-364.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Castilho B. A., Casadaban M. J. In vivo DNA cloning and adjacent gene fusing with a mini-Mu-lac bacteriophage containing a plasmid replicon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1480–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg S., Newman E. B. Studies on L-serine deaminase in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):53–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.53-58.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Rhee S. G., Stadtman E. R. Nonenzymatic cleavage of proteins by reactive oxygen species generated by dithiothreitol and iron. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15394–15397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A. Positive regulatory gene for temperature-controlled proteins in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):894–900. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Ahmad D., Walker C. L-Serine deaminase activity is induced by exposure of Escherichia coli K-12 to DNA-damaging agents. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):702–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.702-705.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Malik N., Walker C. L-serine degradation in Escherichia coli K-12: directly isolated ssd mutants and their intragenic revertants. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):710–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.710-715.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Miller B., Colebrook L. D., Walker C. A mutation in Escherichia coli K-12 results in a requirement for thiamine and a decrease in L-serine deaminase activity. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):272–276. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.272-276.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARDEE A. B., PRESTIDGE L. S. Induced formation of serine and threonine deaminases by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1955 Dec;70(6):667–674. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.6.667-674.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recsei P. A., Huynh Q. K., Snell E. E. Conversion of prohistidine decarboxylase to histidine decarboxylase: peptide chain cleavage by nonhydrolytic serinolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):973–977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
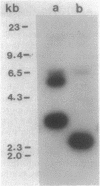
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]