Abstract
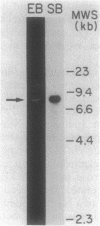
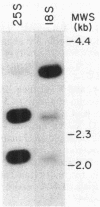
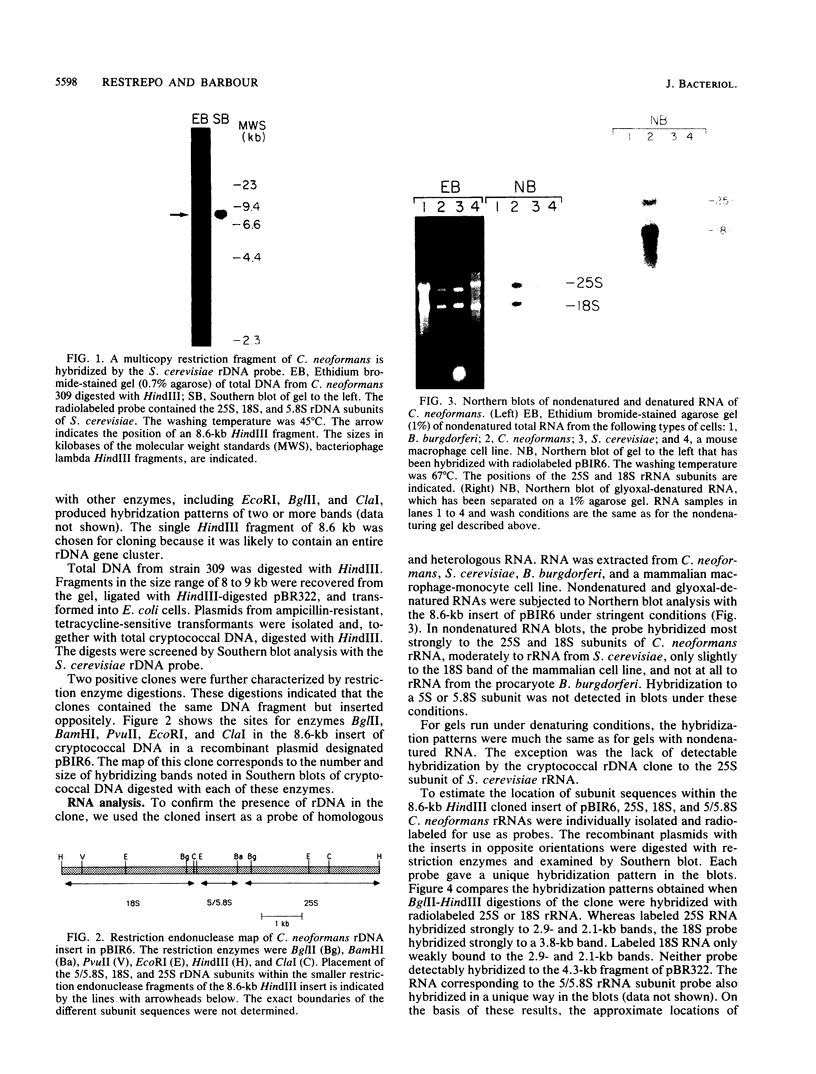
Cryptococcus neoformans is an important pathogenic fungus that has been classified as a basidiomycete. Little is known of the molecular genetics of this fungal pathogen. To begin such studies, we devised a procedure for extraction of DNA from cryptococci; this method involved the use of the cell wall-active enzyme NovoZym 234. Using cloned rDNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a probe, we identified homologous restriction fragments in a Southern blot of digested C. neoformans DNA. An 8.6-kilobase HindIII fragment that hybridized with the yeast rDNA probe was ligated with the vector pBR322 and cloned into Escherichia coli. When the fragment was used as a probe, it hybridized to the 18S and 25S rRNAs of C. neoformans in Northern (RNA) blots of native and denatured RNA. It bound at high stringency only weakly to the rRNAs of the ascomycete S. cerevisiae. The locations of the genes for 5/5.8S, 18S, and 25S subunits in the cloned fragment were identified with labeled rRNA of these different types.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg D. D. Creating a ribonuclease-free environment. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:20–24. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazin J., Jr, Kozel T. R., Lupan D. M., Burt W. R. Extracellular deoxyribonuclease production by yeasts. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):760–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.760-762.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer J. H., Farrelly F. W., Rownd R. H. Restriction endonuclease analysis of ribosomal DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Nov 17;148(3):233–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00332897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes W. E. Cryptococcal meningitis in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):624–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Nakhal H., Phaff H. J. Possible relationship between yeast deoxyribonucleases and deoxyribonucleic Acid yield. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1482–1483. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1482-1483.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A., Shadomy H. J., Jacobson E. S. Decreased virulence in stable, acapsular mutants of cryptococcus neoformans. Mycopathologia. 1982 Jul 23;79(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00636177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Járai G., Financsek I., Járai M. Characterization of the Cephalosporium acremonium ribosomal RNA genes. Gene. 1987;55(1):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. A new genus, filobasidiella, the perfect state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1975 Nov-Dec;67(6):1197–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Polacheck I., Bennett J. E. Improved diagnostic medium for separation of Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformans (serotypes A and D) and Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii (serotypes B and C). J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):535–537. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.535-537.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Henry B., Yeh Y. C. Binding of proteins from the large ribosomal subunits to 5.8 S rRNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):854–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockington R. A., Taylor G. G., Winther M., Scazzocchio C., Davies R. W. A physical map of the ribosomal DNA repeat unit of Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):135–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., D'Souza T. M., Magee P. T. Strain and species identification by restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the ribosomal DNA repeat of Candida species. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1639–1643. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1639-1643.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Necas O. Cell wall synthesis in yeast protoplasts. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):149–170. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.149-170.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R., Olsen G. J., Woese C. R. Ribosomal RNA phylogeny and the primary lines of evolutionary descent. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):325–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90315-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C., Kwon-Chung K. J. Production and regeneration of protoplasts from Cryptococcus. Sabouraudia. 1985 Feb;23(1):77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Haber J. E., Botstein D. Lethal disruption of the yeast actin gene by integrative DNA transformation. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):371–373. doi: 10.1126/science.7046050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen E. R., Nasim A. Production of protoplasts in different yeasts by mutanase. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):550–553. doi: 10.1139/m81-082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent R. D., Goewert R., Goldman W. E., Kobayashi G. S., Lambowitz A. M., Medoff G. Classification of Histoplasma capsulatum isolates by restriction fragment polymorphisms. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):813–818. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.813-818.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Kwon-Chung K. J. Genetic complementation in Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):924–929. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.924-929.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöstemeyer J. Strain-dependent variation in ribosomal DNA arrangement in Absidia glauca. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):443–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge P., de Jongh F. C., Meijers R., Steensma H. Y., Scheffers W. A. Orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis banding patterns of DNA from yeasts. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):193–204. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]