Abstract
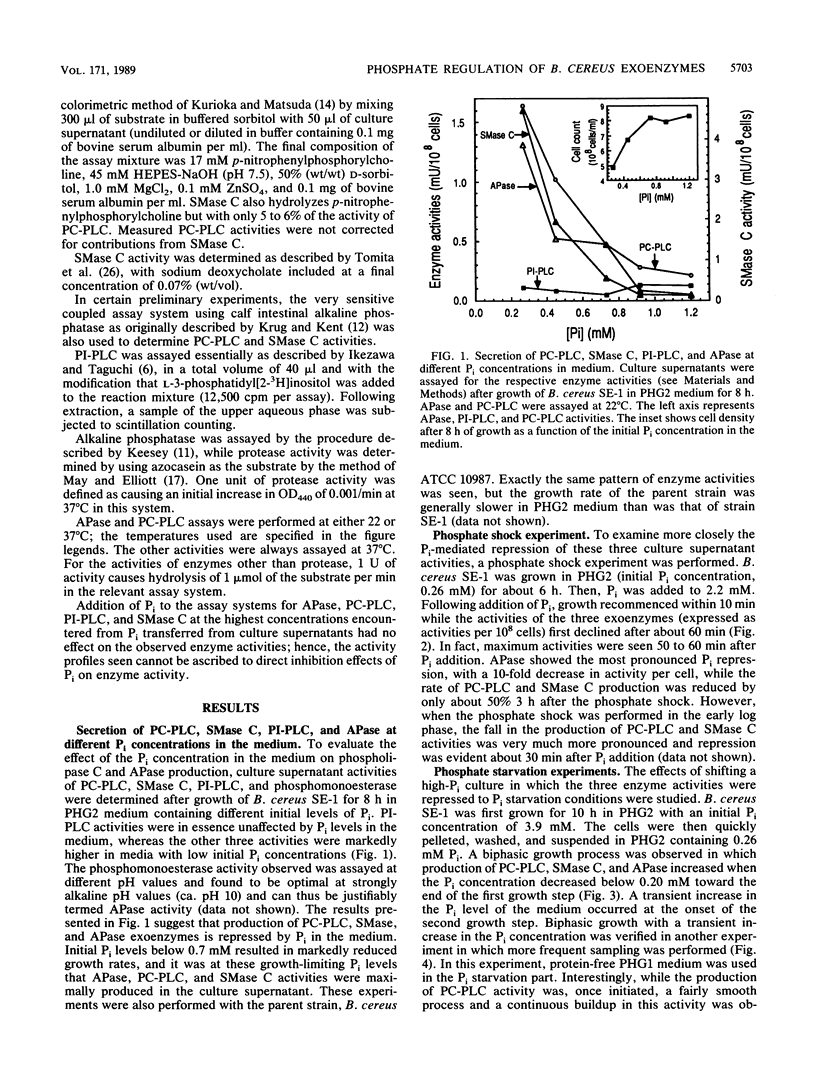
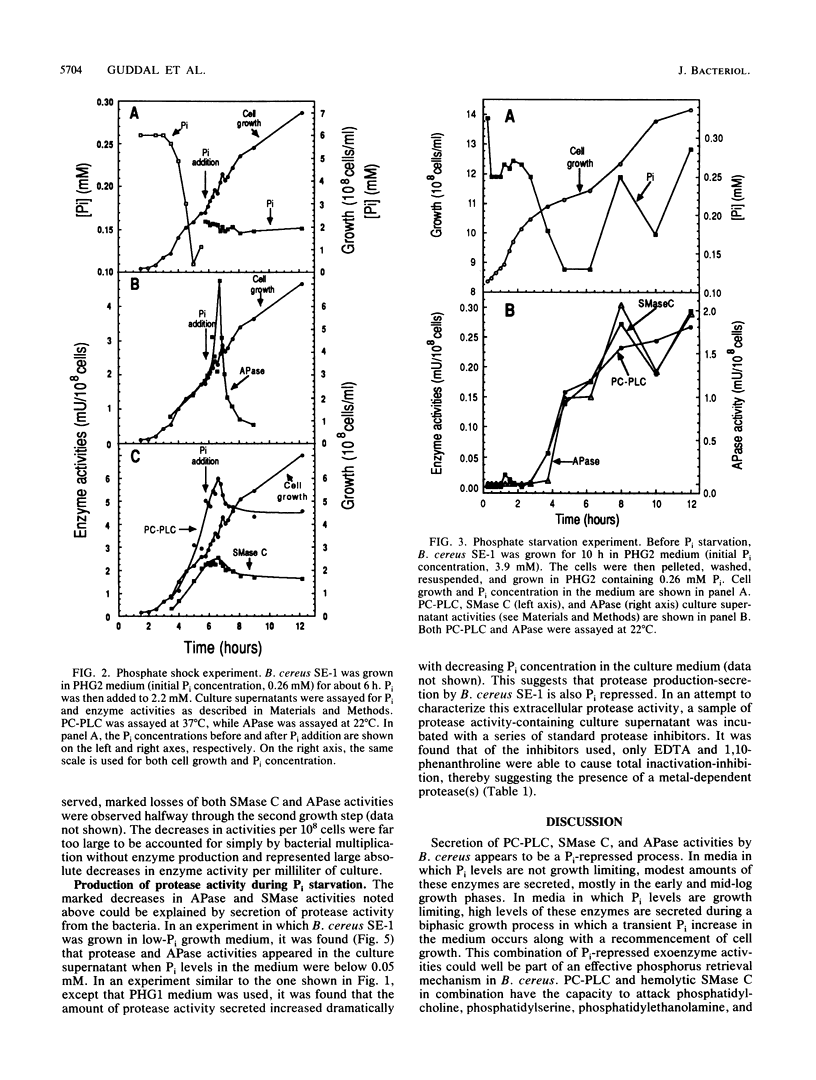
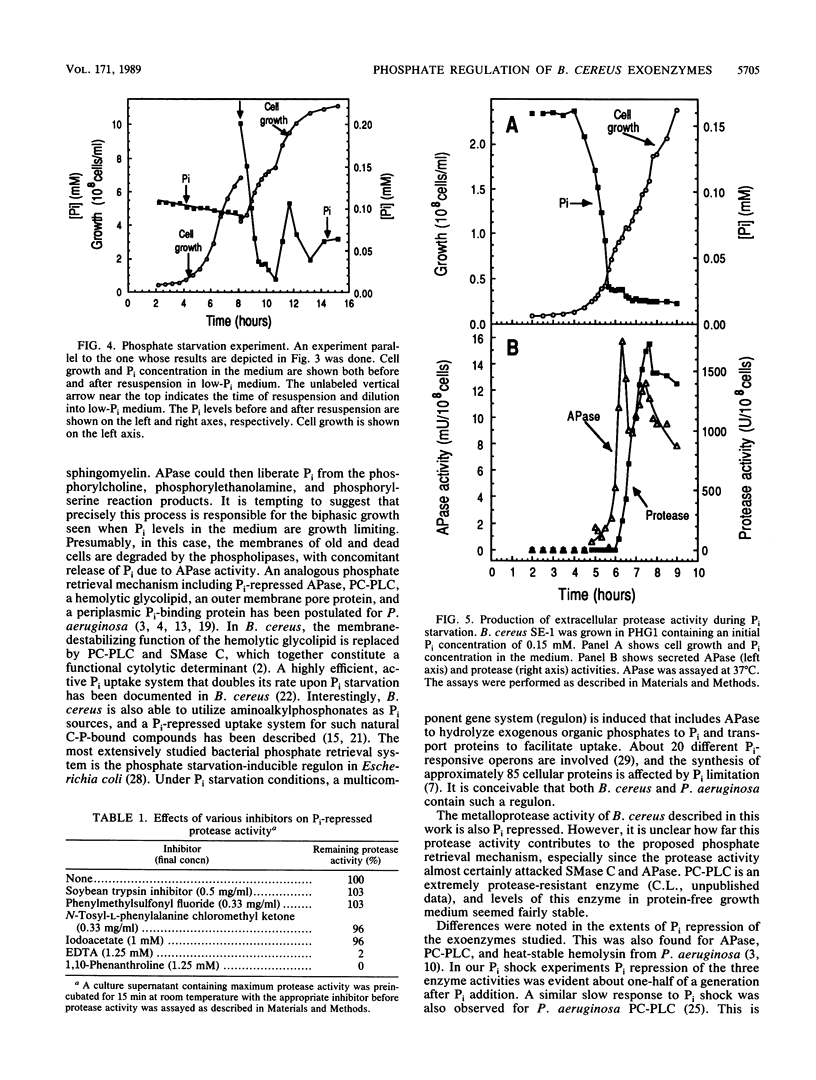
Bacillus cereus secretes three different phospholipases C. We studied the effect of Pi levels in the growth medium on the production of these exoenzymes. Production of both phosphatidylcholine-preferring phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase C was repressed by Pi in the growth medium, whereas production of phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C was unaffected. We also found that B. cereus secretes a phosphate-repressed alkaline phosphatase activity. Together with a previously reported highly efficient, active uptake system for Pi, these three phosphate-repressed exoenzyme activities seem to be part of a phosphate retrieval mechanism that operates under growth-limiting concentrations of Pi. In natural soil systems, which are the natural habitats of B. cereus, the scarcity of Pi is the major growth-limiting factor. A phosphate-repressed metalloprotease activity was also detected in culture supernatants of B. cereus. It is unclear whether this exoenzyme activity also participates in the proposed phosphate-scavenging system.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gilmore M. S., Cruz-Rodz A. L., Leimeister-Wächter M., Kreft J., Goebel W. A Bacillus cereus cytolytic determinant, cereolysin AB, which comprises the phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase genes: nucleotide sequence and genetic linkage. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):744–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.744-753.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Berka R. M., Vasil M. L. A Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant non-derepressible for orthophosphate-regulated proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):675–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.675-678.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T., Haugli F. B., Ikezawa H., Little C. Bacillus cereus strain SE-1: nucleotide sequence of the sphingomyelinase C gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10370–10370. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T., Holm T., Guddal P. H., Sletten K., Haugli F. B., Little C. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the phosphatidylcholine-preferring phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90466-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Boese-Marrazzo D. Production and properties of heat-stable extracellular hemolysin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1028-1033.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug E. L., Kent C. Assay for phospholipase C. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:347–351. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Liu P. V. Effect of the hemolysin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on phosphatides and on phospholipase c activity. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):670–674. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.670-674.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Matsuda M. Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Nauze J. M., Rosenberg H., Shaw D. C. The enzymic cleavage of the carbon-phosphorus bond: purification and properties of phosphonatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 15;212(2):332–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hégarat J. C., Anagnostopoulos C. Purification, subunit structure and properties of two repressible phosphohydrolases of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):525–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May B. K., Elliott W. H. Characteristics of extracellular protease formation by Bacillus subtilis and its control by amino acid repression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 21;157(3):607–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole K., Hancock R. E. Phosphate transport in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Involvement of a periplasmic phosphate-binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):607–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Vasil M. L. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a phosphate-regulated gene encoding a secreted hemolysin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.291-298.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., La Nauze J. M. The metabolism of phosphonates by microorganisms. The transport of aminoethylphosphonic acid in Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 13;141(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Medveczky N., La Nauze J. M. Phosphate transport in Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 14;193(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slein M. W., Logan G. F. Characterization of the Phospholipases of Bacillus cereus and Their Effects on Erythrocytes, Bone, and Kidney Cells. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):69–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.69-81.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. B., Chen C. P., Hulett F. M. Effect of cobalt on synthesis and activation of Bacillus licheniformis alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.926-933.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Hayden C. Secretion of phospholipase C by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):558–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.558-564.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Taguchi R., Ikezawa H. Molecular properties and kinetic studies on sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;704(1):90–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., McSharry R. Phosphate-controlled gene expression in Escherichia coli K12 using Mudl-directed lacZ fusions. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):347–363. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Tsukagoshi N., Udaka S., Sasaki T., Makino S., Nakamura S., Little C., Tomita M., Ikezawa H. Nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene coding for sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Comfurius P., van Deenen L. L. Complete purification and some properties of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):474–479. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90347-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


