Abstract
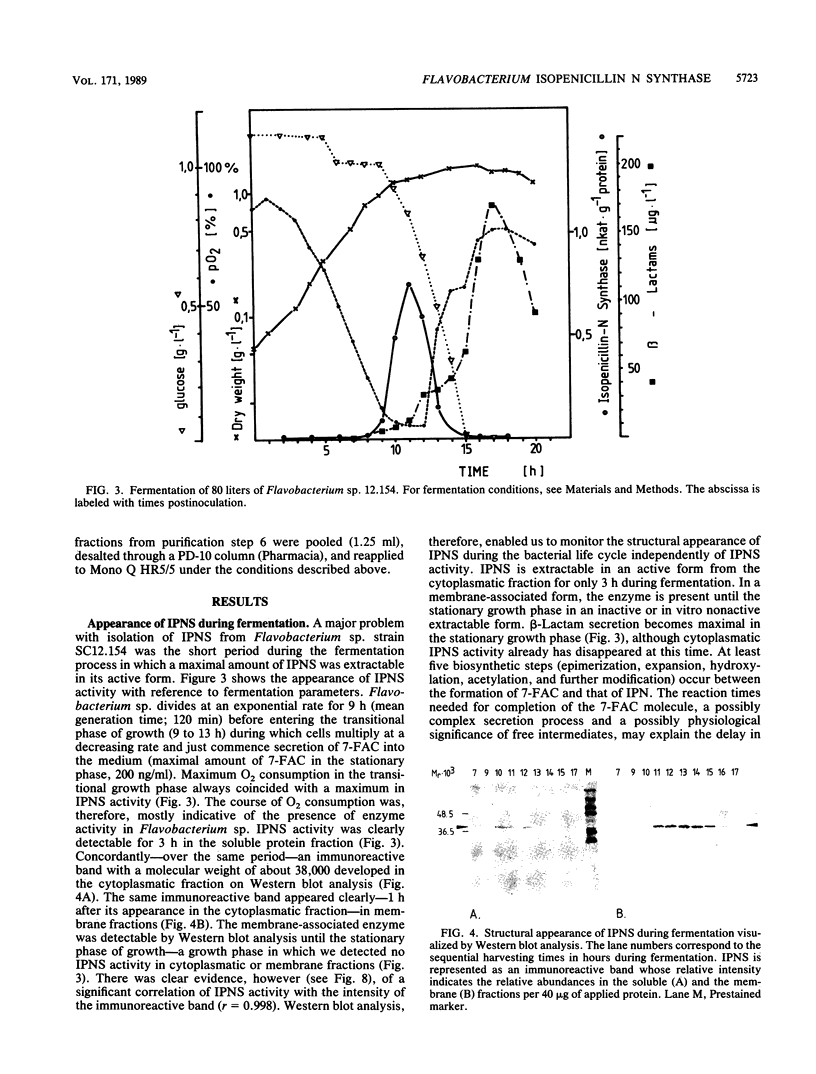
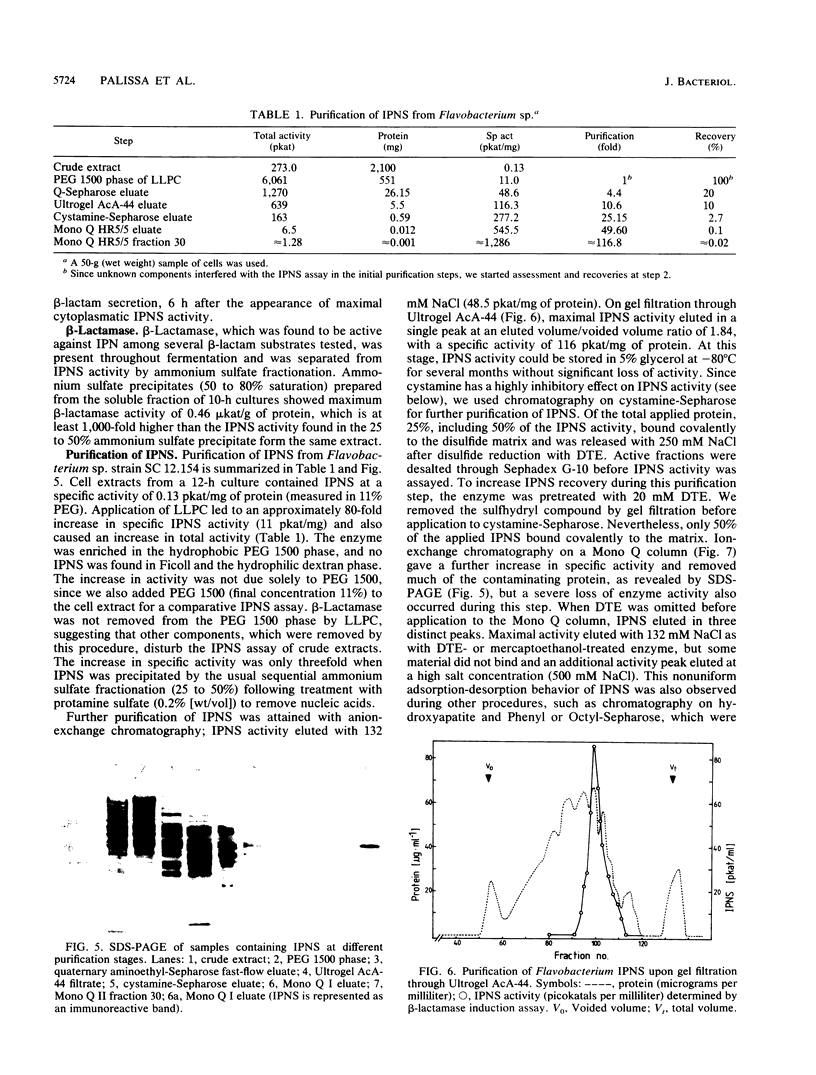
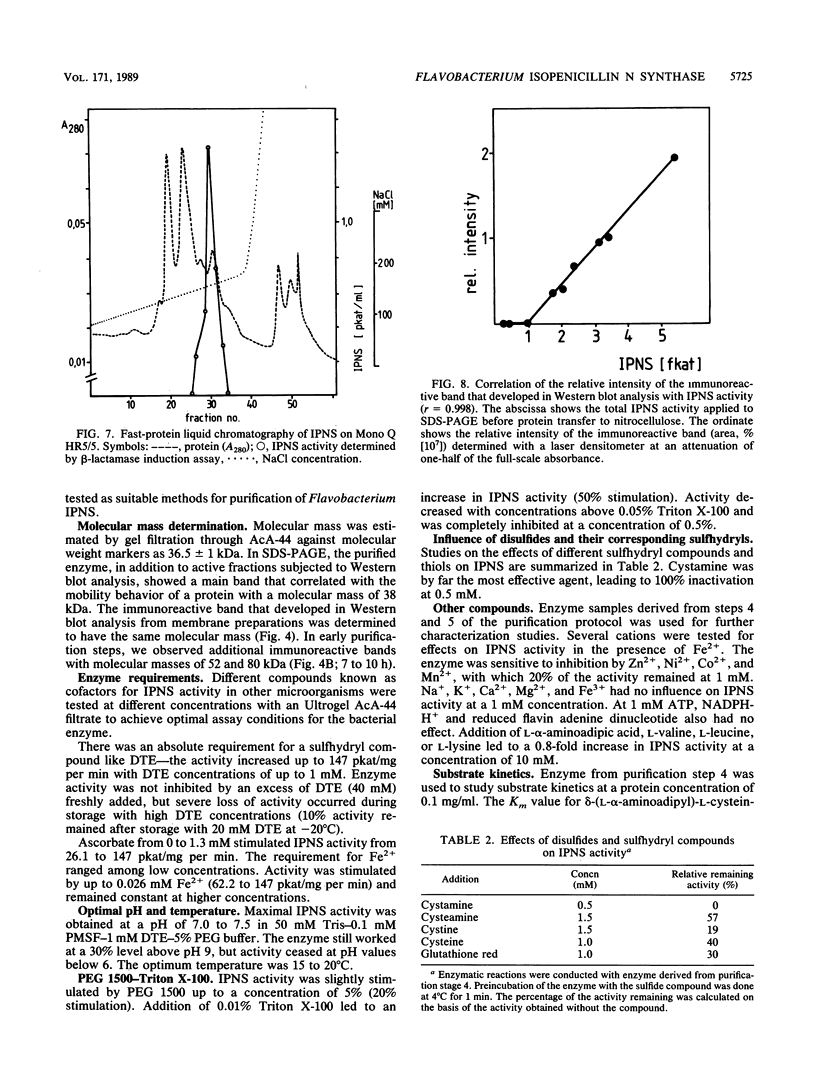
The occurrence, localization, and extraction of isopenicillin N-synthase (IPNS) were investigated in the gram-negative low-level beta-lactam producer Flavobacterium sp. strain SC 12.154, which forms deacetoxycephalosporin and excretes the cephabacin 7-formamidocephalosporin. IPNS was detected with anti-IPNS antibodies raised against the Cephalosporium acremonium enzyme. The flavobacterium enzyme, whose molecular mass (38 kilodaltons) and cofactor requirements resemble those of the fungal and Streptomyces enzymes, is formed at the transition from growth to the stationary phase. It was extracted into the polyethylene glycol phase of a polyethylene glycol-Ficoll-dextran three-phase system and was purified by quaternary aminoethyl ion-exchange chromatography, gel filtration, covalent chromatography on cystamine-Sepharose, and fast-protein liquid chromatography on Mono Q. The enzyme was characterized with respect to sulfhydryl requirement, inhibition by disulfides and metal ions, pH and temperature dependence, and stimulation by polyethylene glycol and low Triton X-100 concentrations, as well as by several amino acids, including alpha-aminoadipic acid and cysteine. The Km for alpha-aminoadipyl-cysteinyl-D-valine was 0.08 mM. An inactive membrane-associated form of IPNS was detected together with a beta-lactamase active on isopenicillin N. The system has been suggested as a model for the study of endogenous functions of beta-lactams in bacteria.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. E., Gagnon J., Ting H. N-terminal amino acid sequence and some properties of isopenicillin-N synthetase from Cephalosporium acremonium. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 2;188(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80382-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. E., Killin S. J., Pratt A. J., Sutherland J. D., Turner N. J., Crabbe M. J., Abraham E. P., Willis A. C. Purification and characterization of cloned isopenicillin N synthetase. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1987 May;40(5):652–659. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.40.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr L. G., Skatrud P. L., Scheetz M. E., 2nd, Queener S. W., Ingolia T. D. Cloning and expression of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Penicillium chrysogenum. Gene. 1986;48(2-3):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro J. M., Liras P., Laíz L., Cortés J., Martín J. F. Purification and characterization of the isopenicillin N synthase of Streptomyces lactamdurans. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jan;134(1):133–141. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P. The eucaryotic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complex: suggestions for its structure and function. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):373–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faupel M., Felix H. R., von Arx E. Fast and simple method for the separation of intermediates and cofactors involved in the biosynthesis of cephalosporin C using chemically bonded C12 reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1980 May 30;193(3):511–514. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)87759-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Ellerbrok H., Briese T., Handwerger S., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and -resistant pneumococci: immunological relatedness of altered proteins and changes in peptides carrying the beta-lactam binding site. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):553–558. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander I. J., Shen Y. Q., Heim J., Demain A. L., Wolfe S. A pure enzyme catalyzing penicillin biosynthesis. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):610–612. doi: 10.1126/science.6546810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada A., Kitano K., Kintaka K., Muroi M., Asai M. Sulfazecin and isosulfazecin, novel beta-lactam antibiotics of bacterial origin. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):590–591. doi: 10.1038/289590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Leskiw B. K., Vining L. C., Aharonowitz Y., Westlake D. W., Wolfe S. Purification of isopenicillin N synthetase from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Dec;32(12):953–958. doi: 10.1139/m86-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Westlake D. W., Wolfe S. Cyclization of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine to penicillins by cell-free extracts of Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Apr;35(4):483–490. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Westlake D. W., Wolfe S. High performance liquid chromatographic assay of cyclization activity in cell-free systems from Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Aug;35(8):1026–1032. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner A., Simonis M., von Döhren H. Preparation of the multienzyme system gramicidin S-synthetase 2 with an aqueous three-phase system. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jun 19;396:199–207. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)94057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leskiw B. K., Aharonowitz Y., Mevarech M., Wolfe S., Vining L. C., Westlake D. W., Jensen S. E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Gene. 1988;62(2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90557-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Okonogi K., Katayama N., Ono H., Harada S., Kondo M., Okazaki H. Cephabacins, new cephem antibiotics of bacterial origin. IV. Antibacterial activities, stability to beta-lactamases and mode of action. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Dec;37(12):1555–1565. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.1555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono H., Nozaki Y., Katayama N., Okazaki H. Cephabacins, new cephem antibiotics of bacterial origin. I. Discovery and taxonomy of the producing organisms and fermentation. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Dec;37(12):1528–1535. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.1528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang C. P., Chakravarti B., Adlington R. M., Ting H. H., White R. L., Jayatilake G. S., Baldwin J. E., Abraham E. P. Purification of isopenicillin N synthetase. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):789–795. doi: 10.1042/bj2220789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos F. R., López-Nieto M. J., Martín J. F. Isopenicillin N synthetase of Penicillium chrysogenum, an enzyme that converts delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine to isopenicillin N. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):380–387. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramón D., Carramolino L., Patiño C., Sánchez F., Peñalva M. A. Cloning and characterization of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene mediating the formation of the beta-lactam ring in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson S. M., Belagaje R., Blankenship D. T., Chapman J. L., Perry D., Skatrud P. L., VanFrank R. M., Abraham E. P., Baldwin J. E., Queener S. W. Isolation, sequence determination and expression in Escherichia coli of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Cephalosporium acremonium. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):191–194. doi: 10.1038/318191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson S. M., Chapman J. L., Belagaje R., Queener S. W., Ingolia T. D. Analysis of the role of cysteine residues in isopenicillin N synthetase activity by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5705–5709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Baldwin J. E., Singh P. D., Solomon N. A., Demain A. L. Cell-free cyclization of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine to isopenicillin N. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):465–470. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji J., Kato T., Sakazaki R., Nagata W., Terui Y., Nakagawa Y., Shiro M., Matsumoto K., Hattori T., Yoshida T. Chitinovorins A, B and C, novel beta-lactam antibiotics of bacterial origin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Nov;37(11):1486–1490. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P. D., Ward P. C., Wells J. S., Ricca C. M., Trejo W. H., Principe P. A., Sykes R. B. Bacterial production of deacetoxycephalosporin C. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Oct;35(10):1397–1399. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P. D., Young M. G., Johnson J. H., Cimarusti C. M., Sykes R. B. Bacterial production of 7-formamidocephalosporins. Isolation and structure determination. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Jul;37(7):773–780. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Cimarusti C. M., Bonner D. P., Bush K., Floyd D. M., Georgopapadakou N. H., Koster W. M., Liu W. C., Parker W. L., Principe P. A. Monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotics produced by bacteria. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):489–491. doi: 10.1038/291489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Wells J. S. Screening for beta-lactam antibiotics in nature. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 Jan;38(1):119–121. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel B. J., Burgett S. G., Chen V. J., Skatrud P. L., Frolik C. A., Queener S. W., Ingolia T. D. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of isopenicillin N synthetase genes from Streptomyces lipmanii and Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3817–3826. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3817-3826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. L., John E. M., Baldwin J. E., Abraham E. P. Stoichiometry of oxygen consumption in the biosynthesis of isopenicillin from a tripeptide. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 1;203(3):791–793. doi: 10.1042/bj2030791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]