Abstract
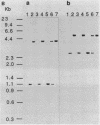
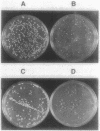
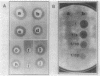
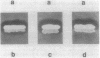
Acetylation is the most frequently occurring chemical modification of the alpha-NH2 group of eucaryotic proteins and is catalyzed by N alpha-acetyltransferase. The yeast enzyme is encoded by the AAA1 (amino-terminal alpha-amino acetyltransferase) gene. A null mutation (aaa1-1) created by gene replacement, while not lethal, slows cell growth and results in heterogeneous colony morphology. In comparison with wild-type cells, aaa1-1/aaa1-1 diploids cannot enter stationary phase, are sporulation defective, and are sensitive to heat shock. In addition, the aaa1-1 mutation specifically reduces mating functions of MATa cells. These results indicate that N alpha acetylation plays a crucial role in yeast cell growth and mating.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani E., Cao L., Kleckner N. A method for gene disruption that allows repeated use of URA3 selection in the construction of multiply disrupted yeast strains. Genetics. 1987 Aug;116(4):541–545. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.541.test. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr Pheromones and pheromone receptors are the primary determinants of mating specificity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 Mar;121(3):463–476. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.3.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L. A comparison of the turnover of alpha-N-acetylated and nonacetylated mouse L-cell proteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1447–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Roberts W. K. Evidence that approximately eighty per cent of the soluble proteins from Ehrlich ascites cells are Nalpha-acetylated. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1009–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen H. P., de Jong W. W., Tesser G. I., Bloemendal H. The mechanism of N-terminal acetylation of proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(4):281–325. doi: 10.3109/10409238509086784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Ozkaynak E., Varshavsky A. The yeast polyubiquitin gene is essential for resistance to high temperatures, starvation, and other stresses. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90711-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick R. L., Shaeffer J. R., Chapman P. B., Kingston R. E., Mazer J. S., Bunn H. F. Synthesis of acetylated human fetal hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1727–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig A., Holly J., Saari G., MacKay V. L. Multiple regulation of STE2, a mating-type-specific gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2106–2114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Heller H., Eytan E., Kaklij G., Rose I. A. Role of the alpha-amino group of protein in ubiquitin-mediated protein breakdown. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7021–7025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks J. B., Herskowitz I. Evidence for a new diffusible element of mating pheromones in yeast. Nature. 1976 Mar 18;260(5548):246–248. doi: 10.1038/260246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. Binding of alpha-factor pheromone to yeast a cells: chemical and genetic evidence for an alpha-factor receptor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90186-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H. Acetylation of Protein N-terminal amino groups structural observations on alpha-amino acetylated proteins. J Theor Biol. 1975 Nov;55(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(75)80105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H. Differences between alcohol dehydrogenases. Structural properties and evolutionary aspects. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Fairwell T., Kratofil P., Wills C. Differences in alpha-amino acetylation of isozymes of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):214–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80796-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Holly J. A., MacKay V. L. A yeast operator overlaps an upstream activation site. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90491-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. J., Lin L. W., Smith J. A. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding N alpha-acetyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12339–12343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. J., Lin L. W., Smith J. A. Purification and characterization of an N alpha-acetyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14948–14955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod A. R., Wong N. C., Dixon G. H. The amino-acid sequence of trout-testis histone H1. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):281–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney W. C., Nute P. E. Fetal hemoglobin of the rhesus monkey, Macaca mulatta: complete primary structure of the gamma chain. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4436–4442. doi: 10.1021/bi00560a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manney T. R. Expression of the BAR1 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: induction by the alpha mating pheromone of an activity associated with a secreted protein. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):291–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.291-301.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Initiation of meiosis in yeast mutants defective in adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90461-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Herskowitz I. The a-factor pheromone of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is essential for mating. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1309–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen J. R., Kayne P. S., Moerschell R. P., Tsunasawa S., Gribskov M., Colavito-Shepanski M., Grunstein M., Sherman F., Sternglanz R. Identification and characterization of genes and mutants for an N-terminal acetyltransferase from yeast. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2067–2075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Shore D. Transcriptional regulation in the yeast life cycle. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1162–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.3306917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Thomas J. H., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Isolation of the beta-tubulin gene from yeast and demonstration of its essential function in vivo. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90350-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Michaelis S., Broek D., Santa Anna S., Field J., Herskowitz I., Wigler M. RAM, a gene of yeast required for a functional modification of RAS proteins and for production of mating pheromone a-factor. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein P., Deuchler J. Acetylated and nonacetylated actins in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11142–11147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. G., Zakarian S. Selective processing of beta-endorphin in regions of porcine pituitary. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):613–615. doi: 10.1038/288613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr, Blair L. C., Thorner J. Cell interactions and regulation of cell type in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:623–660. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I. Control of yeast cell type by the mating type locus. I. Identification and control of expression of the a-specific gene BAR1. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):305–321. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegink L. D., Meyer P. D., Brummel M. C. Human fetal hemoglobin F 1. Acetylation status. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):3001–3007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Odani S., Ono T. Primary structure of rat liver Z-protein. A low-Mr cytosol protein that binds sterols, fatty acids and other small molecules. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 5;140(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80521-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Matsumoto K., Toh-e A. Dual regulation of the expression of the polyubiquitin gene by cyclic AMP and heat shock in yeast. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):495–502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunasawa S., Sakiyama F. Amino-terminal acetylation of proteins: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1984;106:165–170. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)06016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernet T., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y. A family of yeast expression vectors containing the phage f1 intergenic region. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Freedman R., Van Arsdell S., Szostak J. W., Thorner J. The yeast ARD1 gene product is required for repression of cryptic mating-type information at the HML locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3713–3722. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Szostak J. W. The ARD1 gene of yeast functions in the switch between the mitotic cell cycle and alternative developmental pathways. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):483–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L., Herskowitz I. Negative regulation of STE6 gene expression by the alpha 2 product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2420–2427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]