Abstract
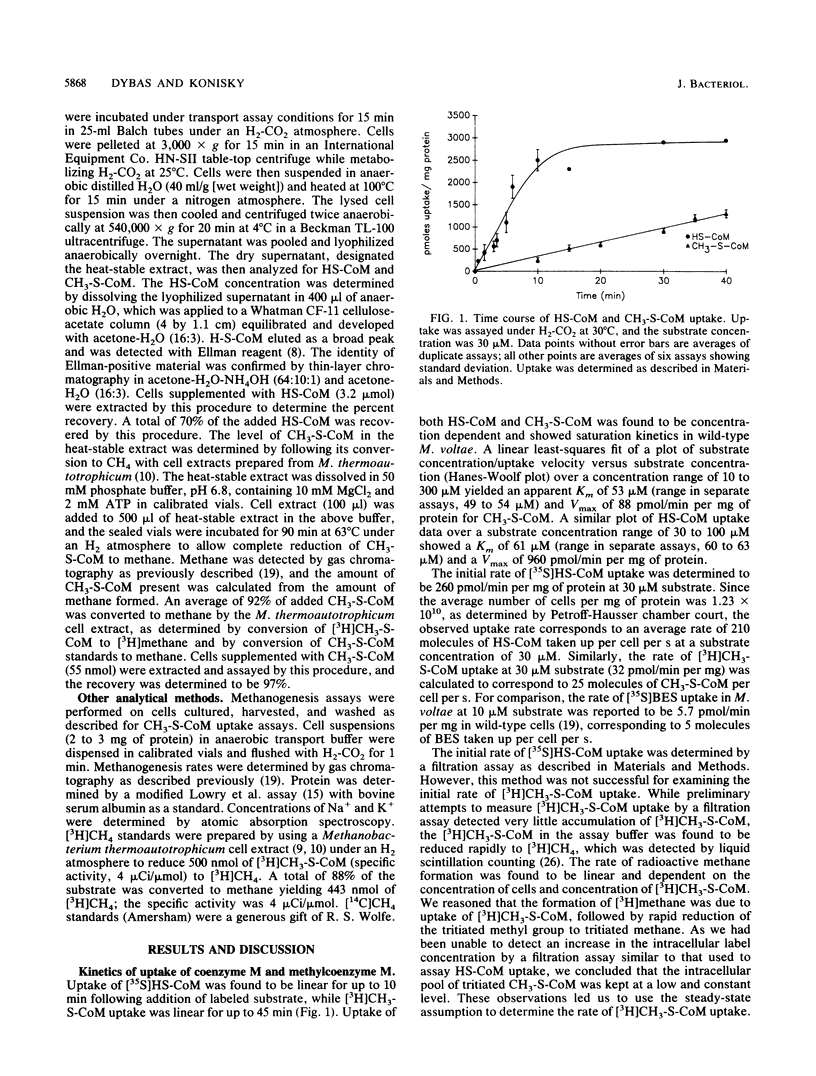
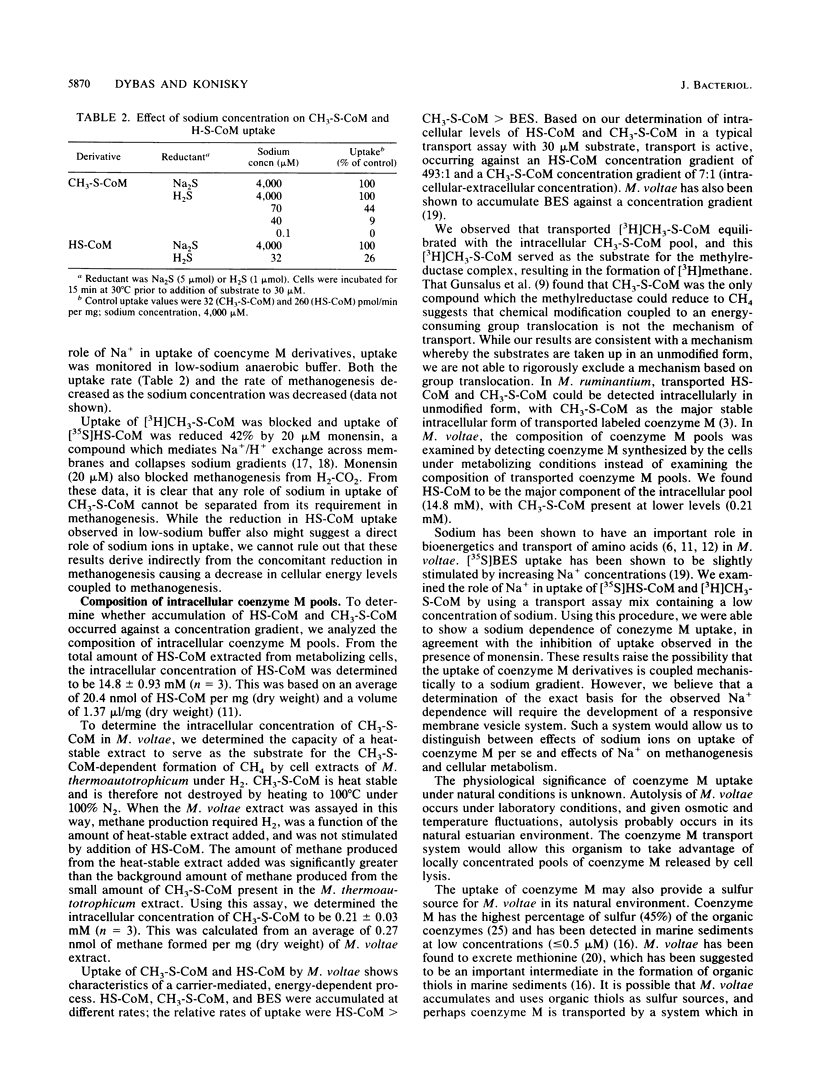
A transport system for coenzyme M (2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid [HS-CoM]) and methylcoenzyme M [(2-(methylthio)ethanesulfonic acid (CH3-S-CoM)] in Methanococcus voltae required energy, showed saturation kinetics, and concentrated both forms of coenzyme M against a concentration gradient. Transport required hydrogen and carbon dioxide for maximal uptake. CH3-S-CoM uptake was inhibited by N-ethylmaleimide and monensin. Both HS-CoM and CH3-S-CoM uptake showed sodium dependence. In wild-type M. voltae, HS-CoM uptake was concentration dependent, with a Vmax of 960 pmol/min per mg of protein and an apparent Km of 61 microM. Uptake of CH3-S-CoM showed a Vmax of 88 pmol/min per mg of protein and a Km of 53 microM. A mutant of M. voltae resistant to the coenzyme M analog 2-bromoethanesulfonic acid (BES) showed no uptake of CH3-S-CoM but accumulated HS-CoM at the wild-type rate. While the higher-affinity uptake system was specific for HS-CoM, the lower-affinity system mediated uptake of HS-CoM, CH3-S-CoM, and BES. Analysis of the intracellular coenzyme M pools in metabolizing cells showed an intracellular HS-CoM concentration of 14.8 mM and CH3-S-CoM concentration of 0.21 mM.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. Specificity and biological distribution of coenzyme M (2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid). J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.256-263.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. Transport of coenzyme M (2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid) in Methanobacterium ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):264–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.264-273.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crider B. P., Carper S. W., Lancaster J. R. Electron transfer-driven ATP synthesis in Methanococcus voltae is not dependent on a proton electrochemical gradient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6793–6796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. A colorimetric method for determining low concentrations of mercaptans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Apr;74(2):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekiel I., Jarrell K. F., Sprott G. D. Amino acid biosynthesis and sodium-dependent transport in Methanococcus voltae, as revealed by 13C NMR. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):437–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellermann J., Hedderich R., Böcher R., Thauer R. K. The final step in methane formation. Investigations with highly purified methyl-CoM reductase (component C) from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum (strain Marburg). Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):669–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Romesser J. A., Wolfe R. S. Preparation of coenzyme M analogues and their activity in the methyl coenzyme M reductase system of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2374–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Wolfe R. S. ATP activation and properties of the methyl coenzyme M reductase system in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.851-857.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R. Minimum threshold for hydrogen metabolism in methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1530–1531. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1530-1531.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Tolbert N. E., Bieber L. L. Protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples: manual and automated procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:296–303. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W. Ionophores. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:435–454. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro N., Konisky J. Characterization of bromoethanesulfonate-resistant mutants of Methanococcus voltae: evidence of a coenzyme M transport system. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):660–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.660-665.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sment K. A., Konisky J. Excretion of amino acids by 1,2,4-triazole-3-alanine-resistant mutants of Methanococcus voltae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1295–1297. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1295-1297.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., McBride B. C., Wolfe R. S., Bryant M. P. Coenzyme M, essential for growth of a rumen strain of Methanobacterium ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):974–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.974-975.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Wolfe R. S. Structure and methylation of coenzyme M(HSCH2CH2SO3). J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4879–4885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W. B., Ankwanda E., Wolfe R. S. Nutrition and carbon metabolism of Methanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):852–863. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.852-863.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Huser B., Brock T. D. Measuring radioactive methane with the liquid scintillation counter. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):897–899. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.897-899.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



