Abstract
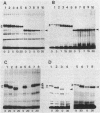
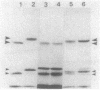
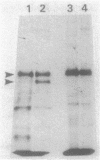
The processing of Escherichia coli penicillin-binding protein 3 (PBP 3) was investigated by gene manipulation for producing hybrid and truncated PBP 3 molecules. The hybrid PBP 3 was processed when the N-terminal 40 residues of PBP 3 were replaced by the murein lipoprotein signal peptide which lacked the cysteine residue for processing and followed by seven extra linker residues. In contrast, the PBP 3 molecules truncated at Thr-560 (28-residue deletion) or at Thr-497 (91-residue deletion) were not processed, and those truncated at Phe-576 (12-residue deletion) were processed at a greatly reduced rate. The results indicate that the C-terminal part, rather than the N-terminal part, is involved in the processing. This was supported by the result that the purified mature PBP 3 retained the complete N-terminal sequence with Met for translation initiation. The cleavage at the C-terminal region was shown by the loss of [35S]cysteine label when the cysteine-free hybrid PBP 3 joined to a cysteine-rich extra peptide tail was processed into the mature form. Confirmative assays for processing of PBP 3 were aided by a newly found prc mutant, defective in the processing involving the C-terminal region. A plasmid that directs PBP 3 truncated at Thr-560 complemented a thermosensitive PBP 3 mutation, but the truncated product was unstable in vivo. This suggests the importance of C-terminal hydrophobic regions that terminate at Leu-558 to PBP 3 functioning and the requirement of further-distal peptides for the stability of PBP 3.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome-Smith J. K., Hedge P. J., Spratt B. G. Production of thiol-penicillin-binding protein 3 of Escherichia coli using a two primer method of site-directed mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):231–235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E., Charles I. G. Sequences of the genes and polypeptide precursors for two bovine protease inhibitors. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 5;194(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90711-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diner B. A., Ries D. F., Cohen B. N., Metz J. G. COOH-terminal processing of polypeptide D1 of the photosystem II reaction center of Scenedesmus obliquus is necessary for the assembly of the oxygen-evolving complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8972–8980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Hara H., Suzuki H., Hirota Y. Lipid modification of Escherichia coli penicillin-binding protein 3. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5392–5395. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5392-5395.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houba-Hérin N., Hara H., Inouye M., Hirota Y. Binding of penicillin to thiol-penicillin-binding protein 3 of Escherichia coli: identification of its active site. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(3):499–504. doi: 10.1007/BF00331346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Suzuki H., Hirota Y. Overlapping of the coding regions for alpha and gamma components of penicillin-binding protein 1 b in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):449–457. doi: 10.1007/BF00436192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Fahey D., Cordova B., Hillman M., Kutny R., Reich N., Blomstrom D. A 15-kDa interferon-induced protein is derived by COOH-terminal processing of a 17-kDa precursor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4520–4522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I. N., Horikoshi K., Nagase Y., Soma M., Nobuhara M., Yasuda S., Hirota Y. A synthetic translation-terminator gene. A tool for dissecting the translation direction of a gene. Gene Anal Tech. 1989 May-Jun;6(3):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(89)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Sakagami Y., Suzuki A., Suzuki H., Hara H., Hirota Y. Determination of the cleavage site involved in C-terminal processing of penicillin-binding protein 3 of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5890–5893. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5890-5893.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Maruyama I. N., Soma M., Kato J., Suzuki H., Horota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequence of the gene for penicillin-binding protein 3. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00330881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas R. A., Strominger J. L., Suzuki H., Hirota Y. Identification of the active site in penicillin-binding protein 3 of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):456–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.456-460.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Wharton R. P., Seltzer S., Kacinski B. M., Clarke N. D., Rupp W. D. Identification of the uvrA gene product. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 5;148(1):45–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Comparison of the binding properties of two 6 beta-amidinopenicillanic acid derivatives that differ in their physiological effects on Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):161–166. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Temperature-sensitive cell division mutants of Escherichia coli with thermolabile penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):293–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.293-305.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Iino T. In vitro synthesis of phase-specific flagellin of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 25;81(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a series of mutants of E. coli altered in the penicillin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Nishimura A., Nishimura Y., Yamada M., Yasuda S., Suzuki H., Hirota Y. Synthetic ColE1 Plasmids carrying genes for penicillin-binding proteins in Escherichia coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):86–98. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamanoi F., Hsueh E. C., Goodman L. E., Cobitz A. R., Detrick R. J., Brown W. R., Fujiyama A. Posttranslational modification of ras proteins: detection of a modification prior to fatty acid acylation and cloning of a gene responsible for the modification. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Mar;36(3):261–273. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240360307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Imae Y., Strominger J. L. Purification to homogeneity and properties of two D-alanine carboxypeptidases I From Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):414–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Mizoguchi J., Hirota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of penicillin-binding proteins 1a, 1b, and 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4499–4503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata H., Ippolito C., Inukai M., Inouye M. Temperature-sensitive processing of outer membrane lipoprotein in an Escherichia coli mutant. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1163–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1163-1168.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida N., Uozumi T., Beppu T. Specific excretion of Serratia marcescens protease through the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):937–944. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.937-944.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]