Abstract
We present a dual-axes confocal microscope that employs postobjective scanning and low-coherence heterodyne detection to collect vertical cross-sectional images from biological tissue with high axial resolution, reduced noise from scattered light, deep tissue penetration, and a large dynamic range. This architecture can be scaled down to millimeter dimensions with microelectromechanical systems technology for performance of in vivo optical biopsy.
In a previous Letter we presented a method for optical imaging of biological tissue with a dual-axes confocal architecture that provides high axial resolution, a long working distance (WD), and a large field of view.1 In this Letter we describe the novel concept of postobjective scanning that allows for the use of simple, low-N.A. lenses and scalability of the design to dimensions compatible with medical endoscopes. In addition, a coherence gate is used to filter out photons scattered within the illumination beam. These features enable high-resolution reflectance images of biological tissue to be collected with a high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), deep tissue penetration, and a large dynamic range. Coupled with optical fibers and fabricated with microelectromechanical systems technology, this technique can be used for in vivo histopathology.
The dual-axes architecture uses separate low-N.A. objectives for illumination (IO) and collection (CO), as shown in Fig. 1.2,3 The illumination beam is focused into the tissue at angle θ to the midline, and the reflected light originating from the focal volume, defined by the intersection of the two beams (black oval), is collected off axis. The point spread function of the either objective has a long axial but narrow transverse dimension. Thus, the overall axial resolution is represented by the length along the z axis of the overlapping region, which depends on the transverse rather than the axial dimensions of the individual beams. Light scattered along the illumination path outside the focal volume (checkered region) is unlikely to arrive at the collection objective with the proper angle necessary for detection because the correct combination of scattering events occurs with low probability. On the other hand, a standard confocal microscope objective has a single axis and requires a much higher N.A. to achieve an equivalent axial resolution. As a result, the light that is collected emerges within the same large-angle cone (dashed lines) as that traversed by the illumination, resulting in increased noise from scattering. The N.A. of each lens is determined by the angles αi and αc.
Fig. 1.
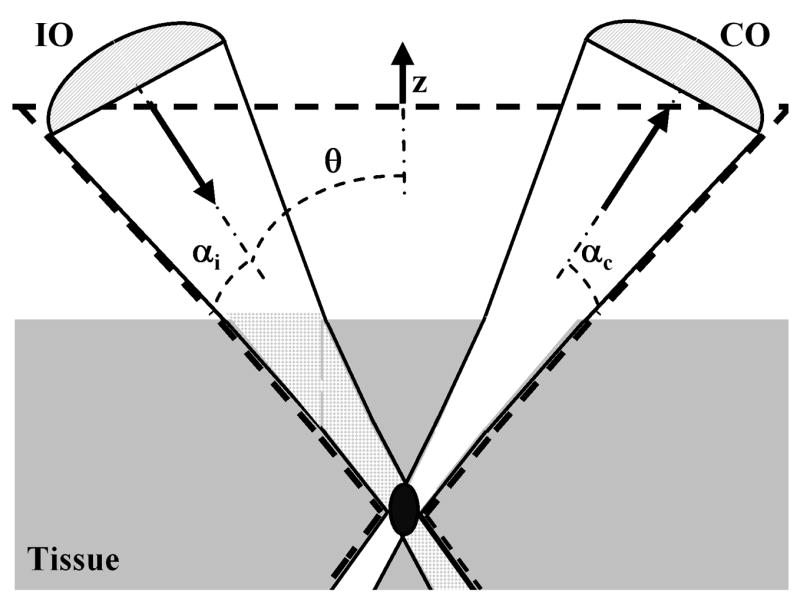
With dual axes, low-N.A. objectives focus the illumination beam into the tissue and collect the reflected light off axis. The total axial resolution (the length of the black oval) is significantly improved, and noise from light scattered along the illumination beam (the checkered area) is reduced.
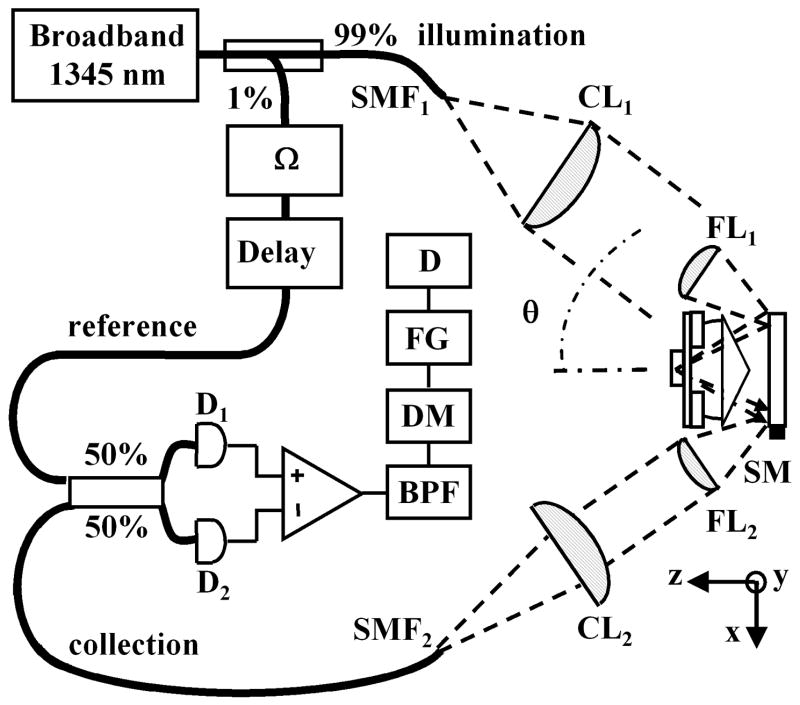
To demonstrate these principles, we construct a fiber-optic Mach–Zehnder interferometer on a breadboard, using readily available optics, as shown in Fig. 2. A broadband infrared source produces light centered at λ = 1345 nm with a 3-dB bandwidth of 35 nm and a coherence length in tissue of ~50 μm. A fiber coupler directs ~99% of the power to the illumination path, which consists of a single-mode optical fiber SMF1 (mode field diameter, 9.2 μm; N.A. = 0.092), a collimating lens CL1 (20-mm diameter, focal length f = 60 mm), and a focusing lens FL1 (9.5-mm diameter, f = 25 mm, N.A. = 0.186) to provide a Gaussian beam with its FWHM at the edge of FL1. The axes of illumination and collection are oriented at θ = 30° to the midline. Light reflected from the tissue is collected by the second set of focusing (FL2)and collimating (CL2)lenses into the single-mode fiber SMF2. The lens and fiber parameters are the same in both the illumination and the collection paths.
Fig. 2.
Schematic of optical circuit. Details are discussed in the text.
A fiber-optic tap coupler directs ~1% of the source to the reference beam, which is frequency shifted by an acousto-optic modulator at Ω/2π = 55 MHz. An adjustable optical delay is used to increase the heterodyne signal. In addition, a polarization controller consisting of two half-wave plates and a single quarter-wave plate is used to maximize the heterodyne signal. The reference and collection beams are combined by a 50/50 coupler and the resulting heterodyne signal is detected by a balanced InGaAs detector (D1, D2)from New Focus at a bandwidth of 80 MHz. The resulting electronic signal is then processed with a bandpass filter (BPF) with a 3-MHz bandwidth centered at 55 MHz, then demodulated (DM), digitized by a frame grabber (FG), and displayed (D). In this heterodyne detection scheme the reference beam essentially provides amplification of the weak collection beam via coherent optical mixing and permits the measurement of reflected light with a dynamic range larger than 70 dB.
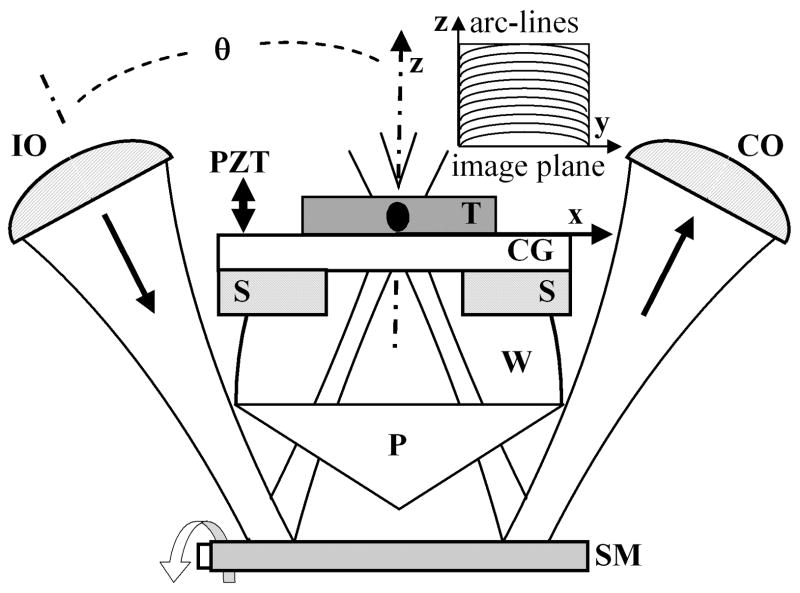
Postobjective scanning is performed with the scan mirror (SM) placed distal to the objective, shown in Fig. 3, rather than proximal, as is usually done in conventional confocal scanning microscopes. This novel method is permitted by the long WD created by the low-N.A. lenses. The illumination and collection beams are scanned synchronously in the y–z plane by the miniature galvanometer scan mirror (GSI Lumonics) that has dimensions of 9 mm × 14 mm and operates in a closed loop at a scan rate of 1 kHz. This mirror rotates about a single axis and preserves the intersection of the two optical axes at constant angle θ. This method results in an overlapping confocal volume that moves without changing shape along an arc line within the tissue. The method preserves a diffraction-limited point spread function over a large field of view, limited only by the maximum size of the scan mirror and its def lection angle. After reflecting off the scan mirror, the illumination beam passes through a prism (P) made from Teflon AF (n = 1.314). A bead of water (W) matches the refractive index between the prism and the tissue. A power of ~2 mW is incident on the specimen, which sits on a cover glass (CG) supported by a stage (S). The axial scan is produced by a closed-loop piezoelectric transducer actuator that translates the stage with a linear ramp over a distance of 300 μm. The resulting reflectance image is collected in a vertical cross section with a field of view of 300 μm ×300 μm at a rate of ~2 frames/s. The final WD between the scan mirror and the tissue is ~7 mm.
Fig. 3.
Postobjective scanning with the scan mirror (SM) located distal to the objectives (IO, CO) is made possible by the long WD and is used to collect vertical cross-sectional images in the y–z plane. T, tissue.
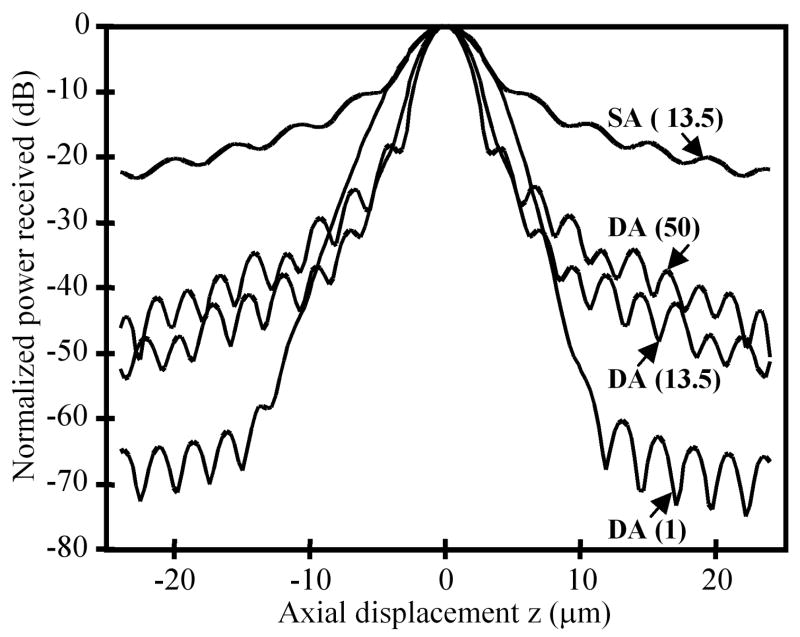
To evaluate the dynamic range, we calculate the axial response of the dual-axes system to a reflecting plane mirror at λ = 1345 nm (narrowband), using ASAP (Breault Research Organization) and Zemax optical modeling software and found an axial resolution of 4.5 μm with a N.A. of 0.246 objectives. Because the axial response of the dual-axes system depends on the transverse dimension of the individual beams, the intensity apodization (truncation edge of a Gaussian beam) determines the trade-off between axial resolution and the sidelobe response, which determines the amount of scattered light collected from outside the focal volume. As shown in Fig. 4, the dual-axes response to a Gaussian apodization cutoff at 1% of peak intensity has a dynamic range of ~70 dB, and the main lobe falls off as exp(−kz2), where k is a constant. With more truncation, such as e−2 (13.5%) or FWHM (50%), the axial resolution improves at the expense of higher sidelobes. In comparison, a conventional, single-axis confocal microscope objective (N.A. 0.47) with an equivalent axial resolution with an apodization of e−2 has a dynamic range of ~20 dB and an axial response that falls off as 1/z2. The dual-axes prototype described above has a FWHM apodization for optimal axial resolution, and the coherence gate is used to reduce the response of the sidelobes.
Fig. 4.
The calculated response to a plane reflecting mirror is shown with different intensity apodizations of a Gaussian beam (percentage of peak intensity in parentheses). The dynamic range of the dual-axes (DA) configuration is superior to that of a conventional single-axis (SA) confocal microscope with same axial resolution.
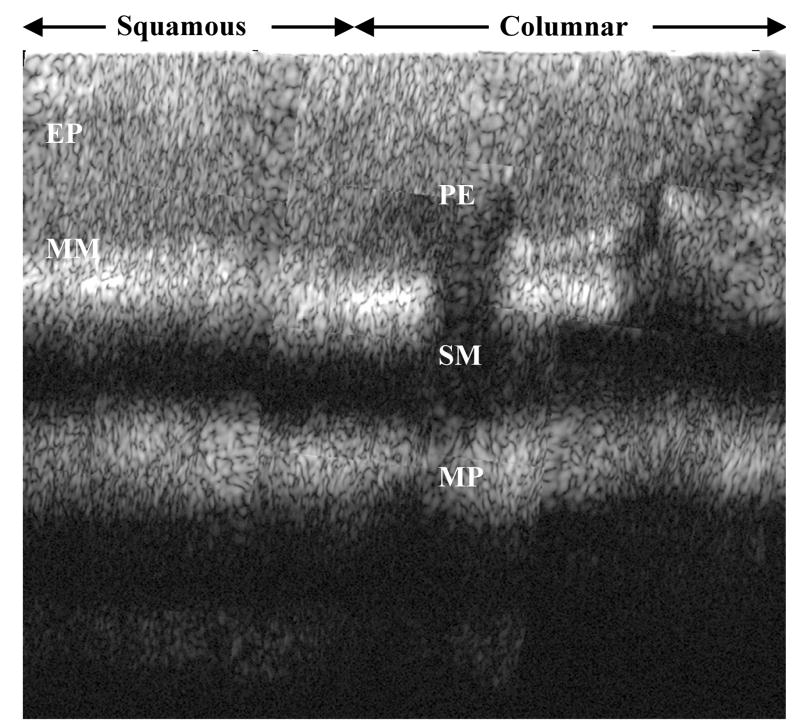
Multiple images were collected from fresh biopsy specimens with the mucosal surface oriented normal to the z axis by translation of the stage in both the y and z directions with micrometers and adjustment of the optical delay and polarization controller for maximum signal. The individual images are combined into a composite image, as shown in Fig. 5. This vertical cross section is achieved over a depth of 1 mm. The specimen was then evaluated by routine histology. From Fig. 6, squamous mucosa is seen in the top left-hand quadrant with an intact epithelium. The other structures of normal esophagus, including the muscularis mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis propria, can also be identified. Columnar mucosa consistent with Barrett’s esophagus is seen in the top right-hand quandrant of the image, revealing pit epithelium, an early stage of intestinal metaplasia.4
Fig. 5.
The squamoneocolumnar metaplastic junction of resected human esophagus is shown in a composite reflectance image over a depth of 1 mm.
Fig. 6.
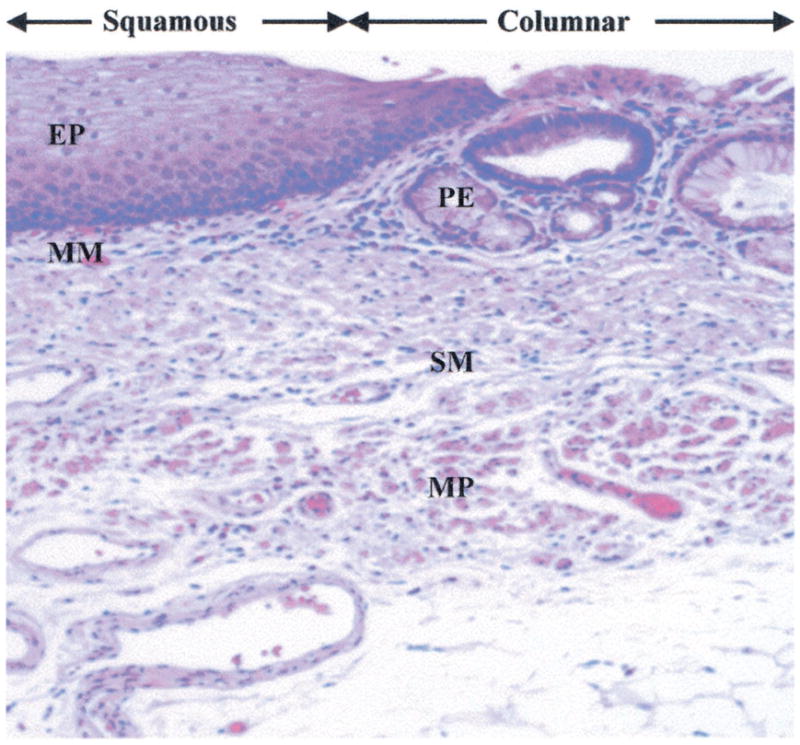
Histology showing squamous epithelium (EP) and muscularis mucosa (MM) on the left, columnar mucosa with pit epithelium (PE) on the right, and submucosa (SM) and muscularis propria (MP) on both sides.
With dual-axes configuration, the ratio of multiple scattered photons to ballistic photons in the collection beam is significantly reduced, and thus diffraction-limited imaging can be achieved over deeper tissue penetration than that allowed by optical coherence tomography or optical coherence microscopy techniques alone. Furthermore, unlike optical coherence tomography and optical coherence microscopy, the sidelobes near the focus are small, and thus there is no artifact seen from speckle formation,5 as the image features showed no change with movement of the stage. The axial resolution of this dual-axes prototype with λ = 1345 nm is not adequate to resolve subcellular structures, such as nuclei, which may be visualized with a shorter-wavelength source or higher-N.A. objectives. Future development of this technique also involves miniaturization of this microscope with microelectromechanical systems technology and in vivo imaging studies.
Acknowledgments
We thank George Triadafilopoulos for technical assistance and Jon Kosek for helpful scientific discussion. This research was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, including T32DK07056-27 (T. D. Wang), 1 R43 RR16130-01 (M. I. Mandella), CA88303, CA92862, and CA86312 (C. H. Contag), and the Bio-X Program. T. D. Wang’s e-mail address is tdwang@stanford.edu.
References
- 1.Wang TD, Mandella MJ, Contag CH, Kino GS. Opt Lett. 2003;28:414. doi: 10.1364/ol.28.000414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Webb RH, Rogomentich F. Appl Opt. 1999;38:4870. doi: 10.1364/ao.38.004870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lindek S, Cremer C, Stelzer EHK. Appl Opt. 1996;35:126. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.000126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Crawford JM. In: Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease. 6. Cotran RS, editor. Saunders; Philadelphia, Pa: 1999. p. 781. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Iftimia N, Bouma BE, Tearney GJ. J Biomed Opt. 2003;8:260. doi: 10.1117/1.1559060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]