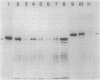
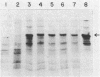
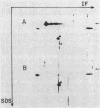
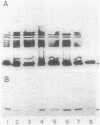
Abstract
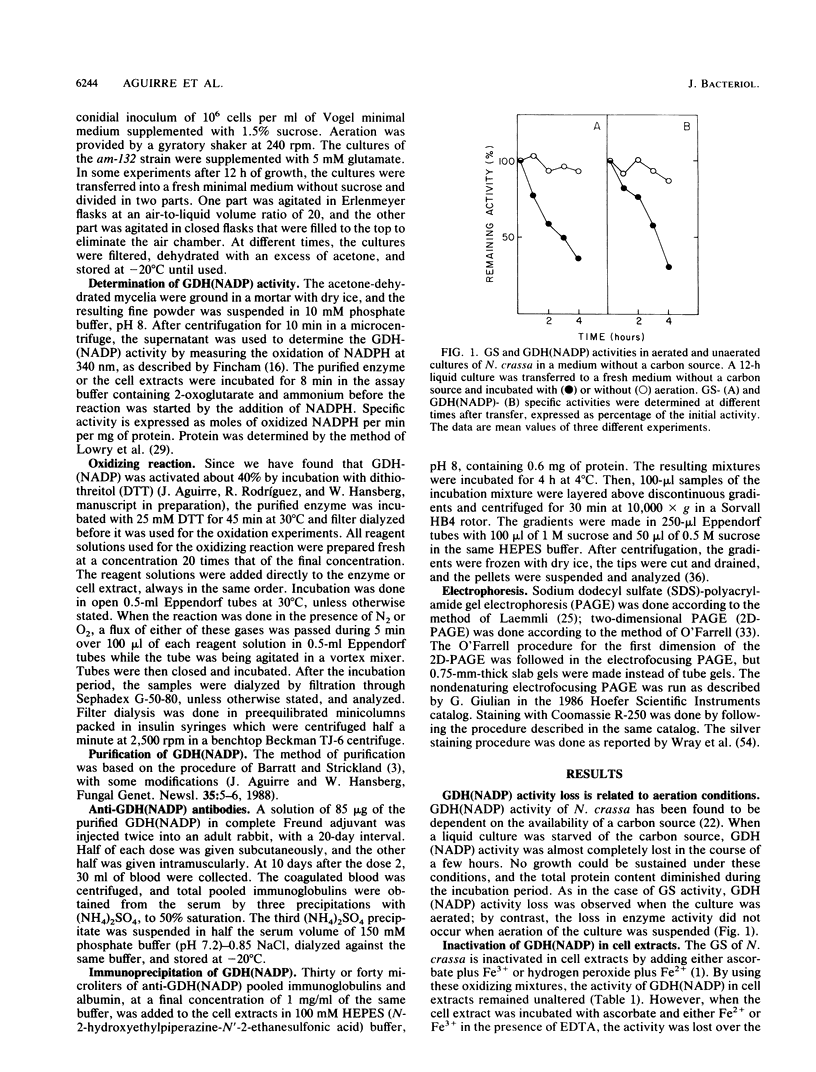
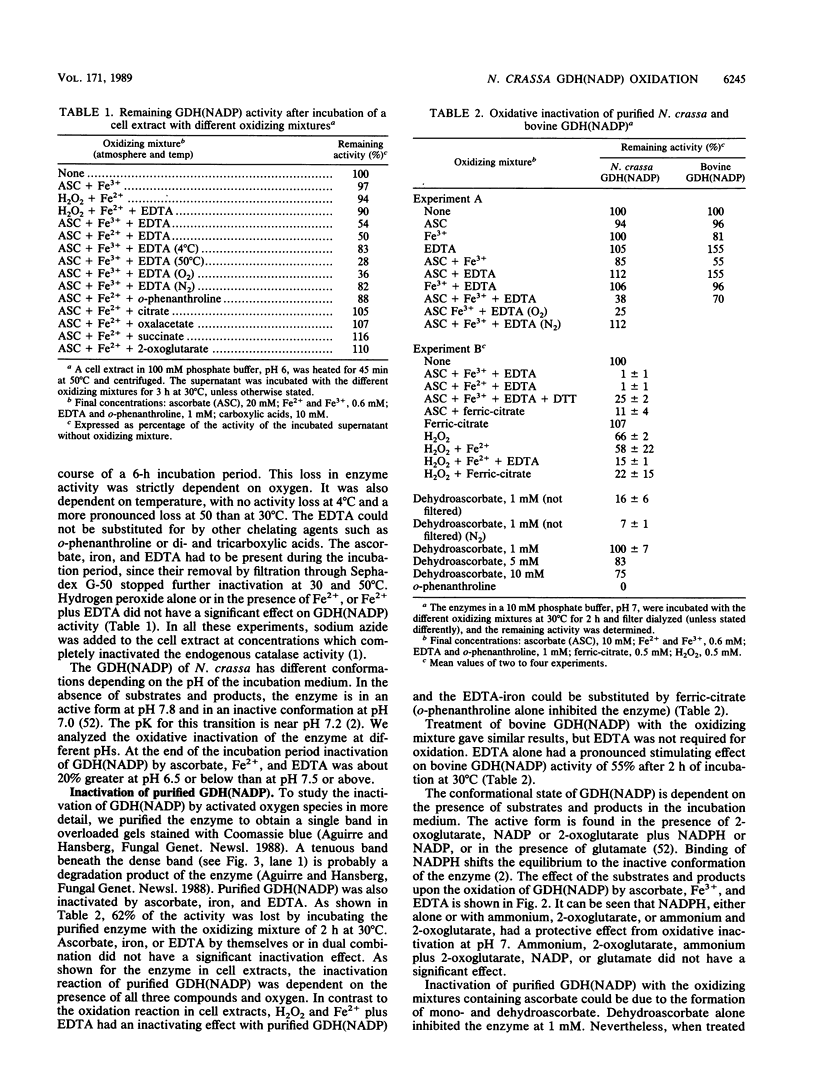
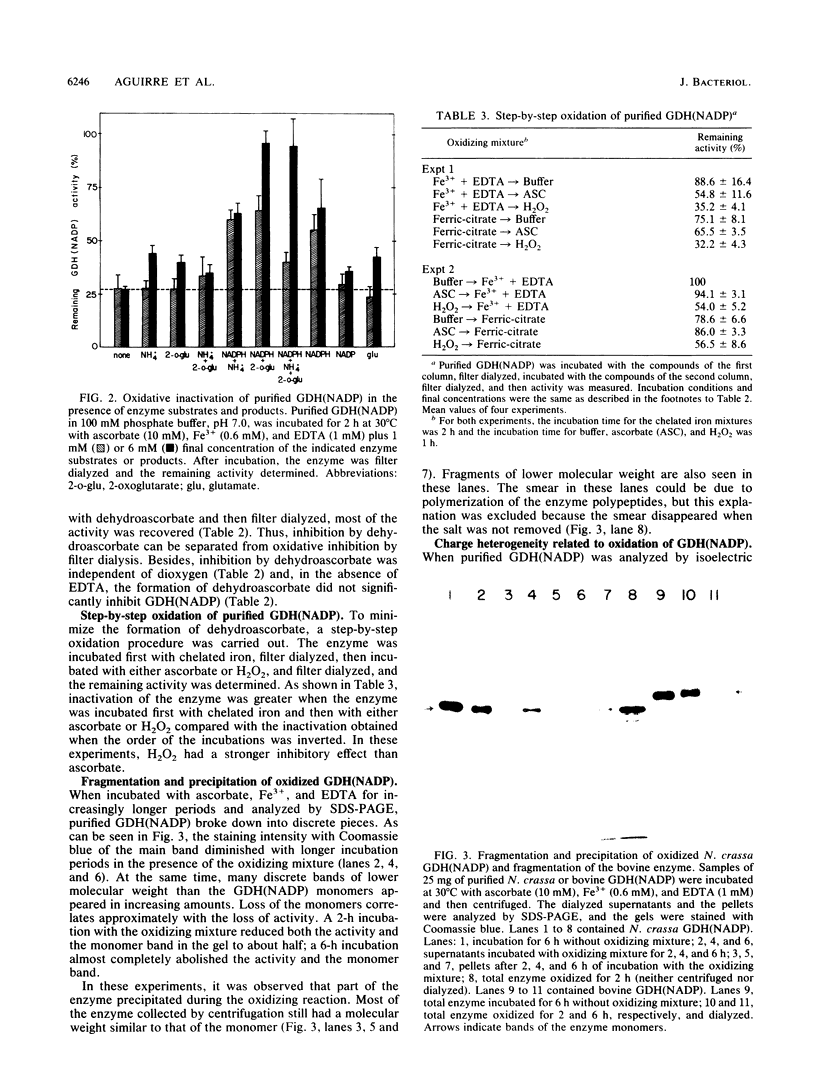
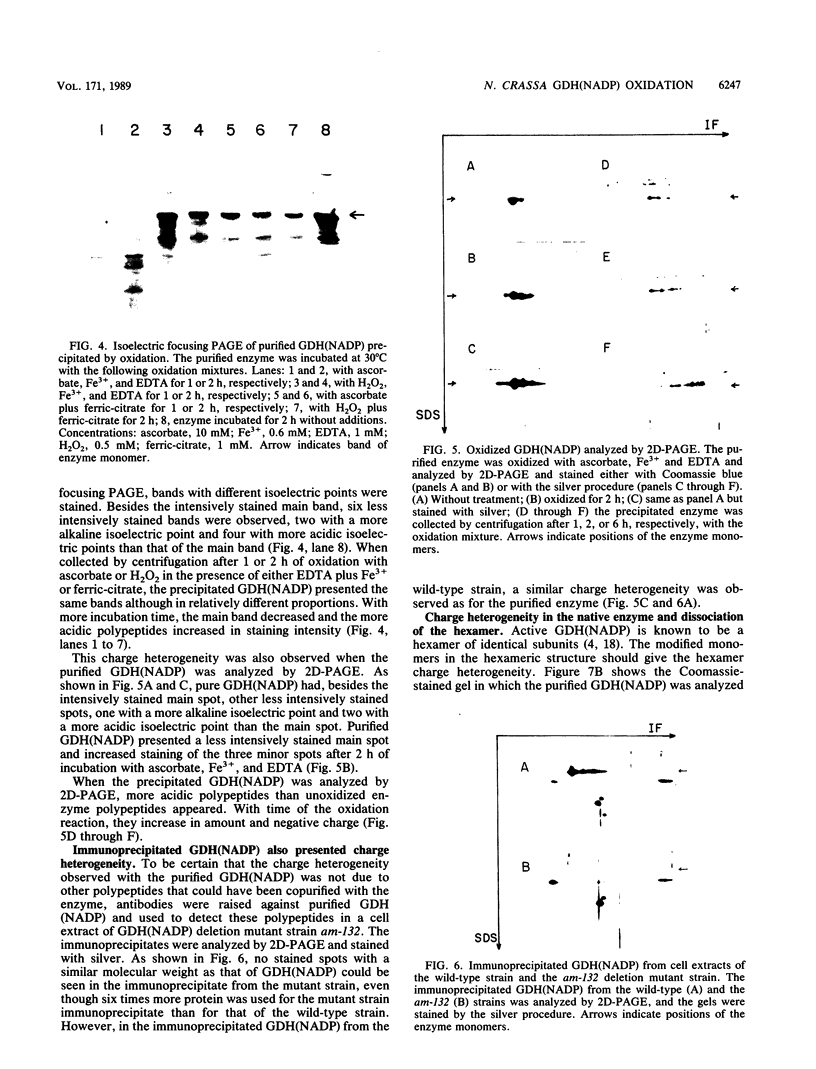
The glutamine synthetase and the NADP-specific glutamate dehydrogenase activities of Neurospora crassa were lost in a culture without carbon source only when in the presence of air. Glutamine synthetase was previously reported to be liable to in vitro and in vivo inactivation by activated oxygen species. Here we report that NADP-specific glutamate dehydrogenase was remarkably stable in the presence of activated oxygen species but was rendered susceptible to oxidative inactivation when chelated iron was bound to the enzyme and either ascorbate or H2O2 reacted on the bound iron. This reaction gave rise to further modifications of the enzyme monomers by activated oxygen species, to partial dissociation of the oligomeric structure, and to precipitation and fragmentation of the enzyme. The in vitro oxidation reaction was affected by pH, temperature, and binding to the enzyme of NADPH. Heterogeneity in total charge was observed in the purified and immunoprecipitated enzymes, and the relative amounts of enzyme monomers with different isoelectric points changes with time of the oxidizing reaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguirre J., Hansberg W. Oxidation of Neurospora crassa glutamine synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1040–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1040-1045.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby B., Wootton J. C., Fincham J. R. Slow conformational changes of a Neurospora glutamate dehydrogenase studied by protein fluorescence. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):317–329. doi: 10.1042/bj1430317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRATT R. W., STRICKLAND W. N. Purification and characterization of a TPN-specific glutamic acid dehydrogenase Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jul;102:66–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90321-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal K. M., Smith E. L. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific glutamate dehydrogenase of Neurospora. III. Inactivation by nitration of a tyrosine residue involved in coenzyme binding. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6560–6563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray R. C., Cockle S. A., Fielden E. M., Roberts P. B., Rotilio G., Calabrese L. Reduction and inactivation of superoxide dismutase by hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;139(1):43–48. doi: 10.1042/bj1390043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. J., Delsignore M. E., Lin S. W. Protein damage and degradation by oxygen radicals. II. Modification of amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9902–9907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. J., Delsignore M. E. Protein damage and degradation by oxygen radicals. III. Modification of secondary and tertiary structure. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9908–9913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. J., Lin S. W., Pacifici R. E. Protein damage and degradation by oxygen radicals. IV. Degradation of denatured protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9914–9920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. J. Protein damage and degradation by oxygen radicals. I. general aspects. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9895–9901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Kettle A. J., Fatur D. J. Mechanism of the inhibition of catalase by ascorbate. Roles of active oxygen species, copper and semidehydroascorbate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1193–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande V. V., Joshi J. G. Vit C.Fe(III) induced loss of the covalently bound phosphate and enzyme activity of phosphoglucomutase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):757–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dávila G., Brom S., Mora Y., Palacios R., Mora J. Genetic and biochemical characterization of glutamine synthetase from Neurospora crassa glutamine auxotrophs and their revertants. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):993–1000. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.993-1000.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCHAM J. R. A modified glutamic acid dehydrogenase as a result of gene mutation in Neurospora crassa. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):721–728. doi: 10.1042/bj0650721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Levine R. L. Sequence of a peptide susceptible to mixed-function oxidation. Probable cation binding site in glutamine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4574–4578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fucci L., Oliver C. N., Coon M. J., Stadtman E. R. Inactivation of key metabolic enzymes by mixed-function oxidation reactions: possible implication in protein turnover and ageing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1521–1525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gore M. G., Iwatsubo M. A deactivating conformational change induced by reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate in a Neurospora glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;147(1):181–184. doi: 10.1042/bj1470181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansberg W., Espín G., Palacios R., Sánchez F. Regulation of glutamine synthetase messenger ribonucleic acid in connidia of Neurospora crassa. Dev Biol. 1979 Nov;73(1):68–75. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson E. K., Fridovich I. The interaction of bovine erythrocyte superoxide dismutase with hydrogen peroxide: inactivation of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 2;14(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00695a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Levine R. L., Lin E. C. Inactivation of glycerol dehydrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae and the role of divalent cations. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):479–483. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.479-483.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor M., Grover A. K. Catabolite-controlled regulation of glutamate dehydrogenases of Neurospora crassa. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;16(1):33–40. doi: 10.1139/m70-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Rhee S. G., Stadtman E. R. Nonenzymatic cleavage of proteins by reactive oxygen species generated by dithiothreitol and iron. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15394–15397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsey J. A., Hung B. S. Mutation at the am locus of Neurospora crassa. Genetics. 1981 Nov-Dec;99(3-4):405–414. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.3-4.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. L., Oliver C. N., Fulks R. M., Stadtman E. R. Turnover of bacterial glutamine synthetase: oxidative inactivation precedes proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2120–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. L. Oxidative modification of glutamine synthetase. I. Inactivation is due to loss of one histidine residue. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11823–11827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. L. Oxidative modification of glutamine synthetase. II. Characterization of the ascorbate model system. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11828–11833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal C. K., Murad F. Activation of guanylate cyclase by superoxide dismutase and hydroxyl radical: a physiological regulator of guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4360–4364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Stadtman E. R. Oxidative inactivation of glutamine synthetase subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2011–2015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver C. N., Ahn B. W., Moerman E. J., Goldstein S., Stadtman E. R. Age-related changes in oxidized proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5488–5491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver C. N. Inactivation of enzymes and oxidative modification of proteins by stimulated neutrophils. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 15;253(1):62–72. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90637-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Campomanes M., Quinto C. Neurospora crassa glutamine synthetase. Translation of specific messenger ribonucleic acid in a cell-free system derived from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):3028–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. Preferential degradation of the oxidatively modified form of glutamine synthetase by intracellular mammalian proteases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. Purification of a liver alkaline protease which degrades oxidatively modified glutamine synthetase. Characterization as a high molecular weight cysteine proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12600–12606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J., Roseman J. E., Oliver C. N., Levine R. L., Stadtman E. R. Covalent modification of proteins by mixed-function oxidation: recognition by intracellular proteases. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;180:317–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseman J. E., Levine R. L. Purification of a protease from Escherichia coli with specificity for oxidized glutamine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2101–2110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuni A., Chevion M., Czapski G. Unusual copper-induced sensitization of the biological damage due to superoxide radicals. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12632–12635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinar E., Navok T., Chevion M. The analogous mechanisms of enzymatic inactivation induced by ascorbate and superoxide in the presence of copper. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14778–14783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Wittenberger M. E. Inactivation of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase by xanthine oxidase, nicotinate hydroxylase, horseradish peroxidase, or glucose oxidase: effects of ferredoxin, putidaredoxin, and menadione. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jun;239(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90703-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke P. E., Oliver C. N., Stadtman E. R. Modification of hepatic proteins in rats exposed to high oxygen concentration. FASEB J. 1987 Jul;1(1):36–39. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.1.2886388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez F., Calva E., Campomanes M., Blanco L., Guzmán J., Saborío J. L., Palacios R. Heterogeneity of glutamine synthetase polypeptides in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2231–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taborsky G. Oxidative modification of proteins in the presence of ferrous ion and air. Effect of ionic constituents of the reaction medium on the nature of the oxidation products. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 27;12(7):1341–1348. doi: 10.1021/bi00731a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. H., Wootton J. C. Affinity chromatography of the Neurospora NADP-specific glutamate dehydrogenase, its mutational variants and hybrid hexamers. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):95–108. doi: 10.1042/bj1670095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Peppin G., Ortiz X., Ragsdale C., Test S. T. Oxidative autoactivation of latent collagenase by human neutrophils. Science. 1985 Feb 15;227(4688):747–749. doi: 10.1126/science.2982211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West D. J., Tuveson R. W., Barratt R. W., Fincham J. R. Allosteric effects in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific glutamate dehydrogenase from Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2134–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]