Abstract
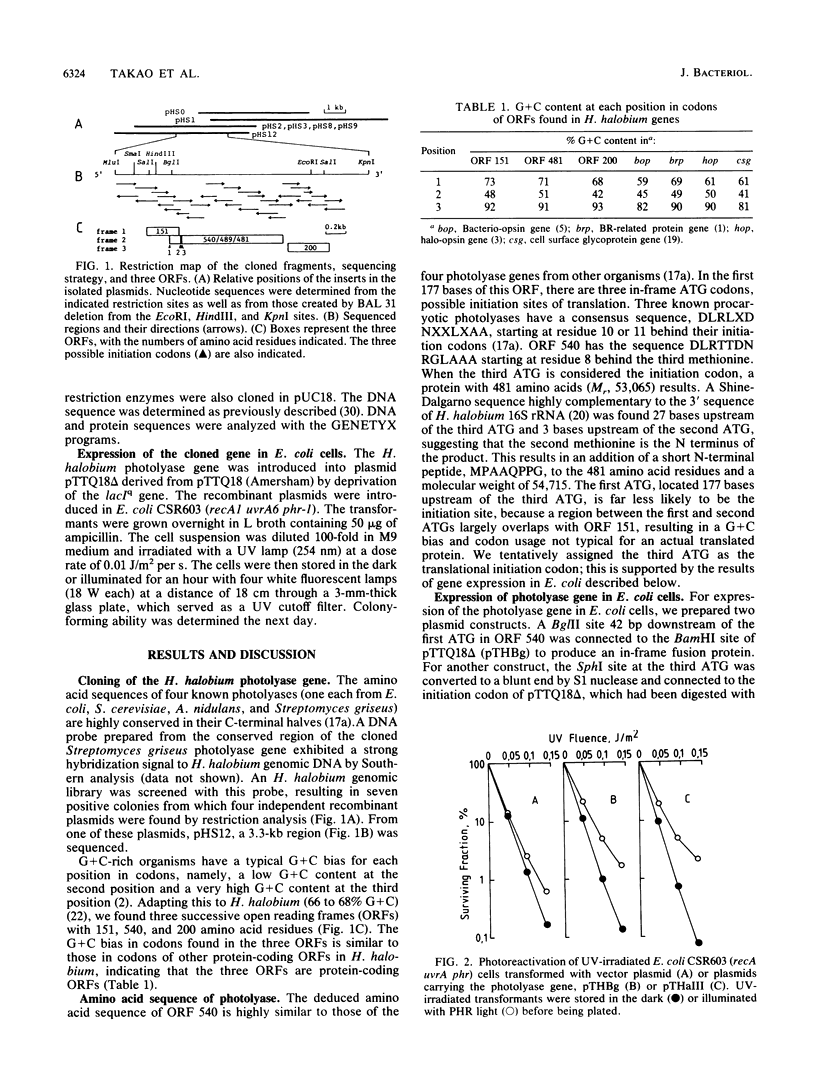
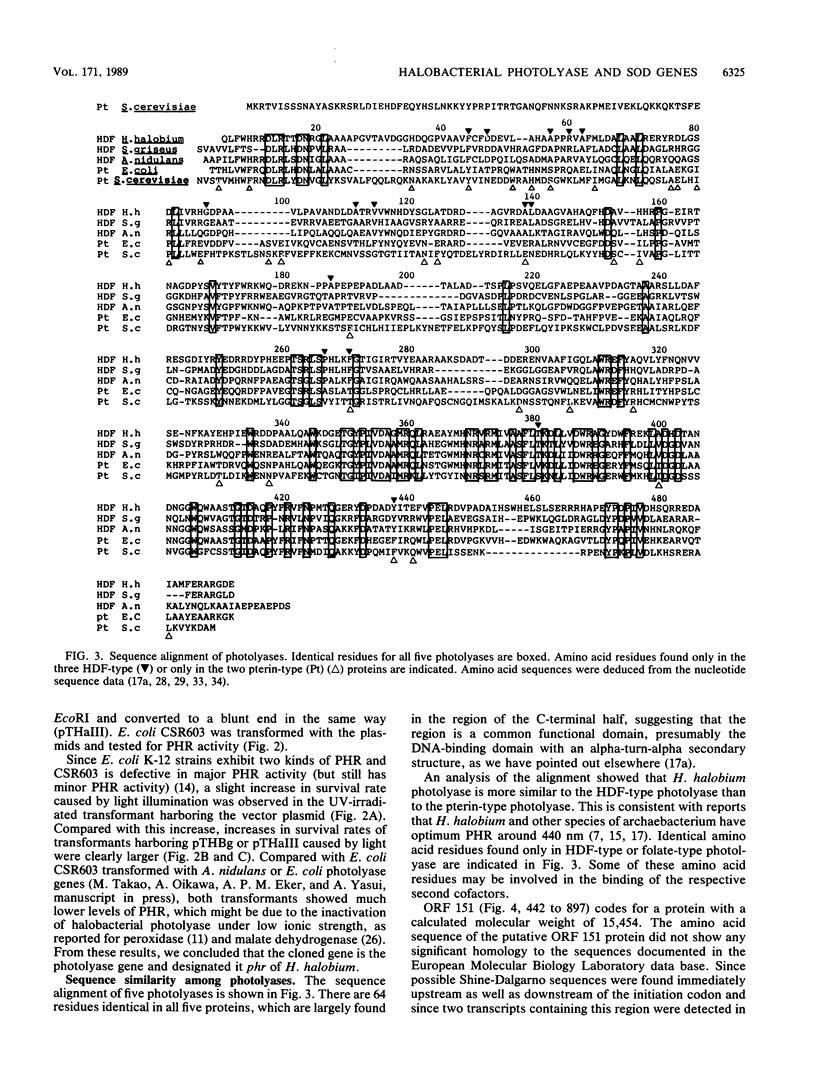
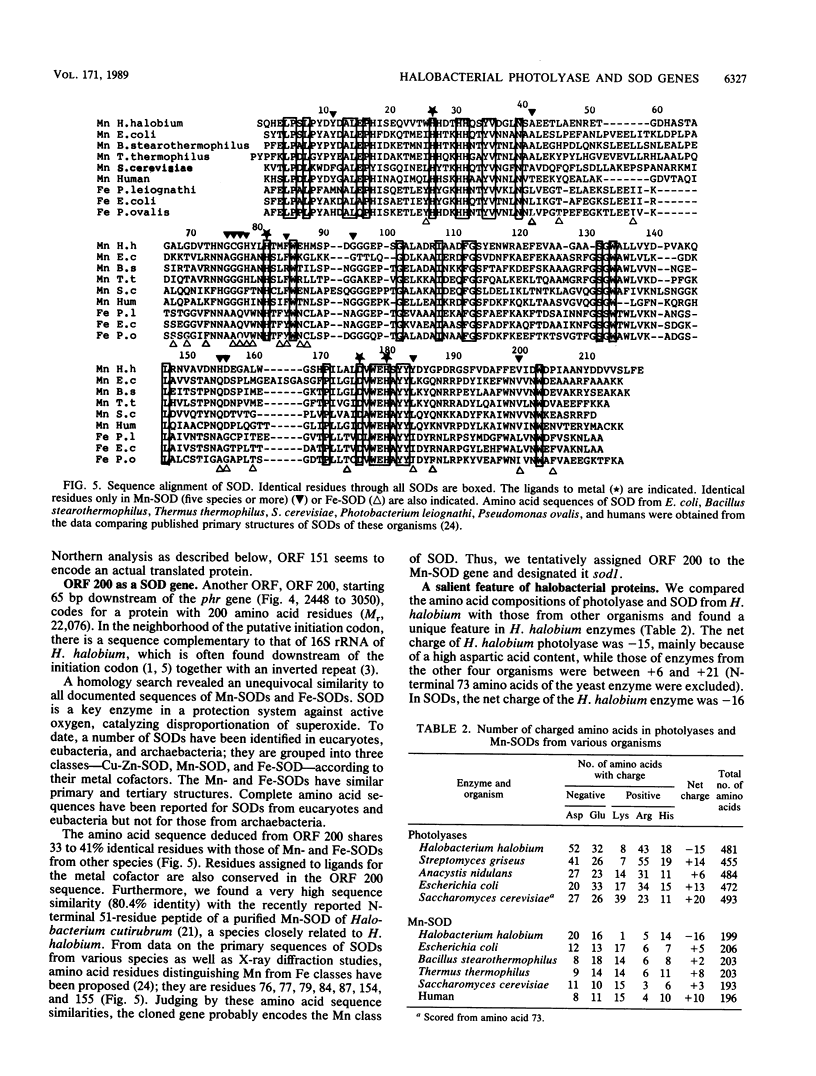
A DNA fragment containing the photolyase gene was cloned from Halobacterium halobium. The deduced amino acid sequence is highly similar to those of four known photolyases from eubacteria and a eucaryote. The cloned gene expressed in Escherichia coli cells the survival of UV-irradiated host cells by photoreactivation. These results indicate that photolyases of eucaryotes, eubacteria, and archaebacteria are derived from a common origin. In this cloned DNA fragment, two additional open reading frames (ORFs), ORF 151 and ORF 200, were found in the 5' and 3' adjacent flanking regions of the photolyase gene. ORF 200 shows unequivocal amino acid sequence homology to all known manganese and iron superoxide dismutases. Northern (RNA) hybridization analysis of H. halobium RNA revealed the existence of three transcripts, one of which covered all three ORFs, indicating that photolyase and superoxide dismutase are partly cotranscribed in this bacterium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanck A., Oesterhelt D. The halo-opsin gene. II. Sequence, primary structure of halorhodopsin and comparison with bacteriorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):265–273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassarma S., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Bacterio-opsin mRNA in wild-type and bacterio-opsin-deficient Halobacterium halobium strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):125–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eker A. P., Hessels J. K., Meerwaldt R. Characterization of an 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin:NADPH oxidoreductase from Streptomyces griseus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 27;990(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(89)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitt P. S., Sharma N., Castellanos G. A comparison of liquid-holding recovery and photoreactivation in halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 20;739(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumori Y., Fujiwara T., Okada-Takahashi Y., Mukohata Y., Yamanaka T. Purification and properties of a peroxidase from Halobacterium halobium L-33. J Biochem. 1985 Oct;98(4):1055–1061. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Chamberlin M. J. Developmental and genetic regulation of Bacillus subtilis genes transcribed by sigma 28-RNA polymerase. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey V. L., Fitt P. S. Evidence for the lack of deoxyribonucleic acid dark-repair in Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):569–575. doi: 10.1042/bj1560569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Sancar A. Photoreactivation in phr mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2367–2372. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2367-2372.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Hamm-Alvarez S., Payne G., Sancar G. B., Rajagopalan K. V., Sancar A. Identification of the second chromophore of Escherichia coli and yeast DNA photolyases as 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2046–2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Takao M., Oikawa A., Yasui A. Molecular characterization of a gene encoding a photolyase from Streptomyces griseus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4731–4744. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J., Sumper M. The primary structure of a procaryotic glycoprotein. Cloning and sequencing of the cell surface glycoprotein gene of halobacteria. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9724–9729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin A. S., Kagramanova V. K., Teterina N. L., Rubtsov P. M., Belova E. N., Kopylov A. M., Baratova L. A., Bogdanov A. A. The nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the 16S rRNA from the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May B. P., Dennis P. P. Superoxide dismutase from the extremely halophilic archaebacterium Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1417–1422. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1417-1422.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., McCarthy B. J. Characterization of the deoxyribonucleic acid of various strains of halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.248-254.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. W., Blake C. C. Iron- and manganese-containing superoxide dismutases can be distinguished by analysis of their primary structures. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 14;229(2):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81160-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peak J. G., Peak M. J., MacCoss M. DNA breakage caused by 334-nm ultraviolet light is enhanced by naturally occurring nucleic acid components and nucleotide coenzymes. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 May;39(5):713–716. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb03914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pundak S., Aloni H., Eisenberg H. Structure and activity of malate dehydrogenase from the extreme halophilic bacteria of the Dead Sea. 2. Inactivation, dissociation and unfolding at NaCl concentrations below 2 M. Salt, salt concentration and temperature dependence of enzyme stability. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Sancar G. B. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:29–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B. Sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PHR1 gene and homology of the PHR1 photolyase to E. coli photolyase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8231–8246. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W., Lorence M. C., Rupert C. S., Sancar A. Sequences of the Escherichia coli photolyase gene and protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):6033–6038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Olsen G. J. Archaebacterial phylogeny: perspectives on the urkingdoms. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1986;7:161–177. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(86)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui A., Langeveld S. A. Homology between the photoreactivation genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;36(3):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui A., Takao M., Oikawa A., Kiener A., Walsh C. T., Eker A. P. Cloning and characterization of a photolyase gene from the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4447–4463. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Palm P., Reiter W. D., Gropp F., Pühler G., Klenk H. P. Comparative evaluation of gene expression in archaebacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 2;173(3):473–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]