Abstract
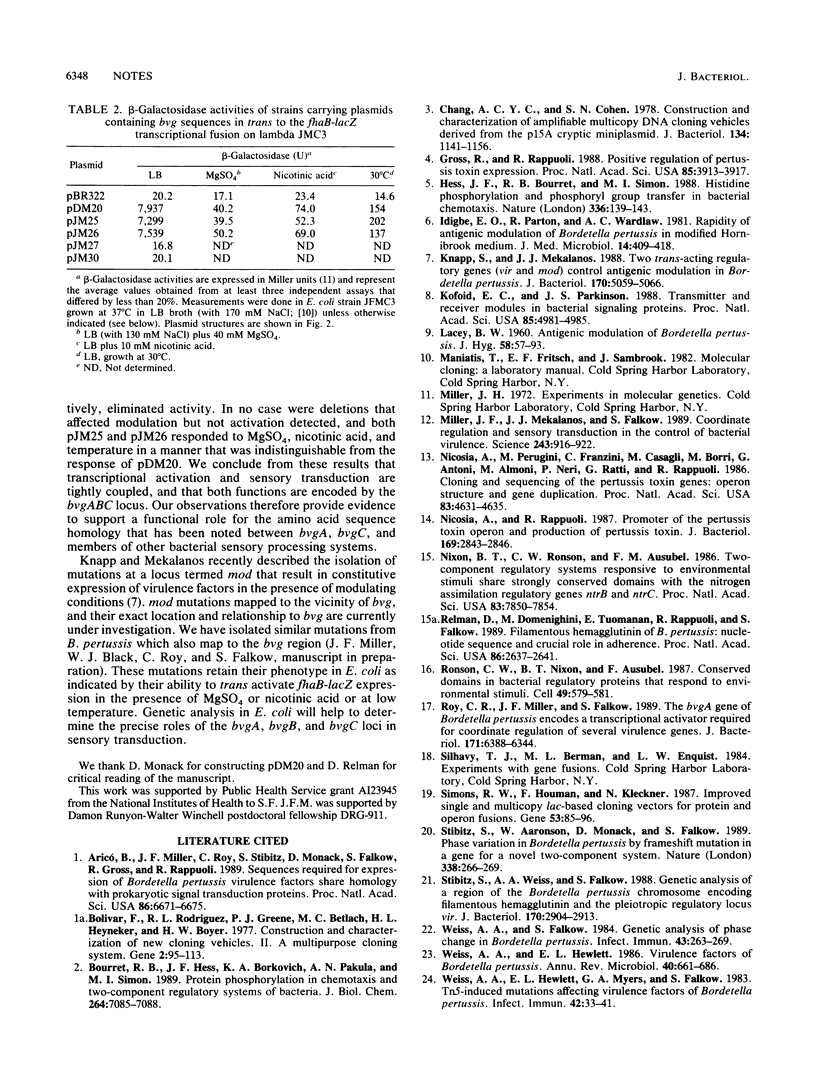
The virulence regulon of Bordetella pertussis includes a trans-acting regulatory locus, bvg, that is required for expression of several virulence factors. The virulence control system also responds to environmental signals. We have reconstructed a bvg-dependent regulatory system in Escherichia coli by using bacteriophage lambda vectors carrying transcriptional fusions to lacZYA. Single-copy lacZYA fusions to the B. pertussis fhaB locus, which encodes the attachment factor filamentous hemagglutinin, were activated nearly 400-fold by pBR322 replicons carrying sequences that included bvg. In contrast, bvg had no effect on the pertussis toxin operon (ptxA-E) promoter in E. coli as measured by ptxA-lacZ expression. Environmental signals that modulate expression of virulence genes in B. pertussis had a pronounced effect on bvg-mediated activation of fhaB-lacZ. MgSO4, nicotinic acid, and low temperature resulted in decreases in beta-galactosidase activities of 175-, 115-, and 45-fold respectively. Sensory transduction and transcriptional activation were tightly coupled, and both required an intact bvg locus as determined by 5' and 3' deletions that eliminated both activities.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aricó B., Miller J. F., Roy C., Stibitz S., Monack D., Falkow S., Gross R., Rappuoli R. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Hess J. F., Borkovich K. A., Pakula A. A., Simon M. I. Protein phosphorylation in chemotaxis and two-component regulatory systems of bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7085–7088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R., Rappuoli R. Positive regulation of pertussis toxin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Histidine phosphorylation and phosphoryl group transfer in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):139–143. doi: 10.1038/336139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idigbe E. O., Parton R., Wardlaw A. C. Rapidity of antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis in modified Hornibrook medium. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(4):409–418. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-4-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. Two trans-acting regulatory genes (vir and mod) control antigenic modulation in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5059–5066. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5059-5066.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofoid E. C., Parkinson J. S. Transmitter and receiver modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):4981–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Rappuoli R. Promoter of the pertussis toxin operon and production of pertussis toxin. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2843–2846. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2843-2846.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon B. T., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Two-component regulatory systems responsive to environmental stimuli share strongly conserved domains with the nitrogen assimilation regulatory genes ntrB and ntrC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7850–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Domenighini M., Tuomanen E., Rappuoli R., Falkow S. Filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis: nucleotide sequence and crucial role in adherence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2637–2641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Conserved domains in bacterial regulatory proteins that respond to environmental stimuli. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):579–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90530-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. R., Miller J. F., Falkow S. The bvgA gene of Bordetella pertussis encodes a transcriptional activator required for coordinate regulation of several virulence genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6338–6344. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6338-6344.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Aaronson W., Monack D., Falkow S. Phase variation in Bordetella pertussis by frameshift mutation in a gene for a novel two-component system. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):266–269. doi: 10.1038/338266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of a region of the Bordetella pertussis chromosome encoding filamentous hemagglutinin and the pleiotropic regulatory locus vir. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2904–2913. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2904-2913.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of phase change in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.263-269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


