Abstract
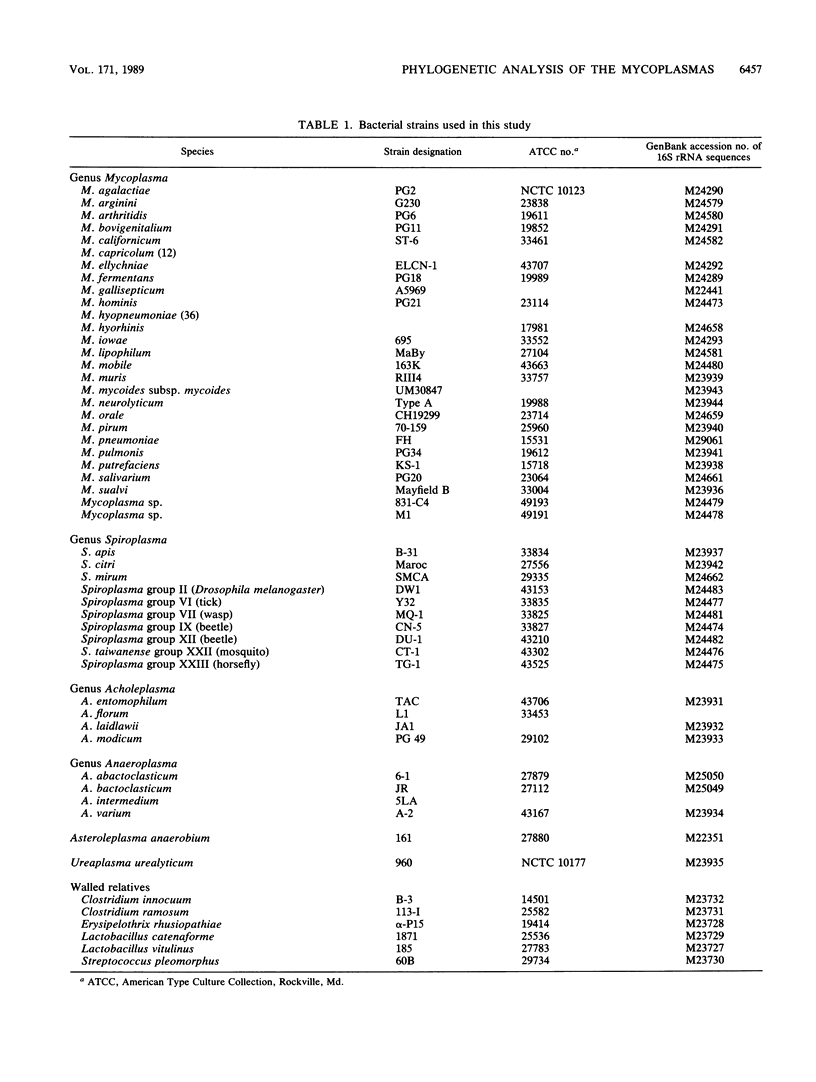
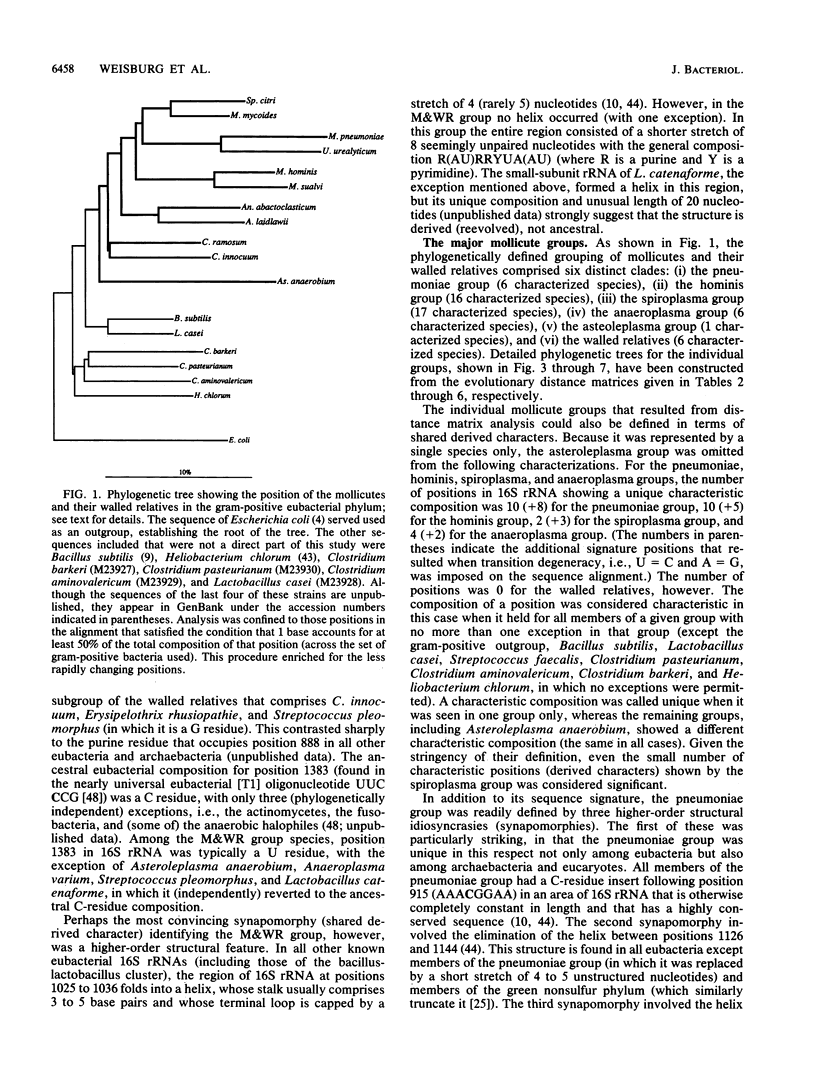
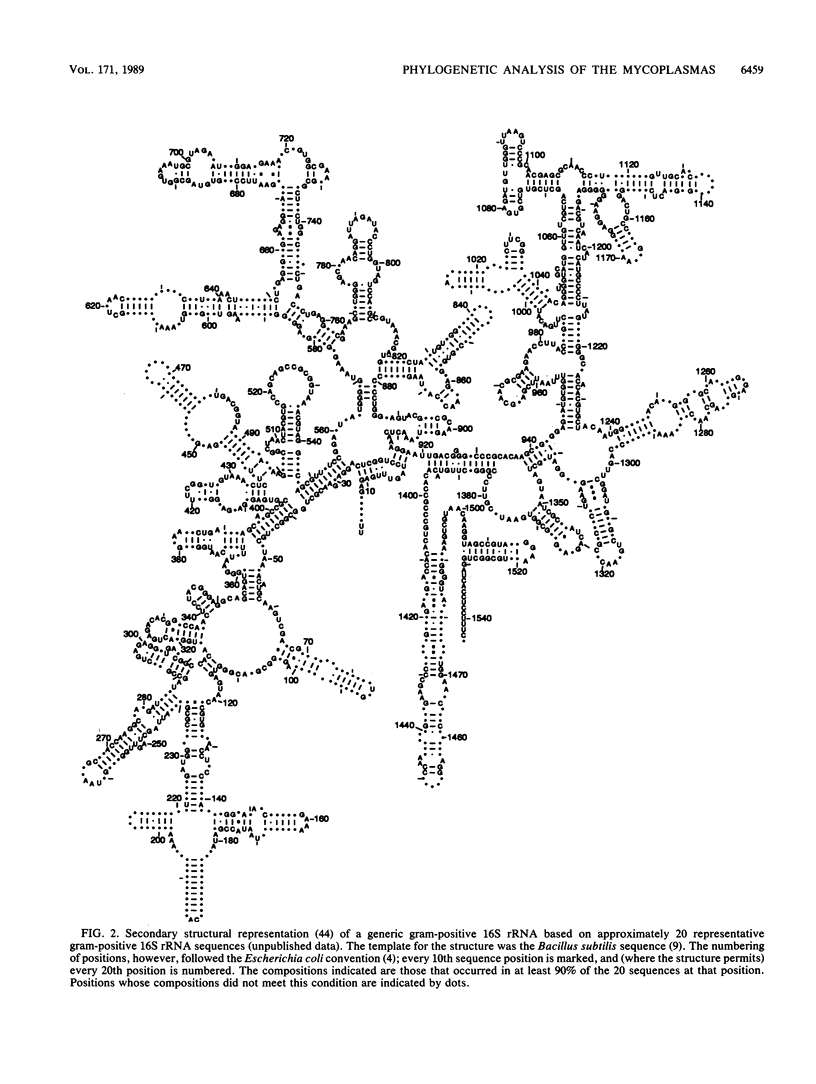
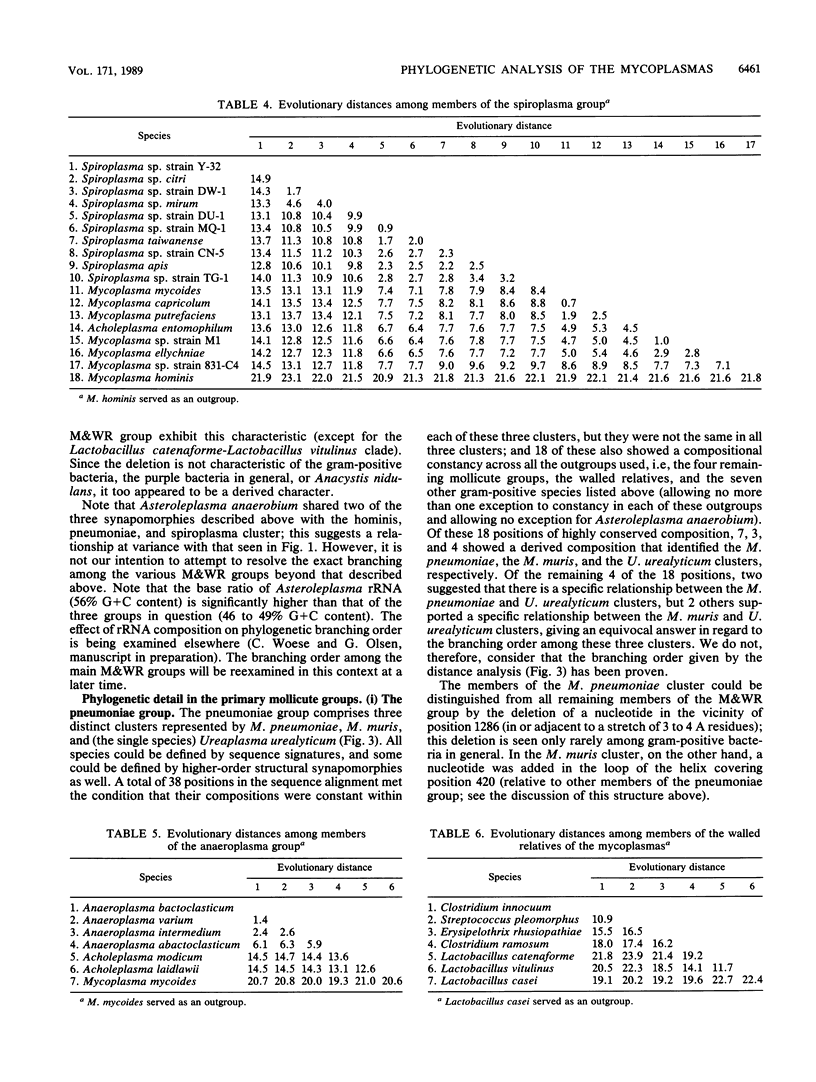
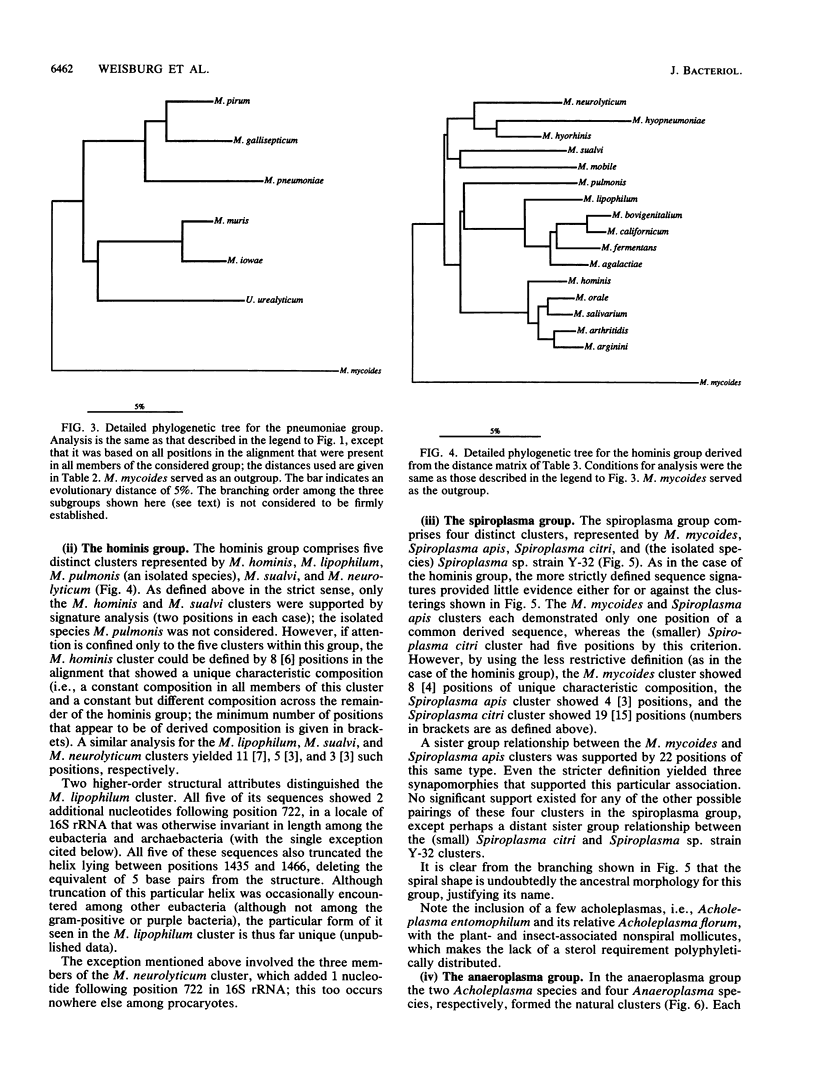
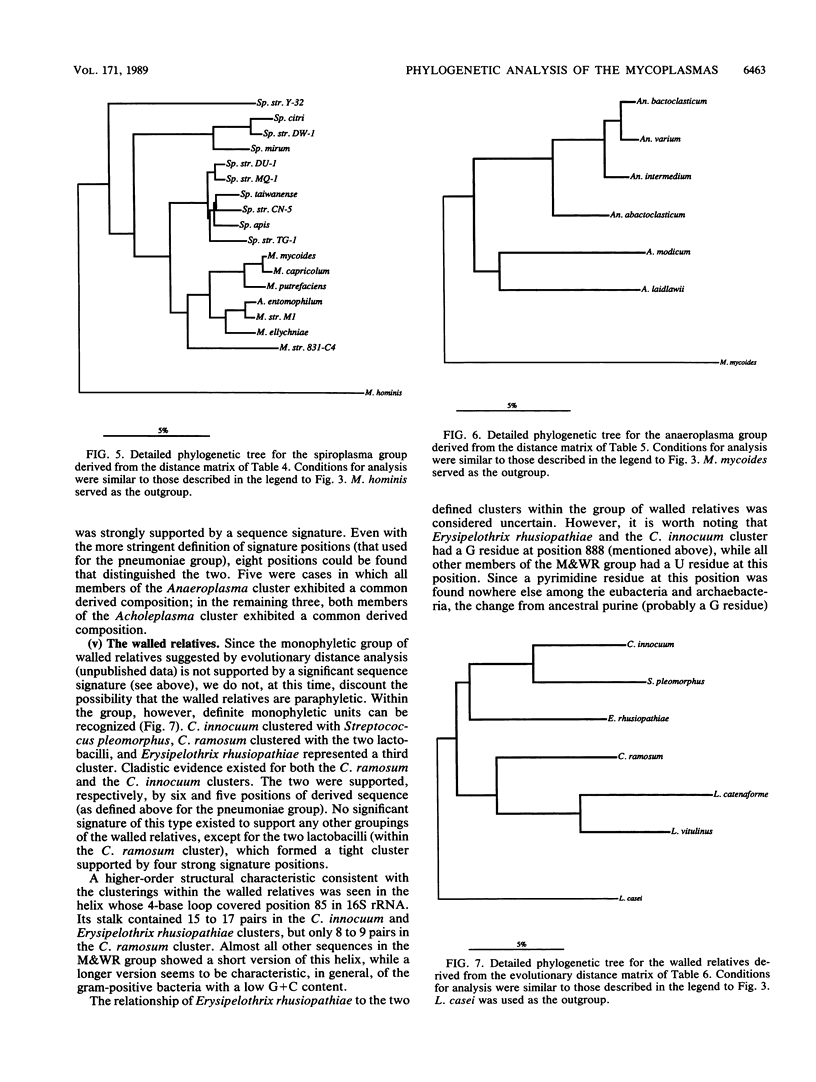
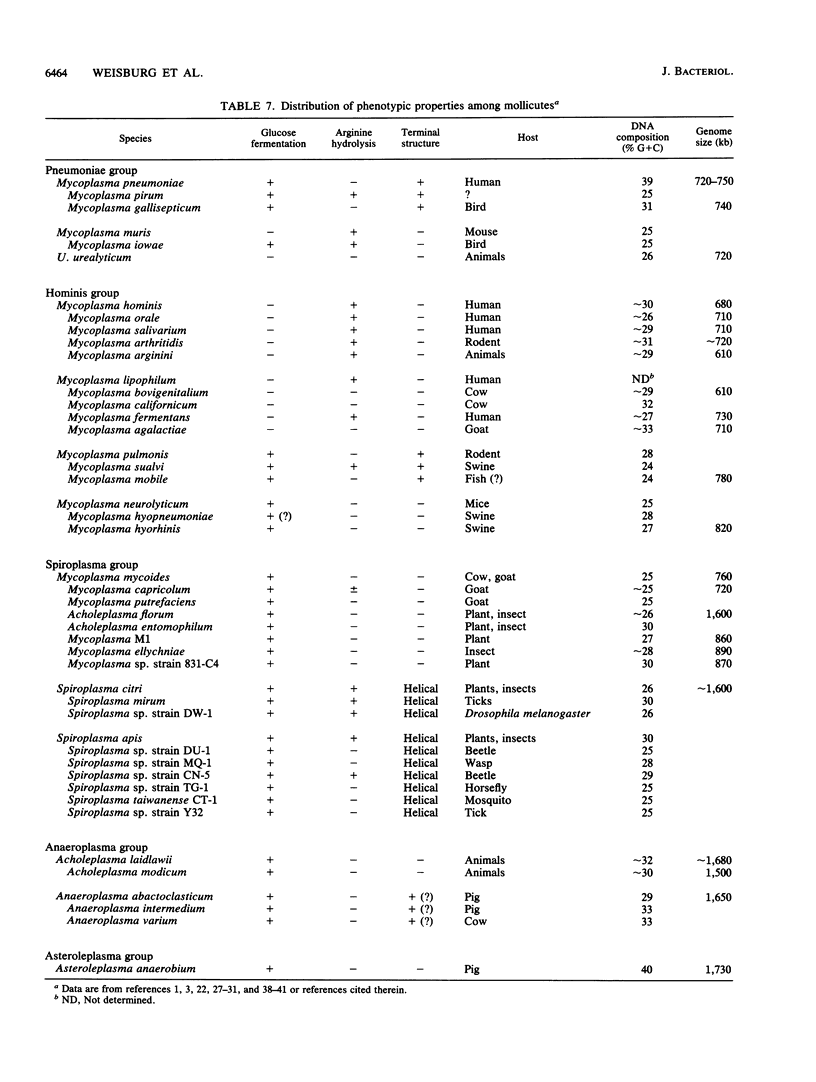
Small-subunit rRNA sequences were determined for almost 50 species of mycoplasmas and their walled relatives, providing the basis for a phylogenetic systematic analysis of these organisms. Five groups of mycoplasmas per se were recognized (provisional names are given): the hominis group (which included species such as Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma lipophilum, Mycoplasma pulmonis, and Mycoplasma neurolyticum), the pneumoniae group (which included species such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma muris), the spiroplasma group (which included species such as Mycoplasma mycoides, Spiroplasma citri, and Spiroplasma apis), the anaeroplasma group (which encompassed the anaeroplasmas and acholeplasmas), and a group known to contain only the isolated species Asteroleplasma anaerobium. In addition to these five mycoplasma groups, a sixth group of variously named gram-positive, walled organisms (which included lactobacilli, clostridia, and other organisms) was also included in the overall phylogenetic unit. In each of these six primary groups, subgroups were readily recognized and defined. Although the phylogenetic units identified by rRNA comparisons are difficult to recognize on the basis of mutually exclusive phenotypic characters alone, phenotypic justification can be given a posteriori for a number of them.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bautsch W. Rapid physical mapping of the Mycoplasma mobile genome by two-dimensional field inversion gel electrophoresis techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11461–11467. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadeau A. P., Mouches C., Bove J. M. Probable insensitivity of mollicutes to rifampin and characterization of spiroplasmal DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):824–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.824-828.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. J., Stewart G. C., Hollis M. A., Vold B. S., Bott K. F. Nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis ribosomal RNA operon, rrnB. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Weiser B., Woese C. R., Noller H. F. Comparative anatomy of 16-S-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:155–216. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Sawada M., Osawa S., Murao K., Ishikura H. The nucleotide sequence of 5S rRNA from Mycoplasma capricolum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5407–5410. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwami M., Muto A., Yamao F., Osawa S. Nucleotide sequence of the rrnB 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Mycoplasma capricolum. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(2):317–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00328065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Brammar W. J. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning large DNA fragments made with several restriction enzymes. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Wagner R., Stutz E. E. coli ribosomes with a C912 to U base change in the 16S rRNA are streptomycin resistant. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3705–3708. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimark H. C. Division of mycoplasmas into subgroups. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):249–263. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimark H., London J. Origins of the mycoplasmas: sterol-nonrequiring mycoplasmas evolved from streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1259–1265. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1259-1265.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyaizu H., Debrunner-Vossbrinck B., Mandelco L., Studier J. A., Woese C. R. The green non-sulfur bacteria: a deep branching in the eubacterial line of descent. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1987;9:47–53. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(87)80055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poddar S. K., Maniloff J. Chromosome analysis by two-dimensional fingerprinting. Gene. 1986;49(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poddar S. K., Maniloff J. Determination of microbial genome sizes by two-dimensional denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2889–2895. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Molecular biology and genetics of mycoplasmas (Mollicutes). Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):419–455. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.419-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. J., Simmons J., Walker R. T., Weisburg W. G., Woese C. R., Tanner R. S., Robinson I. M., Stahl D. A., Olsen G., Leach R. H. Construction of the mycoplasma evolutionary tree from 5S rRNA sequence data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1160–1164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschke C., Ruland K., Herrmann R. Nucleotide sequence of the 16S rRNA of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3918–3918. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from a blue-green alga, Anacystis nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00330888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R., Herrmann R. Physical mapping of the Mycoplasma pneumoniae genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8323–8336. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Debrunner-Vossbrinck B. A., Oyaizu H., Stackebrandt E., Ludwig W. Gram-positive bacteria: possible photosynthetic ancestry. Science. 1985;229:762–765. doi: 10.1126/science.11539659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Maniloff J., Zablen L. B. Phylogenetic analysis of the mycoplasmas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):494–498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Stackebrandt E., Ludwig W. What are mycoplasmas: the relationship of tempo and mode in bacterial evolution. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(4):305–316. doi: 10.1007/BF02115648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Stackebrandt E., Macke T. J., Fox G. E. A phylogenetic definition of the major eubacterial taxa. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1985;6:143–151. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(85)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C., Sogin M., Stahl D., Lewis B. J., Bonen L. A comparison of the 16S ribosomal RNAs from mesophilic and thermophilic bacilli: some modifications in the Sanger method for RNA sequencing. J Mol Evol. 1976 Apr 9;7(3):197–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01731489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamao F., Muto A., Kawauchi Y., Iwami M., Iwagami S., Azumi Y., Osawa S. UGA is read as tryptophan in Mycoplasma capricolum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2306–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D., Oyaizu Y., Oyaizu H., Olsen G. J., Woese C. R. Mitochondrial origins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4443–4447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


