Abstract
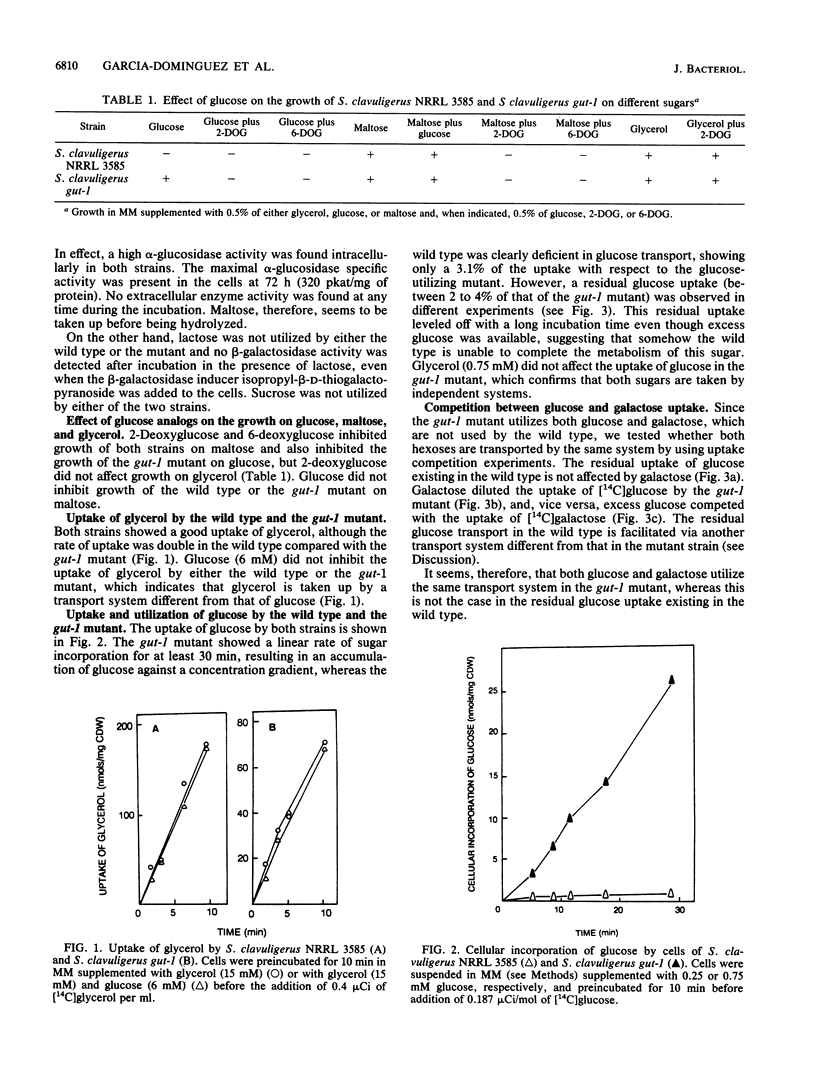
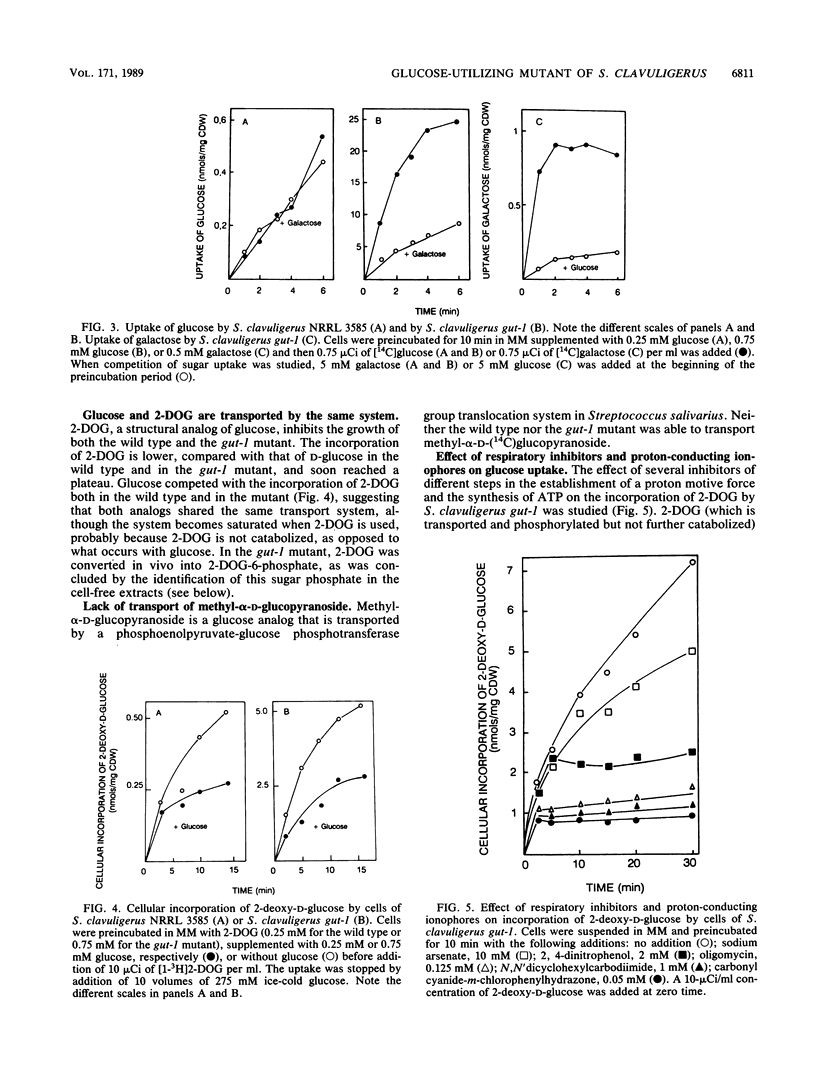
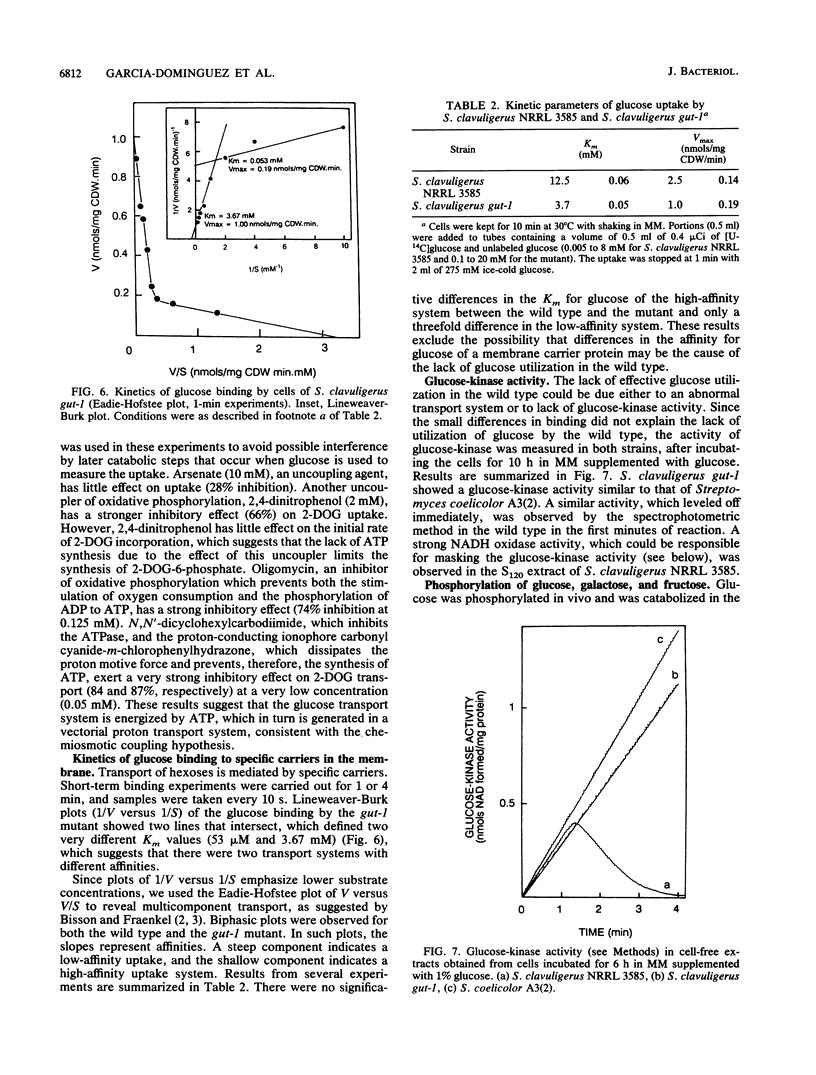
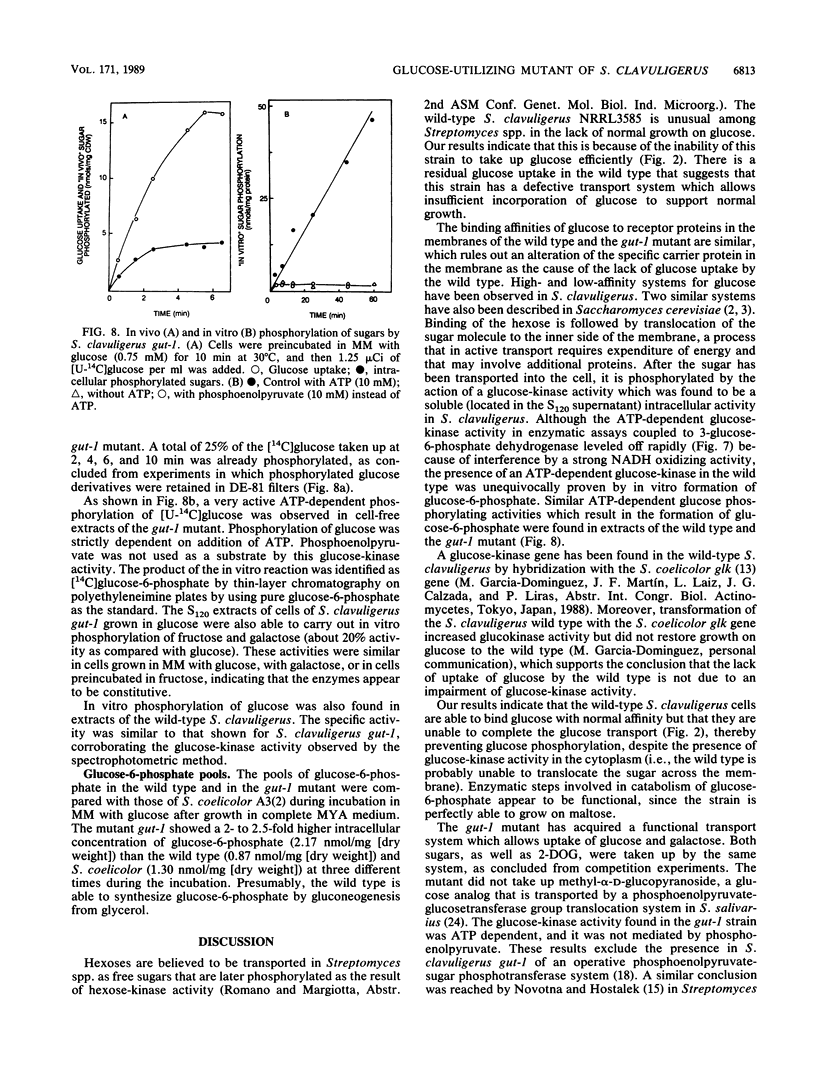
Wild-type Streptomyces clavuligerus NRRL 3585 is unable to utilize glucose. A glucose-utilizing (gut-1) mutant of S. clavuligerus NRRL 3585 has been obtained by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis. The gut-1 mutant is able to grow on glucose or galactose, while the wild type is unable to catabolize these hexoses. Similar binding affinities of glucose by cells of the wild type and the gut-1 mutant were found, but the wild type was unable to complete glucose transport. A soluble intracellular ATP-dependent (but not phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent) glucokinase activity was found both in the wild type and the gut-1 mutant. The gut-1 mutant has acquired a functional transport system that allows transport of glucose, 2-deoxyglucose, and galactose, as shown by hexose competition experiments. The gut-1 transport system concentrates glucose inside the cell at least 10- to 20-fold and is strongly inhibited by respiratory inhibitors, which prevent the establishment of a proton motive force, and by proton-conducting ionophores, suggesting that it is energized by a proton motive force. The new transport system is not completely sugar specific (transporting galactose and glucose through the same system), as opposed to the hexose-specific system reported in wild-type Streptomyces griseus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharonowitz Y., Demain A. L. Carbon catabolite regulation of cephalosporin production in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Aug;14(2):159–164. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson L. F., Fraenkel D. G. Involvement of kinases in glucose and fructose uptake by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson L. F., Fraenkel D. G. Transport of 6-deoxyglucose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):995–1000. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.995-1000.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S., Vining L. C. Nutrient utilization in actinomycetes. Induction of alpha-glucosidases in Streptomyces venezuelae. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jul;27(7):639–645. doi: 10.1139/m81-098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortés J., Liras P., Castro J. M., Martín J. F. Glucose regulation of cephamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces lactamdurans is exerted on the formation of alpha-aminoadipyl-cysteinyl-valine and deacetoxycephalosporin C synthase. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jul;132(7):1805–1814. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-7-1805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortés J., Martín J. F., Castro J. M., Láiz L., Liras P. Purification and characterization of a 2-oxoglutarate-linked ATP-independent deacetoxycephalosporin C synthase of Streptomyces lactamdurans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Nov;133(11):3165–3174. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-11-3165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimarco A. A., Romano A. H. d-Glucose Transport System of Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):151–157. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.151-157.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Seno E. T., Bruton C. J., Chater K. F. Genetic mapping, cloning and physiological aspects of the glucose kinase gene of Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):501–507. doi: 10.1007/BF00436199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaev I. S., Bobyk A. M., Tobek I., Goshtialek Z. O vozmozhnoi roli vysokomolekuliarnykh polifosfatov v biosinteze khlortetratsiklina u Streptomyces aureofaciens. Biokhimiia. 1976 Feb;41(2):343–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Cole M. Clavulanic acid: a beta-lactamase-inhiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):852–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabater B., Asensio C. Transport of hexoses in Streptomyces violaceoruber. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):201–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabater B., Sebastián J., Asensio C. Identification and properties of an inducible and highly specific fructokinase from Streptomyces violaceoruber. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 12;284(2):414–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J., Hardisson C. Induction of beta-galactosidase in Streptomyces violaceus. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jul;25(7):833–840. doi: 10.1139/m79-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno E. T., Chater K. F. Glycerol catabolic enzymes and their regulation in wild-type and mutant strains of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1403–1413. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur C., Trahan L. Glucose transport in Streptococcus salivarius. Evidence for the presence of a distinct phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system which catalyses the phosphorylation of alpha-methyl glucoside. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Feb;28(2):190–199. doi: 10.1139/m82-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


