Abstract
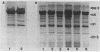
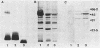
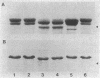
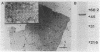
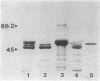
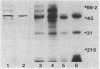
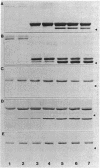
The surface protein composition of members of a serogroup of Aeromonas hydrophila which exhibit high virulence for fish was examined. Treatment of whole cells of representative strain A. hydrophila TF7 with 0.2 M glycine buffer (pH 4.0) resulted in the release of sheets of a tetragonal surface protein array. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis showed that this sheet material was composed primarily of a protein of apparent molecular weight 52,000 (52K protein). A 52K protein was also the predominant protein in glycine extracts of other members of the high-virulence serogroup. Immunoblotting with antiserum raised against formalinized whole cells of A. hydrophila TF7 showed the 52K S-layer protein to be the major surface protein antigen, and impermeant Sulfo-NHS-Biotin cell surface labeling showed that the 52K S-layer protein was the only protein accessible to the Sulfo-NHS-Biotin label and effectively masked underlying outer membrane (OM) proteins. In its native surface conformation the 52K S-layer protein was only weakly reactive with a lactoperoxidase 125I surface iodination procedure. A UV-induced rough lipopolysaccharide (LPS) mutant of TF7 was found to produce an intact S layer, but a deep rough LPS mutant was unable to maintain an array on the cell surface and excreted the S-layer protein into the growth medium, indicating that a minimum LPS oligosaccharide size was required for A. hydrophila S-layer anchoring. The 52K S-layer protein exhibited hear-dependent SDS-solubilization behavior when associated with OM, but was fully solubilized at all temperatures after removal from the OM, indicating a strong interaction of the S layer with the underlying OM. The native S layer was permeable to 125I in the lactoperoxidase radiolabeling procedure, and two major OM proteins of molecular weights 30,000 and 48,000 were iodinated. The 48K species was a peptidoglycan-associated, transmembrane protein which exhibited heat-modifiable SDS solubilization behaviour characteristic of a porin protein. A 50K major peptidoglycan-associated OM protein which was not radiolabeled exhibited similar SDS heat modification characteristics and possibly represents a second porin protein.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belland R. J., Trust T. J. Synthesis, export, and assembly of Aeromonas salmonicida A-layer analyzed by transposon mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):877–881. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.877-881.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingle W. H., Doran J. L., Page W. J. Regular surface layer of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):251–259. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.251-259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Shaw D. H., Ishiguro E. E., Trust T. J. Structural and immunochemical homogeneity of Aeromonas salmonicida lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.16-22.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., MacIntyre S., Buckley J. T., Hancock R. E. Purification and reconstitution in lipid bilayer membranes of an outer membrane, pore-forming protein of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1006–1011. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1006-1011.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Lallier R., Shaw D. H., Trust T. J. Electrophoretic and immunochemical analyses of the lipopolysaccharides from various strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.263-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Lallier R., Trust T. J. Surface antigens of virulent strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jun;12(1-4):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner P. R., Pearson T. W., Clarke M. W., Mutharia L. M. Identification and isolation of a variant surface glycoprotein from Trypanosoma vivax. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):774–777. doi: 10.1126/science.3810164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Role of porins in outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):929–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.929-933.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley W. L., Finkelstein E., Holst B. D. Identification of surface proteins on bovine leukocytes by a biotin-avidin protein blotting technique. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Dec 17;85(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W., Ainsworth T., Chamberlain J. B., Austen R. A., Buckley J. T., Trust T. J. Loss of virulence during culture of Aeromonas salmonicida at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.333-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Isaacson R. E. Proteinaceous bacterial adhesins and their receptors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1983;10(3):229–260. doi: 10.3109/10408418209113564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Buckley J. T., Ishiguro E. E., Phipps B. M., Monette J. P., Trust T. J. Purification and disposition of a surface protein associated with virulence of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1077–1084. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1077-1084.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Phipps B. M., Ishiguro E. E., Trust T. J. Porphyrin binding by the surface array virulence protein of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1332–1336. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1332-1336.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Structural and antigenic heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.210-216.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. C., Doyle D., Burda K., Corbeil L. B., Winter A. J. Superficial antigens of Campylobacter (Vibrio) fetus: characterization of antiphagocytic component. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):517–525. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.517-525.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Lalonde G., Leblanc D., Olivier G., Lallier R. Aeromonas hydrophila in rainbow trout: relation between virulence and surface characteristics. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Dec;26(12):1501–1503. doi: 10.1139/m80-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn C. B., Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Role of surface components in serum resistance of virulent Aeromonas salmonicida. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1069–1075. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1069-1075.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers on bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:311–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]