Abstract
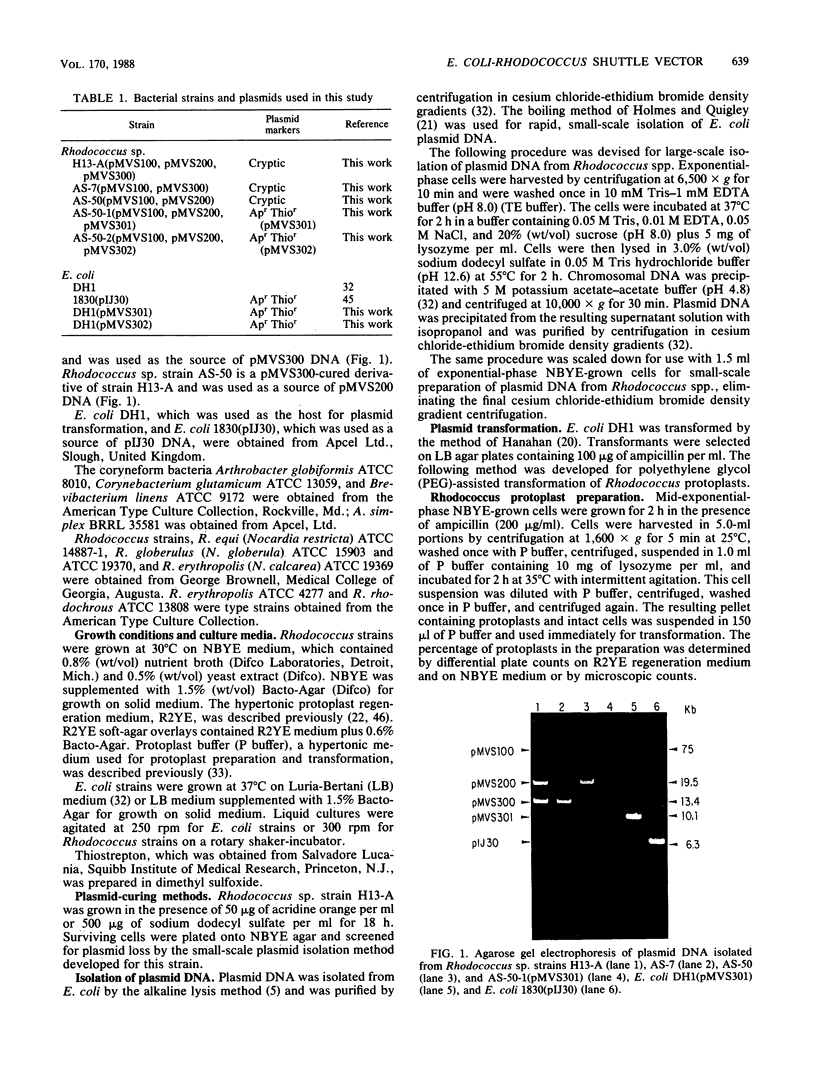
A plasmid transformation system for Rhodococcus sp. strain H13-A was developed by using an Escherichia coli-Rhodococcus shuttle plasmid constructed in this study. Rhodococcus sp. strain H13-A contains three cryptic indigenous plasmids, designated pMVS100, pMVS200, and pMVS300, of 75, 19.5, and 13.4 kilobases (kb), respectively. A 3.8-kb restriction fragment of pMVS300 was cloned into pIJ30, a 6.3-kb pBR322 derivative, containing the E. coli origin of replication (ori) and ampicillin resistance determinant (bla), as well as a Streptomyces gene for thiostrepton resistance, tsr. The resulting 10.1-kb recombinant plasmid, designated pMVS301, was isolated from E. coli DH1(pMVS301) and transformed into Rhodococcus sp. strain AS-50, a derivative of strain H13-A, by polyethylene glycol-assisted transformation of Rhodococcus protoplasts and selection for thiostrepton-resistant transformants. Thiostrepton-resistant transformants were also ampicillin resistant and were shown to contain pMVS301, which was subsequently isolated and transformed back into E. coli. The cloned 3.8-kb fragment of Rhodococcus DNA in pMVS301 contains a Rhodococcus origin of replication, since the hybrid plasmid was capable of replication in both genera. The plasmid was identical in E. coli and Rhodococcus transformants as determined by restriction analysis and was maintained as a stable, independent replicon in both organisms. Optimization of the transformation procedure resulted in transformation frequencies in the range of 10(5) transformants per micrograms of pMVS301 DNA in Rhodococcus sp. strain H13-A and derivative strains. The plasmid host range extends to strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis, R. globulerus, and R. equi, whereas stable transformants were not obtained with R. rhodochrous or with several coryneform bacteria tested as recipients. A restriction map demonstrated 14 unique restriction sites in pMVS301, some of which are potentially useful for molecular cloning in Rhodococcus spp. and other actinomycetes. This is the first report of plasmid transformation and of heterologous gene expression in a Rhodococcus sp.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggag M., Schlegel H. G. Studies on a gram-positive hydrogen bacterium, Nocardia opaca strain 1 b. I. Description and physiological characterization. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;88(4):299–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00409942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Bibb M. J., Ward J. M., Cohen S. N. Nucleotide sequences encoding and promoting expression of three antibiotic resistance genes indigenous to Streptomyces. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):26–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00327505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Cohen S. N. Gene expression in Streptomyces: construction and application of promoter-probe plasmid vectors in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(2):265–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00331128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Ward J. M., Hopwood D. A. Transformation of plasmid DNA into Streptomyces at high frequency. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):398–400. doi: 10.1038/274398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell G. H., Adams J. N. Inheritance of nocardiophage phi EC in matings of nocardial lysogens. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1104–1107. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1104-1107.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell G. H., Enquist L. W., Denniston-Thompson K. An analysis of the genome of actinophage phi EC. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(3-4):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Jacobs W. R., Docherty M. A., Ritchie L. R., Curtiss R., 3rd Molecular analysis of DNA and construction of genomic libraries of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1093-1102.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Z., Kieser T., Hopwood D. A. Expression of a Streptomyces plasmid promoter in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;43(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Alderson G. The actinomycete-genus Rhodococcus: a home for the "rhodochrous" complex. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 May;100(1):99–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-100-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Minnikin D. E. Nocardioform bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:159–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Cohen S. N. Streptomyces contain Escherichia coli-type A + T-rich promoters having novel structural features. Gene. 1985;39(2-3):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Cohen S. N. Streptomyces lividans RNA polymerase recognizes and uses Escherichia coli transcriptional signals. Gene. 1984 Apr;28(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser T., Moss M. T., Dale J. W., Hopwood D. A. Cloning and expression of Mycobacterium bovis BCG DNA in "Streptomyces lividans". J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):72–80. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.72-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer A., Bock H., Wagner F. Chemical and Physical Characterization of Interfacial-Active Lipids from Rhodococcus erythropolis Grown on n-Alkanes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):864–870. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.864-870.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald C. R., Cooper D. G., Zajic J. E. Surface-Active Lipids from Nocardia erythropolis Grown on Hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.117-123.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okanishi M., Suzuki K., Umezawa H. Formation and reversion of Streptomycete protoplasts: cultural condition and morphological study. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Feb;80(2):389–400. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-2-389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensfuss C., Reh M., Schlegel H. G. No correlation exists between the conjugative transfer of the autotrophic character and that of plasmids in Nocardia opaca strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Apr;132(4):997–1007. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-4-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Dauwerse H. G., Das P. K., Groothuis D. G., Schouls L. M., van Embden J. D. Cloning of Mycobacterium bovis BCG DNA and expression of antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):800–806. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.800-806.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. J., Kieser T., Ward J. M., Hopwood D. A. Physical analysis of antibiotic-resistance genes from Streptomyces and their use in vector construction. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. J., Ward J. M., Hopwood D. A. DNA cloning in Streptomyces: resistance genes from antibiotic-producing species. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):525–527. doi: 10.1038/286525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakisaka Y., Koizumi K., Nishimoto Y., Kobayashi M., Tsuji N. Hygromycin and epihygromycin from a bacterium, Corynebacterium equi No. 2841. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1980 Jul;33(7):695–704. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.33.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Maeshima H., Wada M., Chibata I. Production of D-alanine by Corynebacterium fascians. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):636–640. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.636-640.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]