Abstract
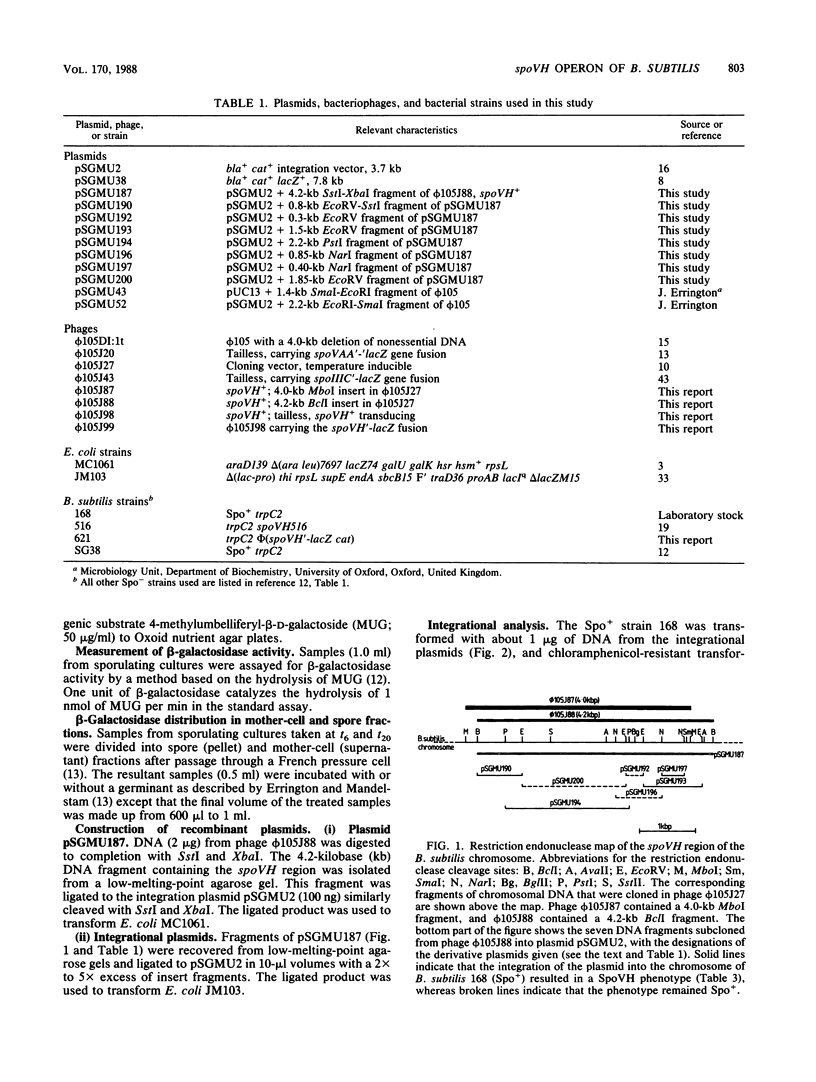
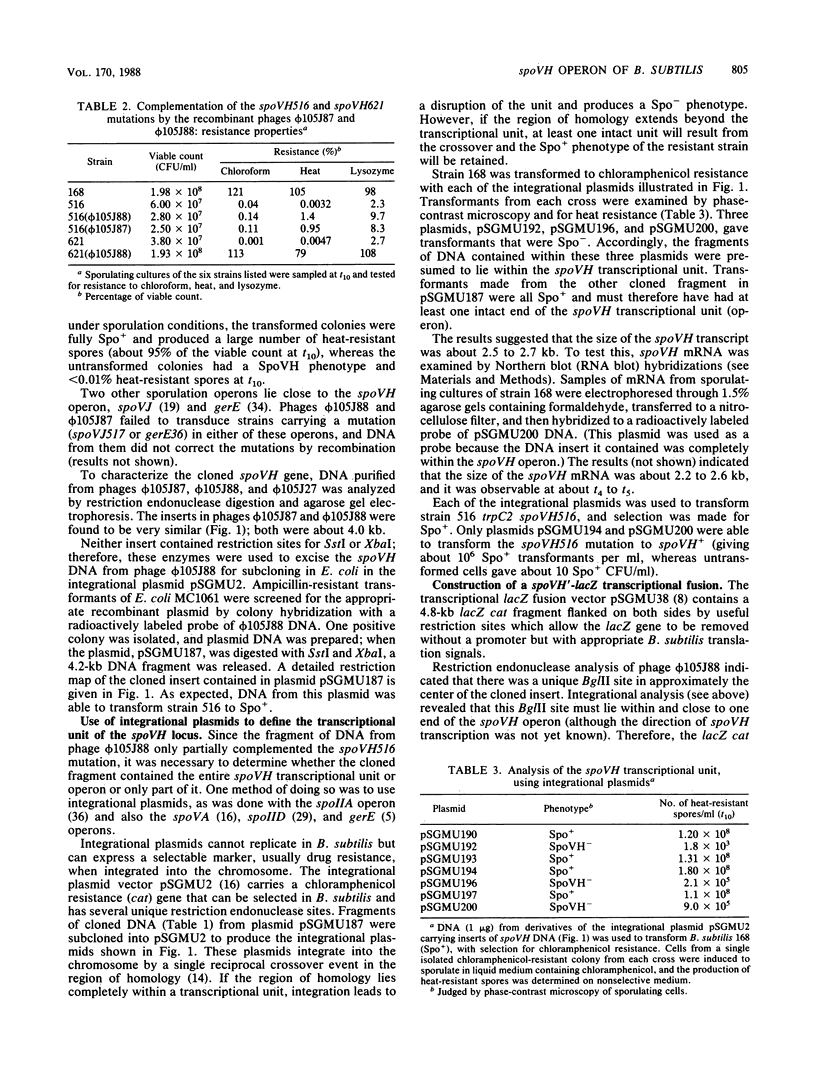
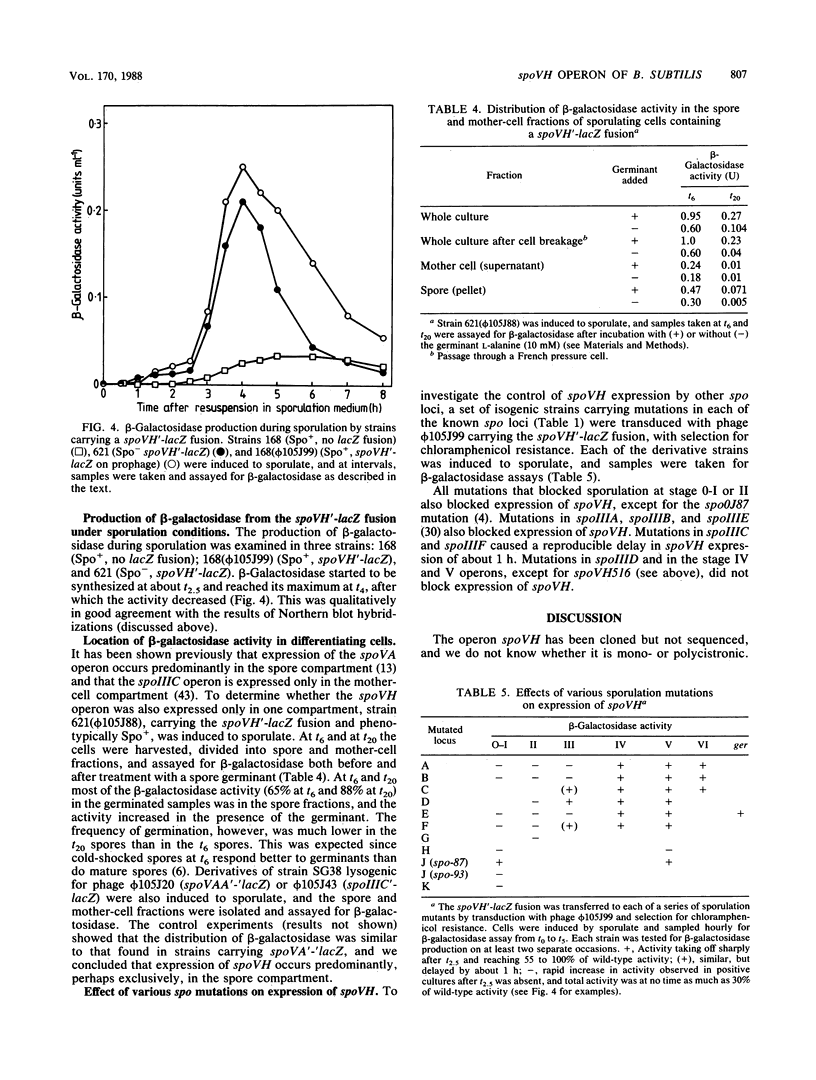
The spoVH locus, involved in the sporulation of Bacillus subtilis, was cloned in derivatives of the temperate bacteriophage luminal diameter 105. Two recombinant phages were obtained which contained 4.2 kilobases of chromosomal DNA. Both phages only partially complemented a mutation in the spoVH operon, spoVH516. Nevertheless, analysis of the cloned locus with integrational plasmids showed that the complete operon had been cloned. A spoVH'-lacZ transcriptional fusion was constructed, and this indicated that the spoVH operon was expressed 2.25 h after the start of sporulation. The distribution of beta-galactosidase in sporulating cells containing a spoVH'-lacZ fusion showed that spoVH was expressed in the spore compartment; lac fusion experiments were also used to study spoVH expression in the presence of other sporulation mutations. Expression of spoVH was prevented by mutations in any of the stage 0 or stage II loci and also by mutations in spoIIIA, spoIIIB, and spoIIIE. A similar pattern of dependence was found previously for the expression of spoVA, which is also expressed in the spore compartment.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bugaichuk U. D., Deadman M., Errington J., Savva D. Restriction enzyme analysis of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 105 DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2165–2167. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugaichuk U. D. Studies of transcriptional regulation of the Bacillus subtilis developmental gene spoVE. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Sep;133(9):2349–2357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-9-2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Mandelstam J. Regulation of stage II of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Sep;133(9):2371–2380. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-9-2371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting S., Mandelstam J. The nucleotide sequence and the transcription during sporulation of the gerE gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):3013–3024. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-3013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion P., Mandelstam J. Germination properties as marker events characterizing later stages of Bacillus subtilis spore formation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):786–792. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.786-792.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J. A general method for fusion of the Escherichia coli lacZ gene to chromosomal genes in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):2953–2966. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-2953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Cutting S. M., Mandelstam J. Branched pattern of regulatory interactions between late sporulation genes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):796–801. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.796-801.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J. Efficient Bacillus subtilis cloning system using bacteriophage vector phi 105J9. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Oct;130(10):2615–2628. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-10-2615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Jones D. Cloning in Bacillus subtilis by transfection with bacteriophage vector phi 105J27: isolation and preliminary characterization of transducing phages for 23 sporulation loci. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):493–502. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Mandelstam J. Genetic and phenotypic characterization of a cluster of mutations in the spoVA locus of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2115–2121. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Mandelstam J. Use of a lacZ gene fusion to determine the dependence pattern and the spore compartment expression of sporulation operon spoVA in spo mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):2977–2985. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-2977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Mandelstam J. Use of a lacZ gene fusion to determine the dependence pattern of sporulation operon spoIIA in spo mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):2967–2976. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-2967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Nguyen A., Lang D., Hoch J. A. Construction and properties of an integrable plasmid for Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1513–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1513-1515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flock J. I. Deletion mutants of temperate Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi105. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Oct 24;155(3):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00272803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Errington J. Nucleotide sequence and complementation analysis of a polycistronic sporulation operon, spoVA, in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 May;131(5):1091–1105. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-5-1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Piggot P. J. Nucleotide sequence of sporulation locus spoIIA in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2147–2153. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. H. SpoVH and spoVJ--new sporulation loci in Bacillus subtilis 168. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Feb;129(2):293–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A. Selection of cells transformed to prototrophy for sporulation markers. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1200–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1200-1201.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hranueli D., Piggot P. J., Mandelstam J. Statistical estimate of the total number of operons specific for Bacillus subtilis sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):684–690. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.684-690.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iijima T., Kawamura F., Saito H., Ikeda Y. A specialized transducing phage constructed from Bacillus subtilis phage phi 105. Gene. 1980 Apr;9(1-2):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James W., Mandelstam J. Protease production during sporulation of germination mutants of Bacillus subtilis and the cloning of a functional gerE gene. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2421–2430. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F. Altered arrangement of proteins in the spore coat of a germination mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jun;129(6):1945–1958. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-6-1945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Kay D., Mandelstam J. Temporal dissociation of late events in Bacillus subtilis sporulation from expression of genes that determine them. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):793–805. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.793-805.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Mandelstam J. Cloning of the Bacillus subtilis lys and spoIIIB genes in phage phi 105. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2229–2240. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D., Errington J. Construction of improved bacteriophage phi 105 vectors for cloning by transfection in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):483–492. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Diaz I., Clarke S., Mandelstam J. spoIID operon of Bacillus subtilis: cloning and sequence. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):341–354. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam J., Errington J. Dependent sequences of gene expression controlling spore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Sci. 1987 Aug;4(8):238–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. Germination properties of a spore coat-defective mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1106–1116. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1106-1116.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Curtis C. A., de Lencastre H. Use of integrational plasmid vectors to demonstrate the polycistronic nature of a transcriptional unit (spoIIA) required for sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2123–2136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Hoch J. A. Revised genetic linkage map of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Jun;49(2):158–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.2.158-179.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savva D., Mandelstam J. Cloning of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIA and spoV A loci in phage phi 105DI:1t. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2137–2145. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterlini J. M., Mandelstam J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1130029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner S. M., Errington J., Mandelstam J. Use of a lacZ gene fusion to determine the dependence pattern of sporulation operon spoIIIC in spo mutants of Bacillus subtilis: a branched pathway of expression of sporulation operons. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):2995–3003. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-2995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman P., Zuber P., Perkins J. B., Sandman K., Igo M., Losick R. New ways to study developmental genes in spore-forming bacteria. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):285–291. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4697.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Use of a lacZ fusion to study the role of the spoO genes of Bacillus subtilis in developmental regulation. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



