Abstract
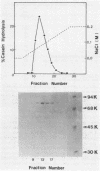
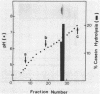
Protease Re, a new cytoplasmic endoprotease in Escherichia coli, was purified to homogeneity by conventional procedures, using [3H]casein as the substrate. The enzyme consists of a single polypeptide of 82,000 molecular weight. It is maximally active between pH 7 and 8.5 and is independent of ATP. It has a pI of 6.8 and a Km of 10.8 microM for casein. Since diisopropyl fluorophosphate and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride inhibited this enzyme, it appears to be a serine protease. Protease Re was sensitive to inhibition by L-1-tosylamido-2-phenylethylchloromethylketone but not to that by 1-chloro-3-tosylamido-7-aminoheptanone, thiol-blocking reagents, chelating agents, or various peptide aldehydes. Re also degraded [125I]globin, [125I]glucagon, and 125I-labeled denatured bovine serum albumin to acid-soluble products (generally oligopeptides of greater than 1,500 daltons), but it showed no activity against serum albumin, growth hormone, insulin, or a variety of fluorometric peptide substrates. It also hydrolyzed oxidatively inactivated glutamine synthetase (generated by ascorbate, oxygen, and iron) four- to fivefold more rapidly than the native protein. Protease Re appears to be identical to the proteolytic enzyme isolated by Roseman and Levine (J. Biol. Chem. 262:2101-2110, 1987) by its ability to degrade selectively oxidatively damaged glutamine synthetase in vivo. Its role in intracellular protein breakdown is uncertain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowles L. K., Konisky J. Cleavage of colicin Ia by the Escherichia coli K-12 outer membrane is not mediated by the colicin Ia receptor. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):668–671. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.668-671.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Lazdunski C. Interaction of colicin E4 with specific receptor sites mediates its cleavage into two fragments inactive towards whole cells. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):525–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Blobel G., Model P. Detection of prokaryotic signal peptidase in an Escherichia coli membrane fraction: endoproteolytic cleavage of nascent f1 pre-coat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):361–365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charette M. F., Henderson G. W., Markovitz A. ATP hydrolysis-dependent protease activity of the lon (capR) protein of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4728–4732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Zipser D. Purification and characterization of protease III from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4698–4706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. H., Goldberg A. L. Purification and characterization of protease So, a cytoplasmic serine protease in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):231–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.231-238.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. H., Goldberg A. L. The product of the lon (capR) gene in Escherichia coli is the ATP-dependent protease, protease La. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4931–4935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. H., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Studies of the protein encoded by the lon mutation, capR9, in Escherichia coli. A labile form of the ATP-dependent protease La that inhibits the wild type protease. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):215–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. J., Goldberg A. L. Oxygen radicals stimulate intracellular proteolysis and lipid peroxidation by independent mechanisms in erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8220–8226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D., Tai P. C. The mechanism of protein secretion across membranes. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):433–438. doi: 10.1038/283433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. M., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Red blood cells contain a pathway for the degradation of oxidant-damaged hemoglobin that does not require ATP or ubiquitin. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5705–5713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Swamy K. H., Chung C. H., Larimore F. S. Proteases in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):680–702. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang B. J., Park W. J., Chung C. H., Goldberg A. L. Escherichia coli contains a soluble ATP-dependent protease (Ti) distinct from protease La. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5550–5554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama-Fujimura Y., Gottesman S., Maurizi M. R. A multiple-component, ATP-dependent protease from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4477–4485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowit J. D., Goldberg A. L. Intermediate steps in the degradation of a specific abnormal protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8350–8357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larimore F. S., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Studies of the ATP-dependent proteolytic enzyme, protease La, from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4187–4195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. L., Oliver C. N., Fulks R. M., Stadtman E. R. Turnover of bacterial glutamine synthetase: oxidative inactivation precedes proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2120–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurizi M. R., Trisler P., Gottesman S. Insertional mutagenesis of the lon gene in Escherichia coli: lon is dispensable. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1124–1135. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1124-1135.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. S., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. The energy utilized in protein breakdown by the ATP-dependent protease (La) from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):722–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Shelton E., Stadtman E. R. Zinc-induced paracrystalline aggregation of glutamine synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jul;163(1):155–171. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Gottesman S. Protein degradation in Escherichia coli: the lon gene controls the stability of sulA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):358–362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W. The genetics of protein degradation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:279–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak P., Ray P. H., Dev I. K. Localization and purification of two enzymes from Escherichia coli capable of hydrolyzing a signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):420–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. Preferential degradation of the oxidatively modified form of glutamine synthetase by intracellular mammalian proteases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W., Craig N. L. Escherichia coli recA gene product inactivates phage lambda repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4714–4718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseman J. E., Levine R. L. Purification of a protease from Escherichia coli with specificity for oxidized glutamine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2101–2110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John A. C., Conklin K., Rosenthal E., Goldberg A. L. Further evidence for the involvement of charged tRNA and guanosine tetraphosphate in the control of protein degradation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3945–3951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Smyrniotis P. Z., Davis J. N., Wittenberger M. E. Enzymic procedures for determining the average state of adenylylation of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase. Anal Biochem. 1979 May;95(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swamy K. H., Chung C. H., Goldberg A. L. Isolation and characterization of protease do from Escherichia coli, a large serine protease containing multiple subunits. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 15;224(2):543–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swamy K. H., Goldberg A. L. E. coli contains eight soluble proteolytic activities, one being ATP dependent. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):652–654. doi: 10.1038/292652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swamy K. H., Goldberg A. L. Subcellular distribution of various proteases in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1027-1033.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Goldberg A. L. Guanosine-5'-diphosphate-3'-diphosphate (ppGpp) and the regulation of protein breakdown in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Protease La from Escherichia coli hydrolyzes ATP and proteins in a linked fashion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4883–4887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Selectivity of intracellular proteolysis: protein substrates activate the ATP-dependent protease (La). Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.2938257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. The assembly of proteins into biological membranes: The membrane trigger hypothesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:23–45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfolk C. A., Shapiro B., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. I. Purification and properties of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):177–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]