Abstract
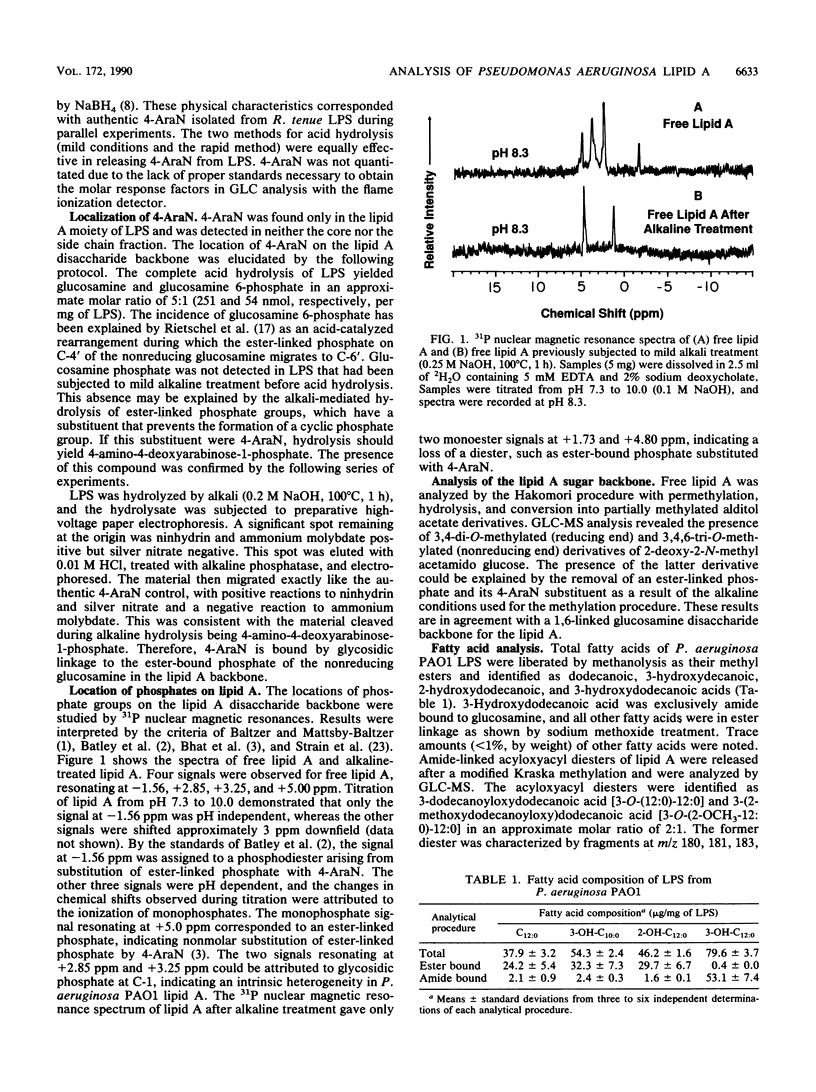
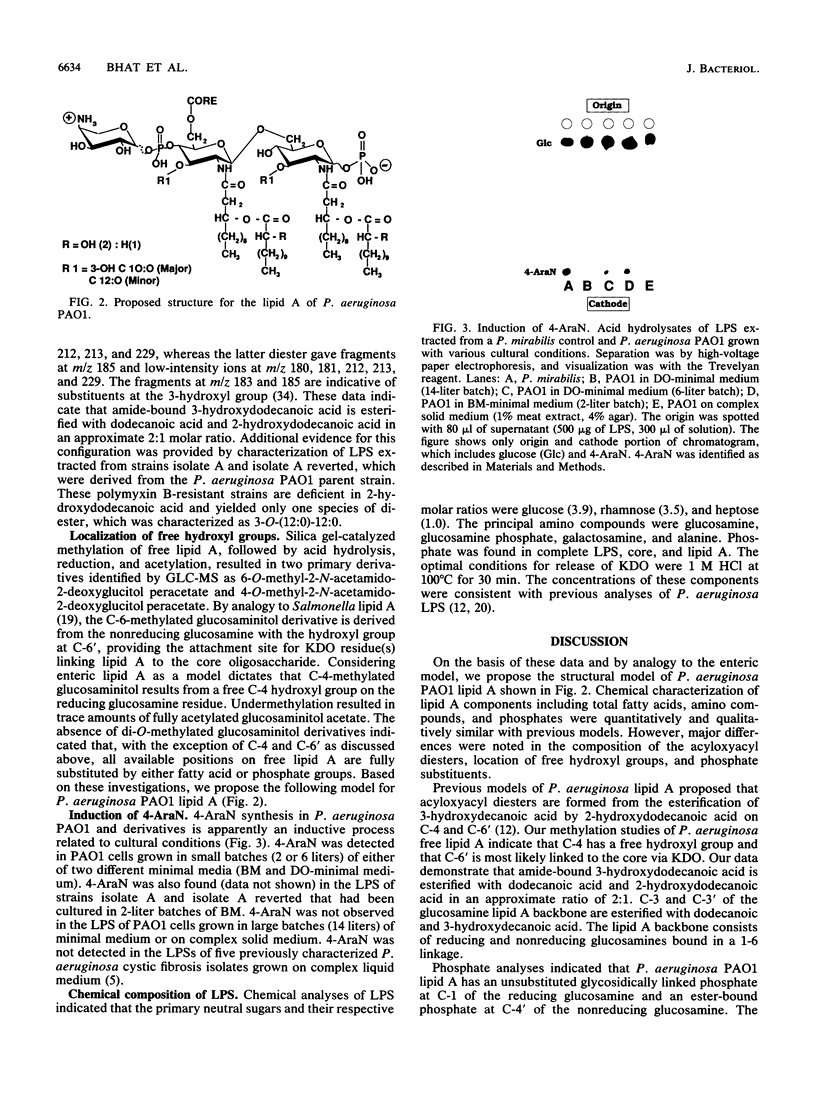
Lipid A derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 contains a biphosphorylated 1-6-linked glucosamine disaccharide backbone. The reducing glucosamine has an unsubstituted glycosidically linked phosphate at C-1. The nonreducing glucosamine has an ester-bound phosphate at C-4' which is nonstoichiometrically substituted with 4-amino-4-deoxyarabinose. Induction of 4-amino-4-deoxyarabinose was dependent on cultural conditions. No pyrophosphate groups were detected. Acyloxyacyl diesters are formed by esterification of the amide-bound 3-hydroxydodecanoic acid with dodecanoic acid and 2-hydroxydodecanoic acids in an approximate molar ratio of 2:1. Dodecanoic and 3-hydroxydecanoic acids are esterified to positions C-3 and C-3' in the sugar backbone. All hydroxyl groups of the glucosamine disaccharide except C-4 and C-6' are substituted. Lipopolysaccharide chemical analyses measured glucose, rhamnose, heptose, galactosamine, alanine, phosphate, and glucosamine. The proposed lipid A structure differs from previous models. There are significant differences in acyloxyacyl diesters, and the proposed model includes an aminopentose substituent.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltzer L. H., Mattsby-Baltzer I. Heterogeneity of lipid A: structural determination by 13C and 31P NMR of lipid A fractions from lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli 0111. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3570–3575. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R. S., Galanos C. Fatty acid alterations and polymyxin B binding by lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa adapted to polymyxin B resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Oct;33(10):1724–1728. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.10.1724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Conrad R. S., Galanos C., Shand G. H., Høiby N. Comparative immunochemistry of lipopolysaccharides from typable and polyagglutinable Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):821–826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.821-826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Lyle R. D. Chemical alterations in cell envelopes of polymyxin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.839-845.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase S., Reitschel E. T. The chemical structure of the lipid A component of lipopolysaccharides from Chromobacterium violaceum NCTC 9694. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):23–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozulić B., Ries B., Mildner P. N-acetylation of amino sugar methyl glycosides for gas-liquid chromatographic analysis. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 1;94(1):36–39. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90786-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Jewell B., Kuzio J., Milazzo F., Berry D. Structure and functions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;36:58–73. doi: 10.1159/000410472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R. R., Tinsley I. J. A simple, sensitive method for lipid phosphorus. Lipids. 1974 Jul;9(7):491–492. doi: 10.1007/BF02534277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Markham R. B., Eardley D. Correlation of the biologic responses of C3H/HEJ mice to endotoxin with the chemical and structural properties of the lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):184–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Gottert H., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Nature and linkages of the fatty acids present in the lipid-A component of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):166–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Wollenweber H. W., Russa R., Brade H., Zähringer U. Concepts of the chemical structure of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):432–438. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe P. S., Meadow P. M. Structure of the Core oligosaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAC1R and its defective mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidorczyk Z., Zähringer U., Rietschel E. T. Chemical structure of the lipid A component of the lipopolysaccharide from a Proteus mirabilis Re-mutant. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 1;137(1-2):15–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain S. M., Armitage I. M., Anderson L., Takayama K., Qureshi N., Raetz C. R. Location of polar substituents and fatty acyl chains on lipid A precursors from a 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid-deficient mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Studies by 1H, 13C, and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16089–16098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W., Weckesser J., Salimath P. V., Galanos C. Nontoxic lipopolysaccharide from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):153–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.153-158.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tharanathan R. N., Weckesser J., Mayer H. Structural studies on the D-arabinose-containing lipid A from Rhodospirillum tenue 2761. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):385–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Jensen M., Helander I., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk W. A., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. The occurrence of 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose as a constituent in Salmonella lipopolysaccharide preparations. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):223–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Broady K. W., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T. The chemical structure of lipid A. Demonstration of amide-linked 3-acyloxyacyl residues in Salmonella minnesota Re lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Seydel U., Lindner B., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T. Nature and location of amide-bound (R)-3-acyloxyacyl groups in lipid A of lipopolysaccharides from various gram-negative bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):265–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


