Abstract
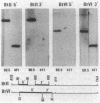
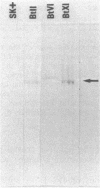
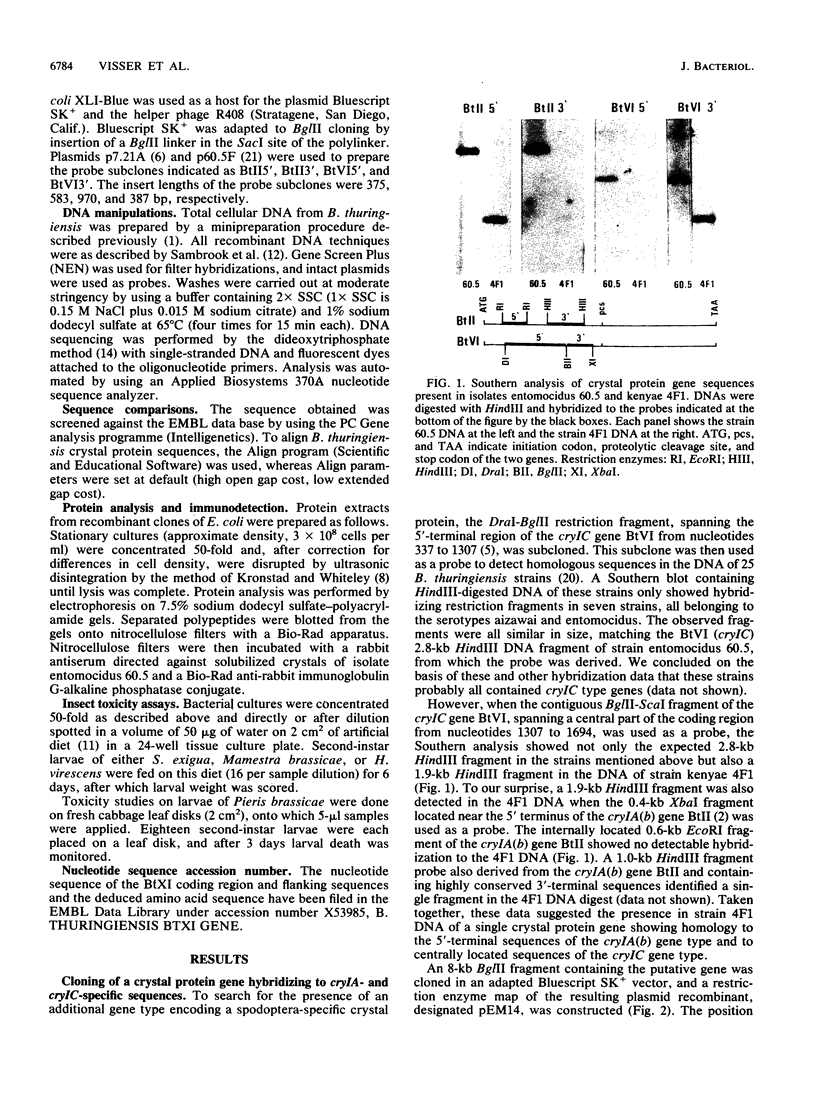
Only one of the four lepidoptera-specific crystal protein subclasses (CryIC) Bacillus thuringiensis was previously shown to be highly toxic against several Spodoptera species. By using a cryIC-derived nucleotide probe, DNA from 25 different strains of B. thuringiensis was screened for the presence of homologous sequences. A putative crystal protein gene, considerably different from the cryIC gene subclass, was identified in the DNA of strain 4F1 (serotype kenyae) and cloned in Escherichia coli. Its nucleotide sequence was determined and appeared to contain several features typical for a crystal protein gene. Furthermore, the region coding for the N-terminal part of the putative toxic fragment showed extensive homology to subclass cryIA sequences derived from gene BtII, whereas the region coding for the C-terminal part appeared to be highly homologous to the cryIC gene BtVI. With an anti-crystal protein antiserum, a polypeptide of the expected size could be demonstrated in Western immunoblots, onto which a lysate of E. coli cells harboring the putative gene, now designated as BtXI, had been transferred. Cells expressing the gene appeared to be equally toxic against larvae of Spodoptera exigua as recombinant cells expressing the BtVI (cryIC)-encoded crystal protein. However, no toxicity against larvae of Heliothis virescens, Mamestra brassicae, or Pieris brassicae could be demonstrated. The nucleotide sequence analysis and the toxicity studies showed that this novel crystal protein gene falls into a new cryl gene subclass. We propose that this subclass be referred to as cryIE.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Geiser M., Schweitzer S., Grimm C. The hypervariable region in the genes coding for entomopathogenic crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis: nucleotide sequence of the kurhd1 gene of subsp. kurstaki HD1. Gene. 1986;48(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90357-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C., Vanderbruggen H., Höfte H., Van Rie J., Jansens S., Van Mellaert H. Specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins is correlated with the presence of high-affinity binding sites in the brush border membrane of target insect midguts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7844–7848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honée G., Vriezen W., Visser B. A Translation Fusion Product of Two Different Insecticidal Crystal Protein Genes of Bacillus thuringiensis Exhibits an Enlarged Insecticidal Spectrum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):823–825. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.823-825.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honée G., van der Salm T., Visser B. Nucleotide sequence of crystal protein gene isolated from B. thuringiensis subspecies entomocidus 60.5 coding for a toxin highly active against Spodoptera species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6240–6240. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfte H., Whiteley H. R. Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):242–255. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.242-255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Whiteley H. R. Three classes of homologous Bacillus thuringiensis crystal-protein genes. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGaughey W. H. Insect Resistance to the Biological Insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):193–195. doi: 10.1126/science.229.4709.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchis V., Lereclus D., Menou G., Chaufaux J., Lecadet M. M. Multiplicity of delta-endotoxin genes with different insecticidal specificities in Bacillus thuringiensis aizawai 7.29. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):393–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnepf H. E., Wong H. C., Whiteley H. R. The amino acid sequence of a crystal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis deduced from the DNA base sequence. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6264–6272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., Jansens S., Höfte H., Degheele D., Van Mellaert H. Receptors on the brush border membrane of the insect midgut as determinants of the specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1378–1385. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1378-1385.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., Jansens S., Höfte H., Degheele D., Van Mellaert H. Specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. Importance of specific receptors on the brush border membrane of the mid-gut of target insects. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):239–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., McGaughey W. H., Johnson D. E., Barnett B. D., Van Mellaert H. Mechanism of insect resistance to the microbial insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2294593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser B. A screening for the presence of four different crystal protein gene types in 25 Bacillus thuringiensis strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Apr;49(2-3):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Schnepf H. E., Whiteley H. R. Transcriptional and translational start sites for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1960–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]