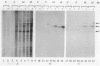
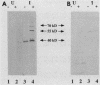
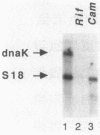
Abstract
We have investigated the heat shock response in the mouse pneumonitis strain of Chlamydia trachomatis. The kinetics of the chlamydial heat shock response resembled that of other procaryotes: the induction was rapid, occurring over a 5- to 10-min time period, and was regulated at the level of transcription. Immunoblot analysis and immunoprecipitations with heterologous antisera to the heat shock proteins DnaK and GroEL demonstrated that the rate of synthesis, but not the absolute amount of these two proteins, increased after heat shock. Using a general screen for genes whose mRNAs are induced by heat shock, we identified and cloned two of these. DNA sequence analysis demonstrated that one of the genes is a homolog of dnaK. Further sequence analysis of the region upstream of the dnaK gene revealed that the chlamydial homolog of the grpE gene is located just adjacent to the dnaK gene. The second locus encoded three potential nonoverlapping open reading frames. One of the open reading frames was 52% homologous to the ribosomal protein S18 of Escherichia coli and thus presumably encodes the chlamydial homolog. Interestingly, this ribosomal protein is not known to be induced by heat shock in E. coli. S1 nuclease and primer extension analyses located the start site of the dnaK transcript to the last nucleotide of the grpE coding sequence, suggesting that these two genes, although tandemly arranged, are transcribed separately. No promoter sequences resembling the E. coli consensus heat shock promoter could be identified upstream of either the C. trachomatis dnaK, grpE, or S18 gene. The induction of the dnaK and S18 mRNAs by heat shock occurred at a transcriptional level; their induction could be blocked by rifampin. The mechanisms of induction for these two loci were not the same, however; they were differentially sensitive to chloramphenicol. Whereas the induction of dnaK mRNA required de novo protein synthesis, the induction of the S18 mRNA did not. Thus, C. trachomatis utilizes at least two different pathways to induce the transcription of mRNAs encoding proteins induced in the heat shock response.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ang D., Georgopoulos C. The heat-shock-regulated grpE gene of Escherichia coli is required for bacterial growth at all temperatures but is dispensable in certain mutant backgrounds. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2748–2755. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2748-2755.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavoil P., Stephens R. S., Falkow S. A soluble 60 kiloDalton antigen of Chlamydia spp. is a homologue of Escherichia coli GroEL. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):461–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y. The chlamydia: molecular biology of procaryotic obligate parasites of eucaryocytes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):274–306. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.274-306.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. D., Fraser C. E. Experimental trachoma in owl monkeys. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Jul;18(4):568–572. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1969.18.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Heffron F. Induction of Salmonella stress proteins upon infection of macrophages. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):730–732. doi: 10.1126/science.1970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B., Walker G. C. Cellular defects caused by deletion of the Escherichia coli dnaK gene indicate roles for heat shock protein in normal metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2337-2346.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilition S. L., Maclean I. W., Peeling R., Winston S., Brunham R. C. The 75-kilodalton protein of Chlamydia trachomatis: a member of the heat shock protein 70 family? Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):189–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.189-196.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. N., Ganem D. A polymerase chain reaction-based approach to cloning sigma factors from eubacteria and its application to the isolation of a sigma-70 homolog from Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2447–2455. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2447-2455.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. N., Ganem D. Chlamydial rRNA operons: gene organization and identification of putative tandem promoters. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5678–5685. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5678-5685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Vaughn V., Walter W. A., Neidhardt F. C., Gross C. A. Regulation of the promoters and transcripts of rpoH, the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):419–432. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayet O., Ziegelhoffer T., Georgopoulos C. The groES and groEL heat shock gene products of Escherichia coli are essential for bacterial growth at all temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1379–1385. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1379-1385.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAYSTON J. T., WOOLRIDGE R. L., WANG S. Trachoma vaccine studies on Taiwan. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Mar 5;98:352–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb30558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Casson L. P., Goldberg A. L. Heat shock regulatory gene htpR influences rates of protein degradation and expression of the lon gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6647–6651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Miceli M., Silverman J. A. Synthesis of protein in host-free reticulate bodies of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):938–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.938-942.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C., Chandrasekhar G. N., Georgopoulos C. Escherichia coli DnaK and GrpE heat shock proteins interact both in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1590–1596. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1590-1596.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Belland R. J., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. The 57-kD chlamydial hypersensitivity antigen is a stress response protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1271–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. Ocular hypersensitivity elicited by a genus-specific 57-kD protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):663–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter S. H., Shapiro L. Asymmetric segregation of heat-shock proteins upon cell division in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardinia L. M., Engel J. N., Ganem D. Chlamydial gene encoding a 70-kilodalton antigen in Escherichia coli: analysis of expression signals and identification of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):335–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.335-341.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardinia L. M., Segal E., Ganem D. Developmental regulation of the cysteine-rich outer-membrane proteins of murine Chlamydia trachomatis. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):997–1004. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J. The intracellular life of Chlamydia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:109–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelly S., Coleman T., Fu C. F., Brot N., Weissbach H. Correlation between the 32-kDa sigma factor levels and in vitro expression of Escherichia coli heat shock genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8365–8369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Wagar E. A., Edman U. Developmental regulation of tandem promoters for the major outer membrane protein gene of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):744–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.744-750.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. E., Straus D. B., Grossman A. D., Burton Z. F., Gross C. A., Burgess R. R. Transcription from a heat-inducible promoter causes heat shock regulation of the sigma subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90492-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V., Neidhardt F. C. Gene for heat-inducible lysyl-tRNA synthetase (lysU) maps near cadA in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1066–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1066-1068.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T., Alexander E. R. Trachoma vaccine studies in monkeys. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967 May;63(5 Suppl):1615–1630. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(67)94155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Pannus with experimental trachoma and inclusion conjunctivitis agent infection of Taiwan monkeys. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967 May;63(5 Suppl):1133–1145. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(67)94095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolridge R. L., Grayston J. T., Chang I. H., Cheng K. H., Yang C. Y., Neave C. Field trial of a monovalent and of a bivalent mineral oil adjuvant trachoma vaccine in Taiwan school children. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967 May;63(5 Suppl):1645–1650. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(67)94158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Elliott T. J. Stress proteins, infection, and immune surveillance. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90861-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]