Abstract
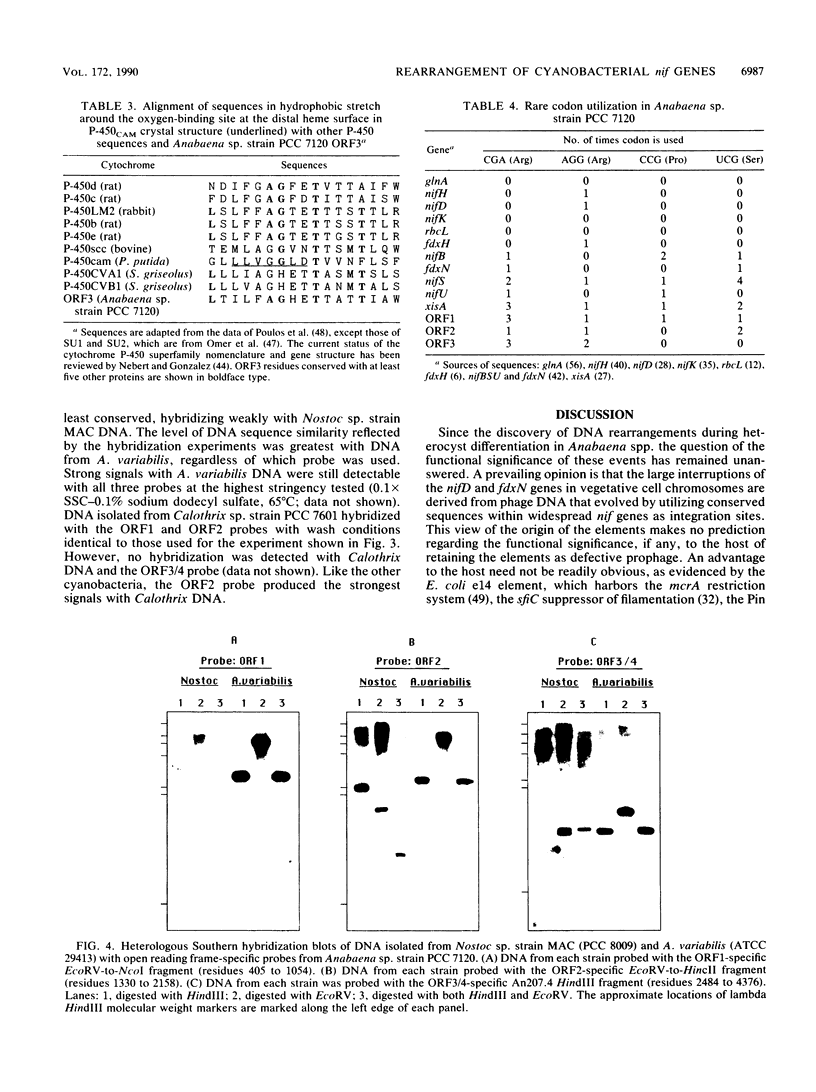
An 11-kbp DNA element of unknown function interrupts the nifD gene in vegetative cells of Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. In developing heterocysts the nifD element excises from the chromosome via site-specific recombination between short repeat sequences that flank the element. The nucleotide sequence of the nifH-proximal half of the element was determined to elucidate the genetic potential of the element. Four open reading frames with the same relative orientation as the nifD element-encoded xisA gene were identified in the sequenced region. Each of the open reading frames was preceded by a reasonable ribosome-binding site and had biased codon utilization preferences consistent with low levels of expression. Open reading frame 3 was highly homologous with three cytochrome P-450 omega-hydroxylase proteins and showed regional homology to functionally significant domains common to the cytochrome P-450 superfamily. The sequence encoding open reading frame 2 was the most highly conserved portion of the sequenced region based on heterologous hybridization experiments with three genera of heterocystous cyanobacteria.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S. G., Kurland C. G. Codon preferences in free-living microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):198–210. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.198-210.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleby C. A. Electron transport systems of Rhizobium japonicum. II. Rhizobium haemoglobin, cytochromes and oxidases in free-living (cultured) cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 14;172(1):88–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleby C. A., Turner G. L., Macnicol P. K. Involvement of oxyleghaemoglobin and cytochrome P-450 in an efficient oxidative phosphorylation pathway which supports nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 17;387(3):461–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonekamp F., Dalbøge H., Christensen T., Jensen K. F. Translation rates of individual codons are not correlated with tRNA abundances or with frequencies of utilization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5812–5816. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5812-5816.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusca J. S., Chastain C. J., Golden J. W. Expression of the Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 xisA gene from a heterologous promoter results in excision of the nifD element. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3925–3931. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3925-3931.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusca J. S., Hale M. A., Carrasco C. D., Golden J. W. Excision of an 11-kilobase-pair DNA element from within the nifD gene in anabaena variabilis heterocysts. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4138–4145. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4138-4145.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme H., Haselkorn R. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the gene coding for heterocyst ferredoxin from the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):278–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00337722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis S. E., Haselkorn R. Isolation and sequence of the gene for the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from the cyanobacterium Anabaena 7120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1835–1839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden G. M., Guzek D. B., Harris R. R., McKie J. E., Potts R. O. Lipid thermotropic transitions in human stratum corneum. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Mar;86(3):255–259. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Carrasco C. D., Mulligan M. E., Schneider G. J., Haselkorn R. Deletion of a 55-kilobase-pair DNA element from the chromosome during heterocyst differentiation of Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5034–5041. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5034-5041.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Mulligan M. E., Haselkorn R. Different recombination site specificity of two developmentally regulated genome rearrangements. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):526–529. doi: 10.1038/327526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Robinson S. J., Haselkorn R. Rearrangement of nitrogen fixation genes during heterocyst differentiation in the cyanobacterium Anabaena. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):419–423. doi: 10.1038/314419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Wiest D. R. Genome rearrangement and nitrogen fixation in Anabaena blocked by inactivation of xisA gene. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.3144039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. P., Song B. J., Huberman E., Gonzalez F. J. Isolation, complementary DNA sequence, and regulation of rat hepatic lauric acid omega-hydroxylase (cytochrome P-450LA omega). Identification of a new cytochrome P-450 gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):801–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallas T., Rebière M. C., Rippka R., Tandeau de Marsac N. The structural nif genes of the cyanobacteria Gloeothece sp. and Calothrix sp. share homology with those of Anabaena sp., but the Gloeothece genes have a different arrangement. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):427–431. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.427-431.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto R. H., Powell A. T., Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D. A., Kerstetter R. A., Nester E. W., Hawes M. C., Gordon M. P. Nucleotide sequence and analysis of the plant-inducible locus pinF from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2506–2512. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2506-2512.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C., Snyder L. The lit gene product which blocks bacteriophage T4 late gene expression is a membrane protein encoded by a cryptic DNA element, e14. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2056–2062. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2056-2062.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambein F., Wolk C. P. Structural studies on the glycolipids from the envelope of the heterocyst of Anabaena cylindrica. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):791–798. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers P. J., Golden J. W., Haselkorn R. Identification and sequence of a gene required for a developmentally regulated DNA excision in Anabaena. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers P. J., Haselkorn R. Sequence of the nifD gene coding for the alpha subunit of dinitrogenase from the cyanobacterium Anabaena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4723–4727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers P. J., Sanders-Loehr J. Active transport of ferric schizokinen in Anabaena sp. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):288–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.288-294.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn M. E., Bantle J. A., Ownby J. D. Estimation of gene expression in heterocysts of Anabaena variabilis by using DNA-RNA hybridization. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):940–946. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.940-946.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguin E., Brody H., Hill C. W., D'Ari R. SOS-associated division inhibition gene sfiC is part of excisable element e14 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):464–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.464-466.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara S., Yamamoto S., Sogawa K., Yokotani N., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Haniu M., Shively J. E., Gotoh O., Kusunose E., Kusunose M. cDNA cloning and inducible expression during pregnancy of the mRNA for rabbit pulmonary prostaglandin omega-hydroxylase (cytochrome P-450p-2). J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13366–13371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur B. J., Chui C. F. Sequence of the gene coding for the beta-subunit of dinitrogenase from the blue-green alga Anabaena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6782–6786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur B. J., Rice D., Haselkorn R. Identification of blue-green algal nitrogen fixation genes by using heterologous DNA hybridization probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):186–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McALEER W. J., JACOB T. A., TURNBULL L. B., SCHOENEWALDT E. F., STOUDT T. H. Hydroxylation of progesterone by Bacillus cereus and Bacillus megaterium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Jan;73(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeks J. C., Joseph C. M., Haselkorn R. Organization of the nif genes in cyanobacteria in symbiotic association with Azolla and Anthoceros. Arch Microbiol. 1988 May;150(1):61–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00409719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevarech M., Rice D., Haselkorn R. Nucleotide sequence of a cyanobacterial nifH gene coding for nitrogenase reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Buikema W. J., Haselkorn R. Bacterial-type ferredoxin genes in the nitrogen fixation regions of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 and Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4406–4410. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4406-4410.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Haselkorn R. Nitrogen fixation (nif) genes of the cyanobacterium Anabaena species strain PCC 7120. The nifB-fdxN-nifS-nifU operon. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19200–19207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narhi L. O., Fulco A. J. Characterization of a catalytically self-sufficient 119,000-dalton cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase induced by barbiturates in Bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7160–7169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gonzalez F. J. P450 genes: structure, evolution, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:945–993. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brian M. R., Maier R. J. Molecular aspects of the energetics of nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium-legume symbioses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 30;974(3):229–246. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(89)80239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omer C. A., Lenstra R., Litle P. J., Dean C., Tepperman J. M., Leto K. J., Romesser J. A., O'Keefe D. P. Genes for two herbicide-inducible cytochromes P-450 from Streptomyces griseolus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3335–3345. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3335-3345.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Finzel B. C., Gunsalus I. C., Wagner G. C., Kraut J. The 2.6-A crystal structure of Pseudomonas putida cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16122–16130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Trimarchi R., Revel H. Genetic and physical mapping of the mcrA (rglA) and mcrB (rglB) loci of Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1989 Jun;122(2):279–296. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D., Mazur B. J., Haselkorn R. Isolation and physical mapping of nitrogen fixation genes from the cyanobacterium Anabaena 7120. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13157–13163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruettinger R. T., Wen L. P., Fulco A. J. Coding nucleotide, 5' regulatory, and deduced amino acid sequences of P-450BM-3, a single peptide cytochrome P-450:NADPH-P-450 reductase from Bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):10987–10995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Kidd S., Kelley M. R. An improved filamentous helper phage for generating single-stranded plasmid DNA. Gene. 1986;45(3):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saville B., Straus N., Coleman J. R. Contiguous organization of nitrogenase genes in a heterocystous cyanobacterium. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):26–29. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Smith T. F. Automatic generation of primary sequence patterns from sets of related protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Structure of human steroid 21-hydroxylase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte P., Plasterk R., Kuijpers A. A Mu gin complementing function and an invertible DNA region in Escherichia coli K-12 are situated on the genetic element e14. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.517-522.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




