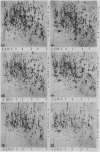
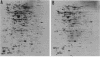
Abstract
Because of the highly conserved pattern of expression of the eucaryotic heat shock genes hsp70 and hsp84 or their cognates during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and development in higher organisms, the role of the Escherichia coli homologs dnaK and htpG was examined during the response to starvation. The htpG deletion mutant was found to be similar to its wild-type parent in its ability to survive starvation for essential nutrients and to induce proteins specific to starvation conditions. The dnaK103 mutant, however, was highly susceptible to killing by starvation for carbon and, to a lesser extent, for nitrogen and phosphate. Analysis of proteins induced under starvation conditions on two-dimensional gels showed that the dnaK103 mutant was defective for the synthesis of some proteins induced in wild-type cells by carbon starvation and of some proteins induced under all starvation conditions, including the stationary phase in wild-type cells. In addition, unique proteins were synthesized in the dnaK103 mutant in response to starvation. Although the synthesis of some proteins under glucose starvation control was drastically affected by the dnaK103 mutation, the synthesis of proteins specifically induced by nitrogen starvation was essentially unaffected. Similarly, the dnaK103 mutant was able to grow, utilizing glutamine or arginine as a source of nitrogen, at a rate approximate to that of the wild-type parent, but it inefficiently utilized glycerol or maltose as carbon sources. Several differences between the protein synthetic pattern of the dnaK103 mutant and the wild type were observed after phosphate starvation, but these did not result in a decreased ability to survive phosphate starvation, compared with nitrogen starvation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Ancient heat shock gene is dispensable. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2977–2983. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2977-2983.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Eukaryotic Mr 83,000 heat shock protein has a homologue in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5177–5181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkovich K. A., Farrelly F. W., Finkelstein D. B., Taulien J., Lindquist S. hsp82 is an essential protein that is required in higher concentrations for growth of cells at higher temperatures. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3919–3930. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B., Walker G. C. Cellular defects caused by deletion of the Escherichia coli dnaK gene indicate roles for heat shock protein in normal metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2337-2346.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. The heat shock response. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(3):239–280. doi: 10.3109/10409238509085135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. The heat shock response is self-regulated at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., Hemmingsen S. M. Molecular chaperones: proteins essential for the biogenesis of some macromolecular structures. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Aug;14(8):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. E., Walton J. K., Dubitsky R., Bensch K. G. Aging results in an unusual expression of Drosophila heat shock proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4099–4103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. P. A new bacterial gene (groPC) which affects lambda DNA replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Feb 28;151(1):35–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00446910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groat R. G., Schultz J. E., Zychlinsky E., Bockman A., Matin A. Starvation proteins in Escherichia coli: kinetics of synthesis and role in starvation survival. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.486-493.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz S., Rossi J., Petko L., Lindquist S. An ancient developmental induction: heat-shock proteins induced in sporulation and oogenesis. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1154–1157. doi: 10.1126/science.3511530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Georgopoulos C., Zylicz M. Role of the Escherichia coli DnaK and DnaJ heat shock proteins in the initiation of bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6632–6636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullin T. W., Hallberg R. L. A highly evolutionarily conserved mitochondrial protein is structurally related to the protein encoded by the Escherichia coli groEL gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):371–380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki M., Uchida H., Tamura F., Ohki R., Nishimura S. The Escherichia coli dnaJ mutation affects biosynthesis of specific proteins, including those of the lac operon. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1917–1922. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1917-1922.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paek K. H., Walker G. C. Escherichia coli dnaK null mutants are inviable at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):283–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.283-290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. Heat-shock proteins DnaK and GroEL facilitate export of LacZ hybrid proteins in E. coli. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):882–884. doi: 10.1038/344882a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading D. S., Hallberg R. L., Myers A. M. Characterization of the yeast HSP60 gene coding for a mitochondrial assembly factor. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):655–659. doi: 10.1038/337655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanzey B. Modulation of gene expression by drugs affecting deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.40-47.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. E., Latter G. I., Matin A. Differential regulation by cyclic AMP of starvation protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3903–3909. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3903-3909.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelly S., Fu C. F., Dalie B., Redfield B., Coleman T., Brot N., Weissbach H. Antibody to sigma 32 cross-reacts with DnaK: association of DnaK protein with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5497–5501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowyra D., Georgopoulos C., Zylicz M. The E. coli dnaK gene product, the hsp70 homolog, can reactivate heat-inactivated RNA polymerase in an ATP hydrolysis-dependent manner. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):939–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90268-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternglanz R., DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y., Becherer K., Zumstein L., Wang J. C. Mutations in the gene coding for Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I affect transcription and transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2747–2751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Escherichia coli heat shock gene mutants are defective in proteolysis. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1851–1858. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., McKittrick N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein modulates the heat-shock response of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., Spence J., Georgopoulos C. Modulation of stability of the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory factor sigma. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1585–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1585-1589.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Overlapping and separate controls on the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):283–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yochem J., Uchida H., Sunshine M., Saito H., Georgopoulos C. P., Feiss M. Genetic analysis of two genes, dnaJ and dnaK, necessary for Escherichia coli and bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Aug 4;164(1):9–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00267593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman J. L., Petri W., Meselson M. Accumulation of a specific subset of D. melanogaster heat shock mRNAs in normal development without heat shock. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1161–1170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]