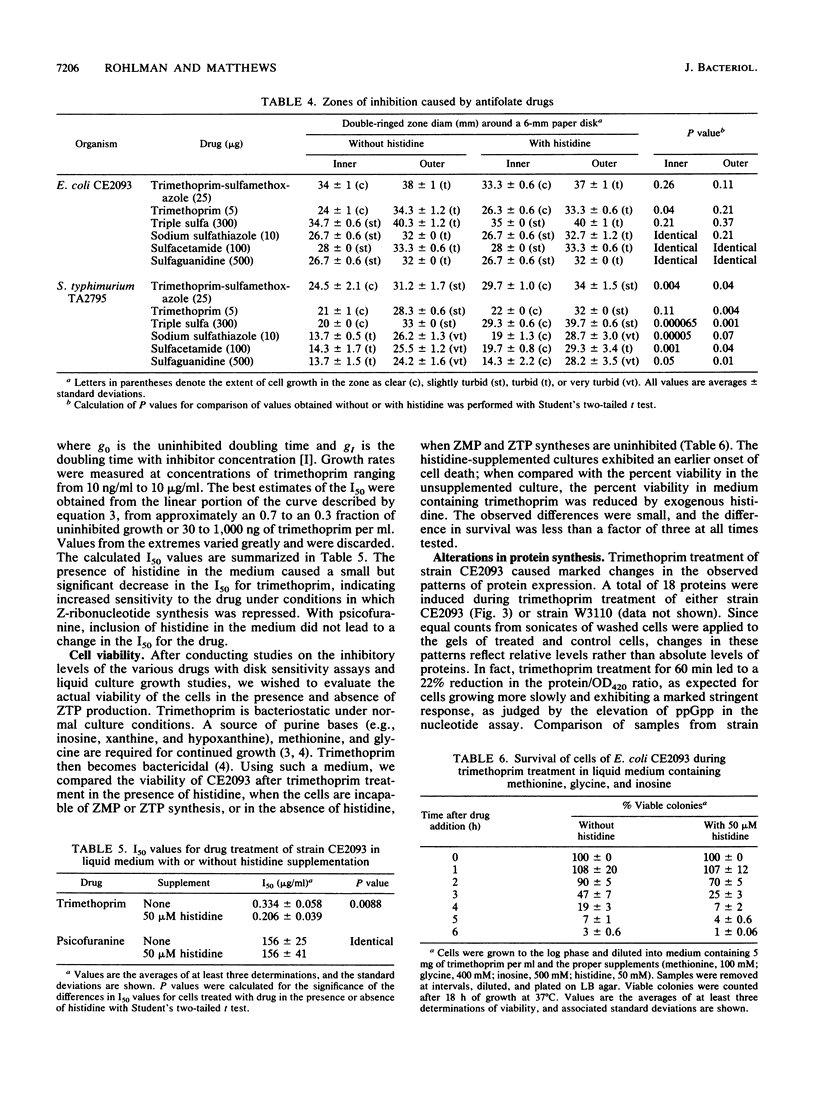
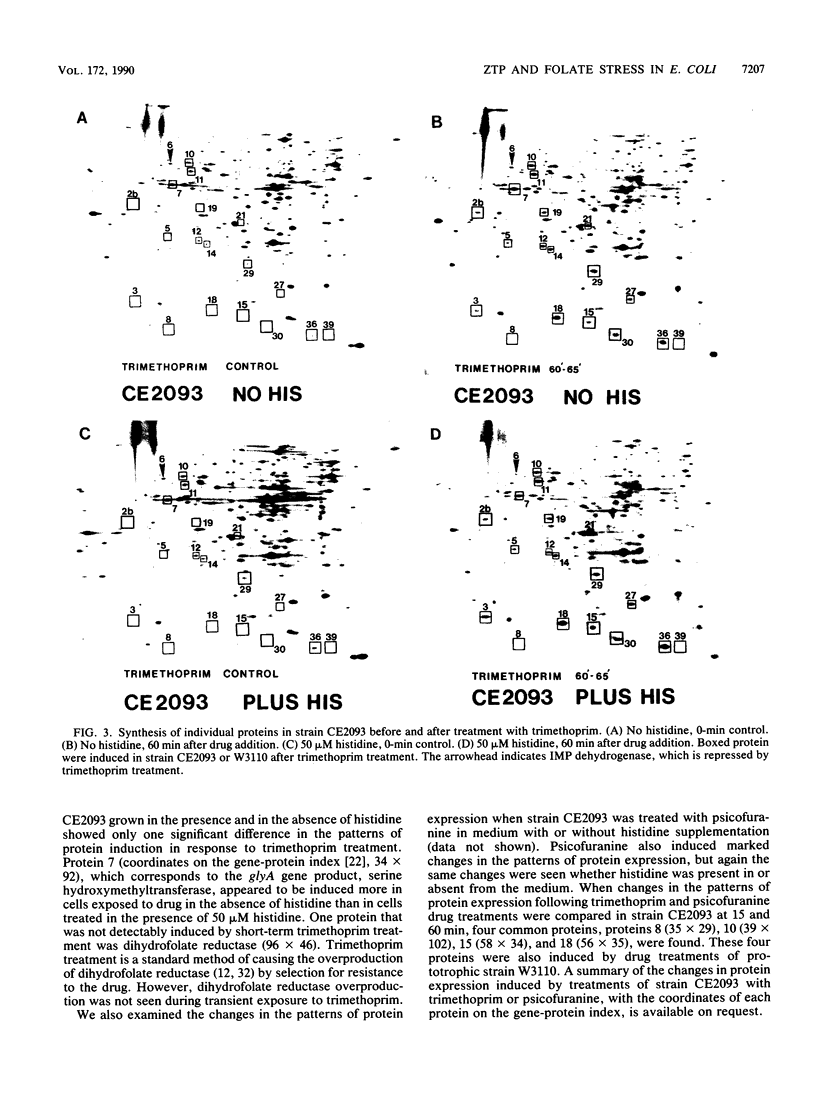
Abstract
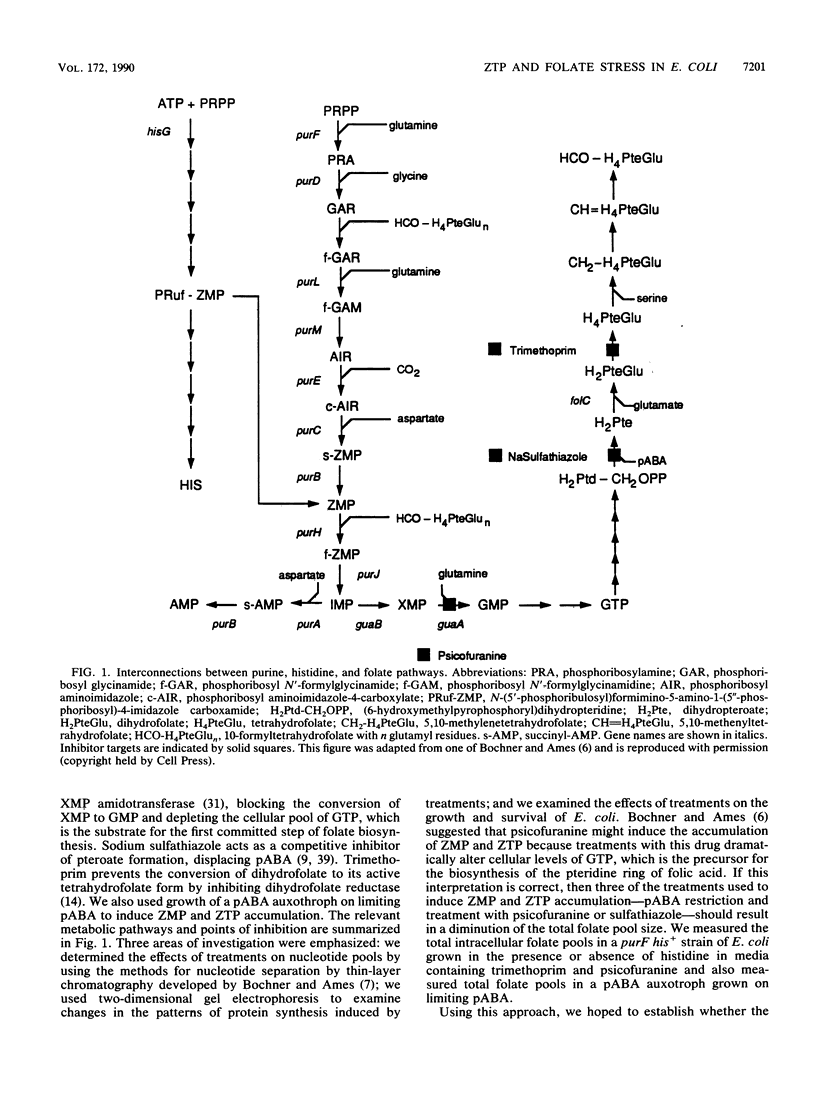
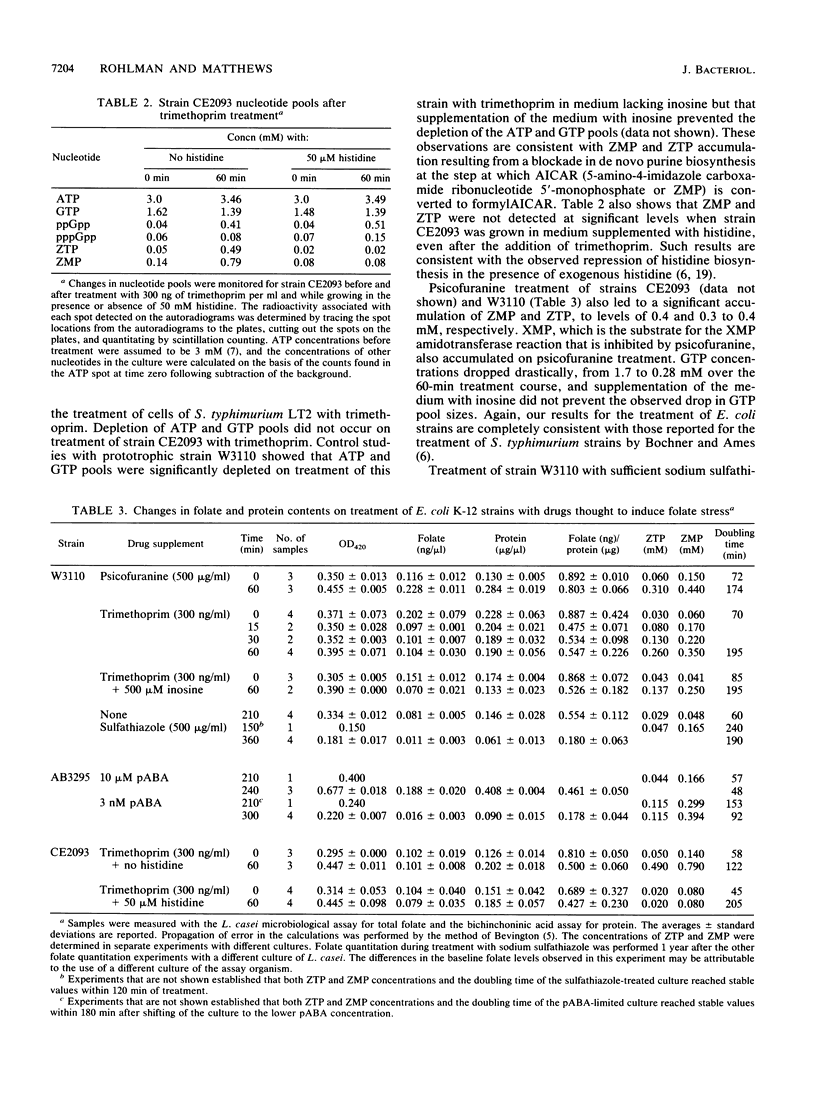
Folic acid plays a central role in anabolic metabolism by supplying single-carbon units at varied levels of oxidation for both nucleotide and amino acid biosyntheses. It has been proposed that 5-amino-4-imidazole carboxamide riboside 5'-triphosphate (ZTP), an intermediate in de novo purine biosynthesis, serves as a signal of cellular folate stress and mediates a physiologically beneficial response to folate stress in Salmonella typhimurium (B. R. Bochner, and B. N. Ames, Cell 29:929-937, 1982). We examined the physiological response of Escherichia coli to folate stress induced by the drugs psicofuranine, trimethoprim, and sodium sulfathiazole or by p-aminobenzoic acid (pABA) starvation. Analysis of nucleotide pools showed that psicofuranine or trimethoprim treatment of a prototrophic strain or growth of a pABA auxotroph on limiting pABA induced the production of the nucleotide ZTP, as previously observed in S. typhimurium by Bochner and Ames. Accumulation of ZTP and its precursor 5-amino-4-imidazole carboxamide riboside 5'-monophosphate (ZMP) did not correlate well with folate stress in E. coli, as measured by determination of the folate/protein ratios of extracts of treated cells. Treatment of cells with psicofuranine caused a marked accumulation of 5-amino-4-imidazole carboxamide ribonucleotides (Z-ribonucleotides) but a statistically insignificant drop in the folate/protein ratio of cell extracts. Sodium sulfathiazole treatment at a drug concentration that led to a threefold drop in the growth rate and in the folate/protein ratio of treated cells led to little accumulation of Z-ribonucleotides in E. coli A purF his+ strain which produces ZTP and ZMP when treated with trimethoprim was constructed. In this strain, histidine represses the synthesis of both ZMP and ZTP. Treatment of cells of this strain with trimethoprim resulted in a decrease in the folate/protein ratio of cell extracts, but a blockade of Z-ribonucleotide accumulation did not affect the extent of folate depletion seen in treated cells and had only a small effect on the resistance of this strain to growth inhibition by trimethoprim. The patterns of protein expression induced by treatment of this strain with trimethoprim or psicofuranine were examined by two-dimensional electrophoretic resolution of the total cellular proteins. No differences in protein expression were seen when the treatment were performed in media containing or lacking histidine. These studies failed to provide evidence in E. coli for a folate stress regulon controlled by ZTP.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allegra C. J., Hoang K., Yeh G. C., Drake J. C., Baram J. Evidence for direct inhibition of de novo purine synthesis in human MCF-7 breast cells as a principal mode of metabolic inhibition by methotrexate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13520–13526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper M. D., Ames B. N. Transport of antibiotics and metabolite analogs by systems under cyclic AMP control: positive selection of Salmonella typhimurium cya and crp mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):149–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.149-157.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amyes S. G., Smith J. T. Trimethoprim action and its analogy with thymine starvation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):169–178. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angehrn P., Then R. Nature of trimethoprim-induced death in Escherichia coli. Arzneimittelforschung. 1973 Mar;23(3):447–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN G. M. The biosynthesis of folic acid. II. Inhibition by sulfonamides. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:536–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. Complete analysis of cellular nucleotides by two-dimensional thin layer chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9759–9769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. Selective precipitation orthophosphate from mixtures containing labile phosphorylated metabolites. Anal Biochem. 1982 May 1;122(1):100–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90257-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. ZTP (5-amino 4-imidazole carboxamide riboside 5'-triphosphate): a proposed alarmone for 10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate deficiency. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dev I. K., Harvey R. J. Sources of one-carbon units in the folate pathway of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1980–1986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerich R. V., Hirshfield I. N. Mapping of the constitutive lysyl-tRNA synthetase gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5311–5313. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5311-5313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flensburg J., Sköld O. Massive overproduction of dihydrofolate reductase in bacteria as a response to the use of trimethoprim. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 2;162(3):473–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Harnish B. W. Inversions between ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7069–7072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchings G. H., Burchall J. J. Inhibition of folate biosynthesis and function as a basis for chemotherapy. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1965;27:417–468. doi: 10.1002/9780470122723.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Pittard J. Genetic analysis of mutant strains of Escherichia coli requiring p-aminobenzoic acid for growth. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1938–1942. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1938-1942.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckie M. P., Porter S. E., Tieber V. L., Dietzler D. N. Regulation of the basal and cyclic AMP-stimulated rates of glycogen synthesis in Escherichia coli by an intermediate of purine biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1433–1442. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Vaughn V., Phillips T. A., Bloch P. L. Gene-protein index of Escherichia coli K-12. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):231–284. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.231-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattishall K. H., Acar J., Burchall J. J., Goldstein F. W., Harvey R. J. Two distinct types of trimethoprim-resistant dihydrofolate reductase specified by R-plasmids of different compatibility groups. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2319–2323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Bloch P. L., Reeh S., Neidhardt F. C. Patterns of protein synthesis in E. coli: a catalog of the amount of 140 individual proteins at different growth rates. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabina R. L., Holmes E. W., Becker M. A. The enzymatic synthesis of 5-amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide riboside triphosphate (ZTP). Science. 1984 Mar 16;223(4641):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.6199843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabina R. L., Patterson D., Holmes E. W. 5-Amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide riboside (Z-riboside) metabolism in eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6107–6114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of dihydrofolate reductase genes from trimethoprim-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. Evidence that dihydrofolate reductase interacts with another essential gene product. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(1):72–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00384386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Hoess R. The molecular genetics of bacteriophage P1. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:123–154. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Acton M. A., Neidhardt F. C. Induction of the heat shock regulon does not produce thermotolerance in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Aug;1(6):525–531. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.6.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. D., Horne D. W. Use of glycerol-cryoprotected Lactobacillus casei for microbiological assay of folic acid. Clin Chem. 1982 May;28(5):1198–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]