Abstract
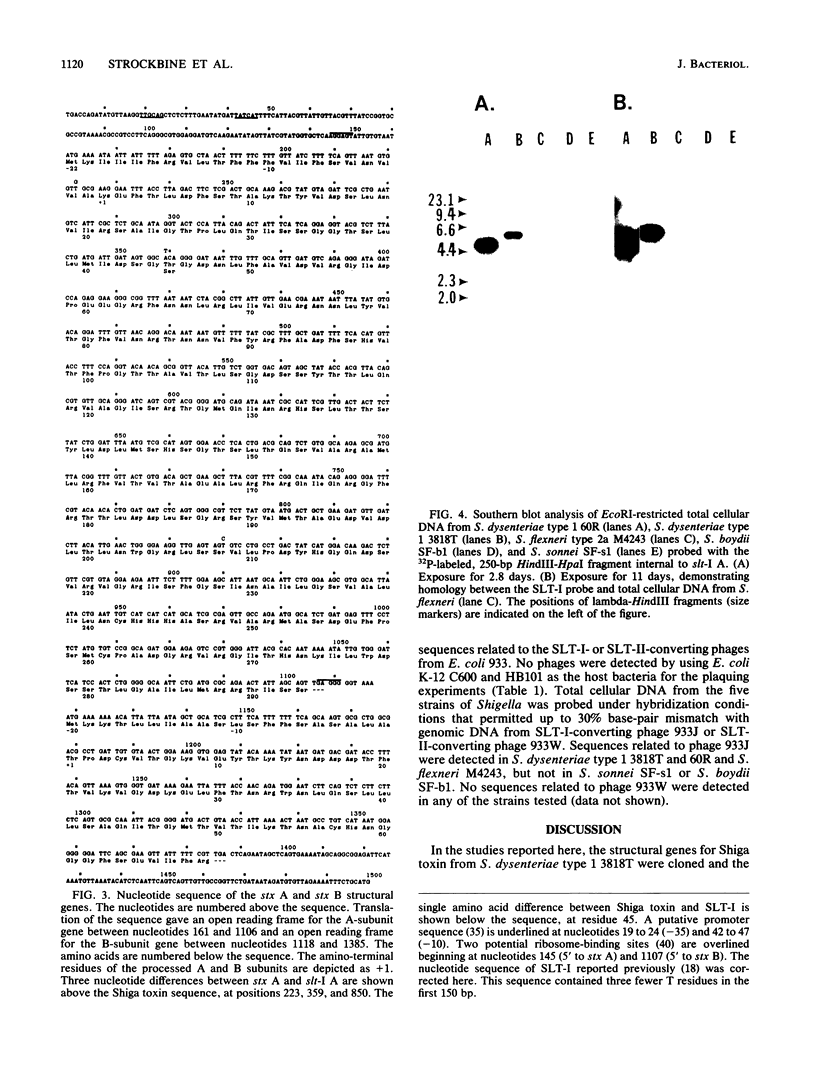
The structural genes for Shiga toxin, designated stx A and stx B, were cloned from Shigella dysenteriae type 1 3818T, and a nucleotide sequence analysis was performed. Both stx A and stx B were present on a single transcriptional unit, with stx A preceding stx B. The molecular weight calculated for the processed A subunit was 32,225, while the molecular weight of the processed B subunit was 7,691. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences for Shiga toxin and Shiga-like toxin I (SLT-I) from Escherichia coli revealed that the genes for Shiga toxin and SLT-I were greater than 99% homologous; three nucleotide changes were detected in three separate codons of the A subunits. Only one of these codon differences resulted in a change in the amino acid sequence: a threonine in Shiga toxin at position 45 of the A subunit compared with a serine in the corresponding position in SLT-I. Furthermore, Shiga toxin and SLT-I had identical signal peptides for the A and B subunits, as well as identical ribosome-binding sites, a putative promoter, and iron-regulated operator sequences. These findings indicate that Shiga and SLT-I are essentially the same toxin. Southern hybridization studies with total cellular DNA from several Shigella strains and internal toxin probes for SLT-I and its antigenic variant SLT-II showed that a single fragment in S. dysenteriae type 1 hybridized strongly with the internal SLT-I probe. Fragments with weaker homology to the SLT-I probe were detected in S. flexneri type 2a but no other shigellae. No homology between the Shiga-like toxin II (SLT-II) probe and any of the Shigella DNAs was detected. Whereas SLT-I and SLT-II are phage encoded, no phage could be induced from S. dysenteriae type 1 or other Shigella spp. tested. These results suggest that the Shiga (SLT-I) toxin genes responsible for high toxin production are present in a single copy in S. dysenteriae type 1 but not in other shigellae. The findings further suggest that SLT-II genes are absent in shigellae, as are toxin-converting phages.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. I., Fisher W. D., Cohen A., Hardigree A. A. MINIATURE escherichia coli CELLS DEFICIENT IN DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):321–326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. B., Auclair F., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the Shiga-like toxin genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4364–4368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. B., Mekalanos J. J. Iron regulation of Shiga-like toxin expression in Escherichia coli is mediated by the fur locus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4759–4764. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4759-4764.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary T. G., Mathewson J. J., Faris E., Pickering L. K. Shiga-like cytotoxin production by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serogroups. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):335–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.335-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Grandis S., Ginsberg J., Toone M., Climie S., Friesen J., Brunton J. Nucleotide sequence and promoter mapping of the Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin operon of bacteriophage H-19B. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4313–4319. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4313-4319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Edson C., Thorley-Lawson D., Jacewicz M. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. IX. Simplified high yield purification of Shigella toxin and characterization of subunit composition and function by the use of subunit-specific monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1767–1781. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., O'Brien A. D., Wohlhieter J. A. Cellular release of heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage induction. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1076–1082. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1076-1082.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Dalrymple J. M. Quantitative microtiter cytotoxicity assay for Shigella toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.361-366.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Twiddy E. M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies that react with unique and cross-reacting determinants of cholera enterotoxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):914–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.914-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. P., Newland J. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the structural genes for Shiga-like toxin I encoded by bacteriophage 933J from Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1987 Feb;2(2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques L. R., Moore M. A., Wells J. G., Wachsmuth I. K., O'Brien A. D. Production of Shiga-like toxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):338–341. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L. J., Gangarosa E. J., Cáceres A., Perera D. R., Mejicanos M. L. Epidemic Shiga bacillus dysentery in Central America. I. Etiologic investigations in Guatemala, 1969. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):170–180. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meagher R. B., Tait R. C., Betlach M., Boyer H. W. Protein expression in E. coli minicells by recombinant plasmids. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):521–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Strockbine N. A., Miller S. F., O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Cloning of Shiga-like toxin structural genes from a toxin converting phage of Escherichia coli. Science. 1985 Oct 11;230(4722):179–181. doi: 10.1126/science.2994228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Griffin D. E., Thompson M. R. Characterization of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) toxin purified by anti-Shiga toxin affinity chromatography. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):170–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.170-179.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D. Purification and characterization of a Shigella dysenteriae 1-like toxin produced by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):675–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.675-683.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Newland J. W., Miller S. F., Holmes R. K., Smith H. W., Formal S. B. Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):694–696. doi: 10.1126/science.6387911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Thompson M. R., Gemski P., Doctor B. P., Formal S. B. Biological properties of Shigella flexneri 2A toxin and its serological relationship to Shigella dysenteriae 1 toxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):796–798. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.796-798.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Donohue-Rolfe A., Lazure C., Auclair F., Keusch G. T., Chrétien M. Complete amino acid sequence of Shigella toxin B-chain. A novel polypeptide containing 69 amino acids and one disulfide bridge. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13928–13931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizaki T., Harayama S., Brazil G. M., Timmis K. N. Localization of stx, a determinant essential for high-level production of shiga toxin by Shigella dysenteriae serotype 1, near pyrF and generation of stx transposon mutants. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2208–2214. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2208-2214.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Green P., Parsell Z. Vero cell toxins in Escherichia coli and related bacteria: transfer by phage and conjugation and toxic action in laboratory animals, chickens and pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3121–3137. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]