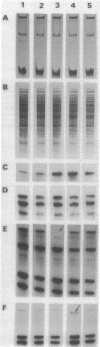
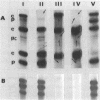
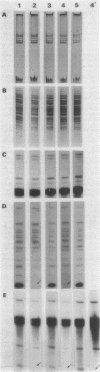
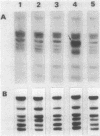
Abstract
Experience from different laboratories indicates that Rhizobium strains can generate variability in regard to some phenotypic characteristics such as colony morphology or symbiotic properties. On the other hand, several reports suggest that under certain stress conditions or genetic manipulations Rhizobium cells can present genomic rearrangements. In search of frequent genomic rearrangements, we analyzed three Rhizobium strains under laboratory conditions that are not considered to cause stress in bacterial populations. DNAs from direct descendants of a single cell were analyzed in regard to the hybridization patterns obtained, using as probes different recombinant plasmids or cosmids; while most of the probes utilized did not show differences in the hybridization patterns, some of them revealed the occurrence of frequent genomic rearrangements. The implications and possible biological significance of these observations are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry J. O., Atherly A. G. Induced plasmid-genome rearrangements in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):218–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.218-224.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A. H., Schubert K. R. Identification of a Rhizobium trifolii plasmid coding for nitrogen fixation and nodulation genes and its interaction with pJB5JI, a Rhizobium leguminosarum plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):592–599. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.592-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic M. A., Zurkowski W., Rolfe B. G. Plasmids and stability of symbiotic properties of Rhizobium trifolii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):560–568. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.560-568.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic M. A., Zurkowski W., Shine J., Rolfe B. G. Sym plasmid transfer to various symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium trifolii, R. leguminosarum, and R. meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1035–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1035-1045.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Brom S., Martínez E., Piñero D., Romero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Reiterated DNA sequences in Rhizobium and Agrobacterium spp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5782–5788. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5782-5788.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman J. D., Schalkwyk L. C., Doolittle W. F. ISH51: a large, degenerate family of insertion sequence-like elements in the genome of the archaebacterium, Halobacterium volcanii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6983–7000. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza K., Hahn M., Hennecke H. Repeated sequences similar to insertion elements clustered around the nif region of the Rhizobium japonicum genome. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):535–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.535-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Sanchez A., Fernandez L., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A. Rhizobium phaseoli symbiotic mutants with transposon Tn5 insertions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.148-155.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Betlach M. Genome organization in Halobacterium halobium: a 70 kb island of more (AT) rich DNA in the chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(3):449–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00332938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priefer U. B., Burkardt H. J., Klipp W., Pühler A. ISR1: an insertion element isolated from the soil bacterium Rhizobium lupini. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):87–91. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinto C., De La Vega H., Flores M., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A., Pardo M. A., Azpiroz R., De Lourdes Girard M., Calva E., Palacios R. Nitrogenase reductase: A functional multigene family in Rhizobium phaseoli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1170–1174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Long S. R., Meade H. M., van den Bos R. C., Ausubel F. M. ISRm1: A Rhizobium meliloti insertion sequence that transposes preferentially into nitrogen fixation genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):405–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Rose M. R., Doolittle W. F. High-frequency genomic rearrangements involving archaebacterial repeat sequence elements. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):182–185. doi: 10.1038/299182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00436188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberón-Chávez G., Nájera R., Olivera H., Segovia L. Genetic rearrangements of a Rhizobium phaseoli symbiotic plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):487–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.487-491.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurkowski W. Molecular mechanism for loss of nodulation properties of Rhizobium trifolii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):999–1007. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.999-1007.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]