Abstract
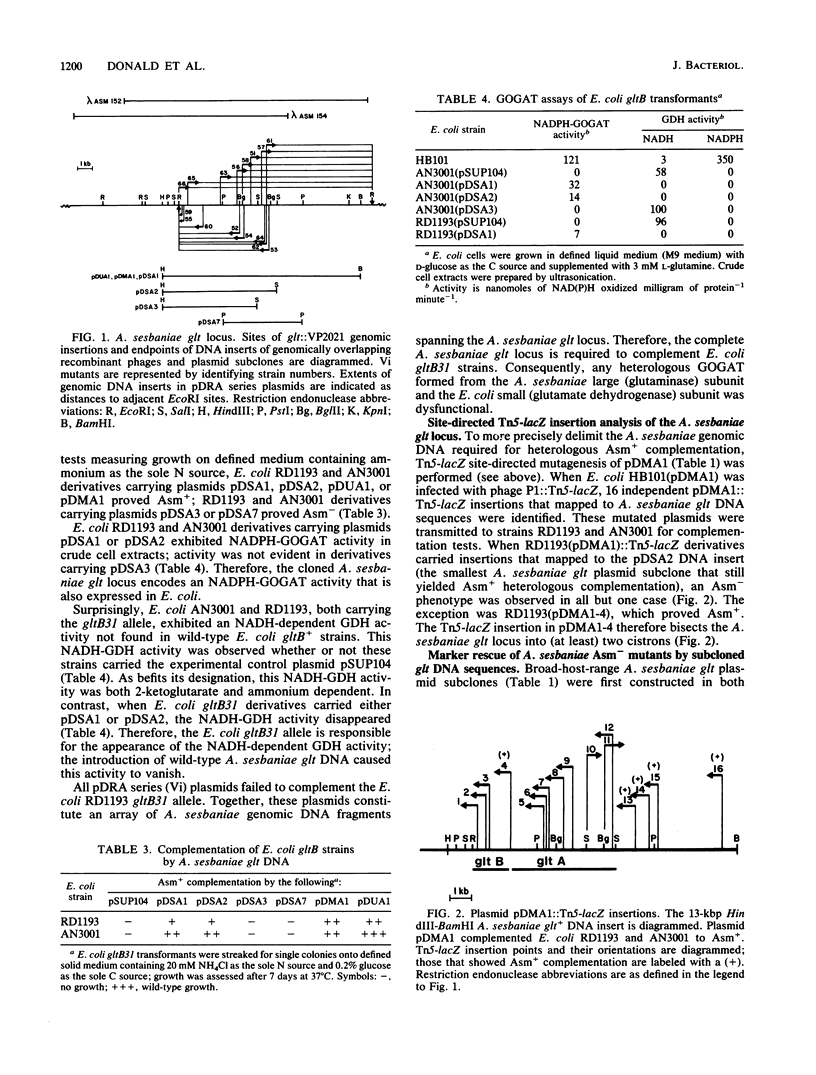
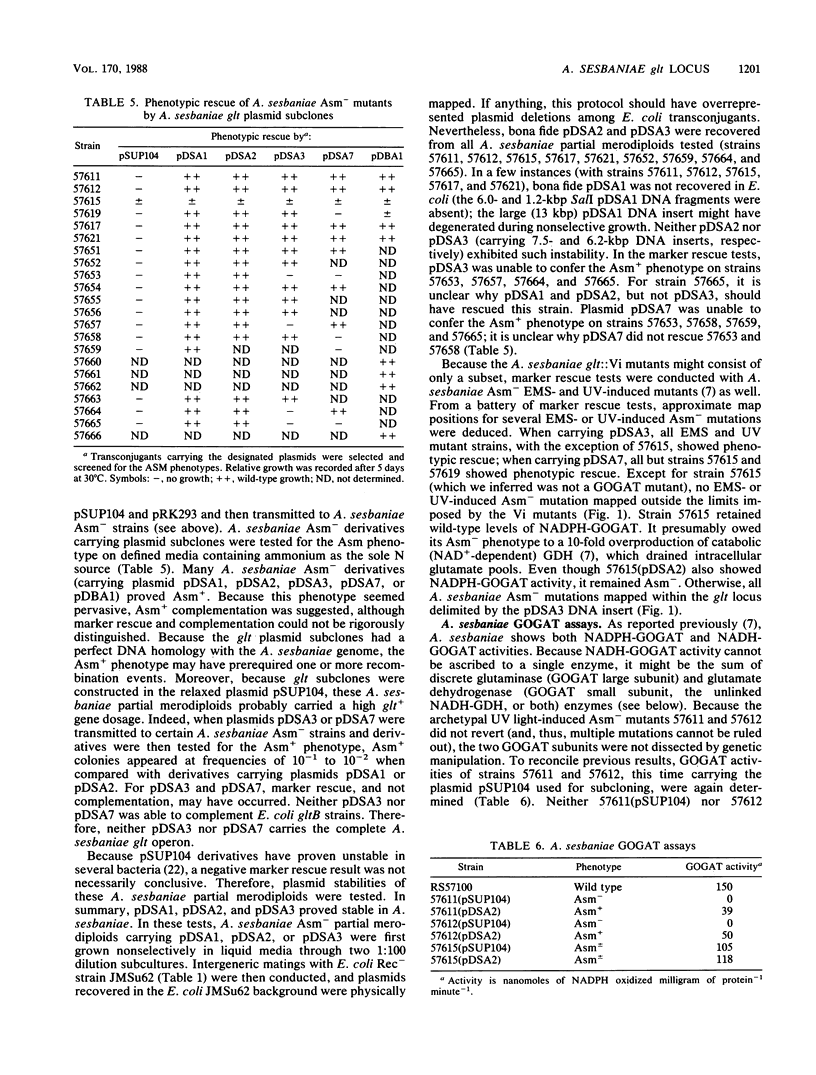
Sixteen independent Azorhizobium sesbaniae ORS571 vector insertion (Vi) mutants defective in ammonium assimilation (Asm-) were selected; genomic DNA sequences flanking the insertion endpoints were cloned directly. Resulting recombinant plasmids were used to identify, by hybridization, corresponding wild-type DNA sequences from an A. sesbaniae lambda EMBL3 genomic library (lambda Asm phages). All 16 Asm- Vi mutants physically mapped to a single genomic locus. Plasmid subclones of recombinant phage lambda Asm152 were able to complement both Escherichia coli gltB and A. sesbaniae Asm- Vi mutants; NADPH-glutamate synthase activity was detected in all such strains complemented to Asm+. Heterologous and homologous complementations required both A. sesbaniae gltA+ and (inferred) gltB+ genes. Eleven A. sesbaniae Asm- Vi mutants mapped to a 4-kilobase-pair (kbp) DNA region that exhibited homology with Bacillus subtilis gltA+. In E. coli maxicell labeling experiments, this 4-kbp DNA region encoded a 165-kilodalton polypeptide that was inferred to be the product of the A. sesbaniae gltA+ gene (glutaminase NADPH-dependent L-glutamate synthase subunit). Site-directed Tn5-lacZ mutagenesis of a glt plasmid subclone identified a region that bisected this locus into (at least) two cistrons. Because the remaining five A. sesbaniae Asm- mutants mapped to a 1.5-kbp region adjacent to gltA+, these mutants probably define a single gltB+ gene (glutamate dehydrogenase NADPH-dependent L-glutamate synthase subunit); this region did not exhibit homology with the B. subtilis gltB+ gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berberich M. A. A glutamate-dependent phenotype in E. coli K12: the result of two mutations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1498–1503. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohannon D. E., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamate synthase genes by the nitrogen source. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):957–964. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.957-964.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Dilworth M. J. Ammonia assimilation by rhizobium cultures and bacteroids. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):39–48. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande K. L., Kane J. F. Glutamate synthase from Bacillus subtilis: in vitro reconstitution of an active amidotransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):308–314. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Ludwig R. A. Rhizobium sp. strain ORS571 ammonium assimilation and nitrogen fixation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1144–1151. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1144-1151.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Nees D. W., Raymond C. K., Loroch A. I., Ludwig R. A. Characterization of three genomic loci encoding Rhizobium sp. strain ORS571 N2 fixation genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):72–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.72-81.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Raymond C. K., Ludwig R. A. Vector insertion mutagenesis of Rhizobium sp. strain ORS571: direct cloning of mutagenized DNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):317–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.317-323.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton J., Michaelis S., Wright A. Mutations in two unlinked genes are required to produce asparagine auxotrophy in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):221–228. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.221-228.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary L. E., Meister A. On the mechanism of glutamine-dependent reductive amination of alpha-ketoglutarate catalyzed by glutamate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3501–3508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Construction of Tn5 lac, a transposon that fuses lacZ expression to exogenous promoters, and its introduction into Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5816–5820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Hirschman J., Burton D., Jelesko J., Meeks J. C. Covalent modification of bacterial glutamine synthetase: physiological significance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):309–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00330979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozoya E., Sanchez-Pescador R., Covarrubias A., Vichido I., Bolivar F. Tight linkage of genes that encode the two glutamate synthase subunits of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):616–621. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.616-621.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madonna M. J., Fuchs R. L., Brenchley J. E. Fine structure analysis of Salmonella typhimurium glutamate synthase genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):353–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.353-360.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Ganem D., Lu P., Schmitz A. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. I. Correlation of mutational sites with specific amino acid residues: construction of a colinear gene-protein map. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 15;109(2):275–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Stadtman E. R. Glutamate synthase from Escherichia coli. An iron-sulfide flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7407–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntsälä P., Zalkin H. Properties of apoglutamate synthase and comparison with glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3300–3305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahel G., Zelenetz A. D., Tyler B. M. gltB gene and regulation of nitrogen metabolism by glutamine synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):139–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.139-148.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priefer U. B., Simon R., Pühler A. Extension of the host range of Escherichia coli vectors by incorporation of RSF1010 replication and mobilization functions. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):324–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.324-330.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]